(Press-News.org) Currently accepted wisdom in the corporate world is that in order to motivate frontline employees who serve customers, corporations need to increase their salary, make them feel more positive about the company, or give them more explicit instructions on how to interact with customers. A new study led by Drexel University's Daniel Korschun, PhD, an assistant professor at the LeBow College of Business, examines how frontline employees respond to corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities such as charitable giving, environmental programs and ethical practices. The study was published in the May issue of the Journal of Marketing.
While such activities have become mainstream, this is the first study to trace the effects of CSR all the way from perceptions of the CSR activities to actual job performance. More than 200 employees at a major financial services company were surveyed for the study.
"What we found is that CSR motivates employees in an entirely different way," said Korschun. "Because CSR communicates the values of the company, it can become a window into the values of the customer."
More specifically, if an employee believes that customers share their excitement about the company's CSR activities, it can break the ice and make conversations easier with those customers.
"Employees become more confident that they know what customers want," said Korschun. "And they become more motivated to serve those customers because they see that they care about the same sorts of things."
The research suggests that while traditional means of improving performance can be effective, CSR represents an entirely new way to motivate the frontline workforce.
"This is an exciting finding for executives because we not only show that CSR can lead to better job performance, but we also document the entire thought process of employees. Now executives can create CSR initiatives that maximize these benefits in job performance," said Korschun.
INFORMATION:
The Journal of Marketing is published by the American Marketing Association, the professional association for individuals and organizations who are leading the practice, teaching and development of marketing worldwide. Learn more at ama.org.
New study reveals corporate social responsibility can lead to better customer service
2014-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New guidelines and technology needed for placement of feeding tubes in pediatric patients
2014-05-21
Universal guidelines and improvements in technology are needed to reduce injuries and deaths from improper placement of nasogastric feeding tubes in pediatric patients, according to a comprehensive review of published literature.
The review, conducted by the New Opportunities for Verification of Enteral Tube Location (NOVEL) Work Group Project of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) found that while the bedside placement of a nasogastric feeding tube is a common procedure conducted by nurses, incorrect placement can have serious and ...
New, fossil-fuel-free process makes biodiesel sustainable
2014-05-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A new fuel-cell concept, developed by an Michigan State University researcher, will allow biodiesel plants to eliminate the creation of hazardous wastes while removing their dependence on fossil fuel from their production process.
The platform, which uses microbes to glean ethanol from glycerol and has the added benefit of cleaning up the wastewater, will allow producers to reincorporate the ethanol and the water into the fuel-making process, said Gemma Reguera, MSU microbiologist and one of the co-authors.
"With a saturated glycerol market, traditional ...
Risky alcohol use in male-dominated industries
2014-05-21
New Rochelle, NY, May 21, 2014—The workplace can provide an ideal environment to implement support, well-being, and testing interventions aimed at reducing risky alcohol use among men. By targeting male-dominated industries, in particular, alcohol screening and prevention efforts may be effective in reducing alcohol use, according to a Review article in Journal of Men's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Men's Health website.
A team of Australian researchers led by Nicole Lee, ...
Phase III clinical trial shows image fusion-guided biopsy significantly improves accuracy of prostate
2014-05-21
NEW HYDE PARK, NY – A recent study by investigators from LIJ Medical Center demonstrated that using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in men with an elevated prostate specific antigen (PSA) resulted in a prostate cancer detection rate that was twice as high as data reported in the March 1999 Prostate journal that analyzed men undergoing the standard 12-core biopsy with an elevated PSA. Physicians in the recent trial used a targeted approach to evaluate prostate cancer that combines MR imaging and transrectal ultrasound fusion guided prostate biopsy.
Given the limitations ...
Carnegie Mellon, Microsoft Research automate privacy compliance for big data systems
2014-05-21
PITTSBURGH—Web services companies, such as Facebook, Google and Microsoft, all make promises about how they will use personal information they gather. But ensuring that millions of lines of code in their systems operate in ways consistent with privacy promises is labor-intensive and difficult. A team from Carnegie Mellon University and Microsoft Research, however, has shown these compliance checks can be automated.
The researchers developed a prototype automated system that is now running on the data analytics pipeline of Bing, Microsoft's search engine. According to ...
Funny River Fire, Alaska
2014-05-21
According to the Alaskan Division of Forestry the Funny River fire was very active overnight (May 20) because of low humidity. Currently the fire is estimated to be near 7,000 acres and has reached Tustumena Lake. It is spreading east and west along the shore, is 10 miles long, and is about a mile wide with broadening at the lake shore. There have been no evacuations or reports of any structures lost.
Early this morning (May 21), flame lengths of 125 feet with erratic fire behavior were reported. Winds for today are forecasted to remain out of the north keeping the fire ...
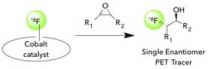
A faster track to the tools that track disease
2014-05-21
Radioactivity is usually associated with nuclear fallout or comic-book spider bites, but in very small amounts it can be a useful tool for diagnosing diseases.
Small molecules containing a radioactive isotope of fluorine called "18F radiotracers" are used to detect and track certain diseases in patients. Once injected into the body, these molecules accumulate in specific targets, such as tumors, and can be visualized by their radioactive tag on a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. The 18F tags quickly decay so no radioactivity remains after about a day.
But there ...
PMS may spell menopause symptoms later -- but not hot flashes
2014-05-21
CLEVELAND, Ohio (May 21, 2014)—Having premenstrual syndrome (PMS) before menopause does not mean women will be troubled by hot flashes afterward. But they may face more menopause complaints other than hot flashes, such as trouble with memory and concentration, finds a new study published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
The research team at the Helsinki University Central Hospital and Folkhälsan Research Institute in Helsinki, Finland, are the first to show a link between PMS and a worse quality of life after menopause. They ...
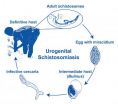
Scientist uncovers links connecting environmental changes with spike in infectious disease
2014-05-21
National Museum of Natural History scientist Bert Van Bocxlaer and an international team of researchers revealed that anthropogenic changes in Africa's Lake Malaŵi are a driving force behind the increase of urogenital schistosomiasis, a debilitating tropical disease caused by parasitic flatworms. Scientists estimate that 250 million people are affected by schistosomiasis worldwide, and 600 million more are at risk of contracting it. In some villages along the shorelines of Lake Malaŵi, 73 percent of the people and up to 94 percent of the schoolchildren are infected ...
Scaly gem discovered in South American cloudforests
2014-05-21
Field and laboratory work by Omar Torres-Carvajal from Museo de Zoología QCAZ, Pontificia Universidad Católica del Ecuador, and his former undergraduate student Simón Lobos has resulted in the discovery of a gem-looking new species of shade lizard from the cloudforests in northwestern Ecuador. This region is part of the 274,597 km2 Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena hotspot that lies west of the Andes. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
Shade lizards (genus Alopoglossus) are widely distributed across tropical South America. They differ from most other lizards ...