(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
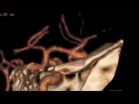
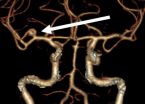
This video depicts microneurosurgical clipping of an unruptured intracranial aneurysm,
which is arising from the bifurcation i.e. branching point of two right
middle cerebral arteries.
In brief, the aneurysm locates in this...
Click here for more information.
The lifetime risk for rupture of a brain aneurysm depends heavily on the patient's overall load of risk factors. However, a recent study by researchers from the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Central Hospital demonstrated that the size of an aneurysm has no great significance on the risk of rupture.
This is a unique study in that it monitored aneurysm patients over their entire lifetimes, whereas typical follow-up studies last only between one and five years in duration. The study is also exceptionally broad in scope; Dr. Seppo Juvela points out that the only other place where a study of similar scope has been conducted is Japan.
"It is unlikely that another similar, non-selected lifetime follow-up study on aneurysm patients will ever be conducted again," he states.
Current care practices are based largely on the results of previous, shorter studies. Such studies have shown that the size of the aneurysm is the most significant factor predicting its risk for rupture. Consequently, small ( END
One-third of all brain aneurysms rupture: the size is not a significant risk factor
2014-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clinical trials designed to block autophagy in multiple cancers show promise
2014-05-22
PHILADELPHIA— In the largest group of results to date, researchers from Penn Medicine's Abramson Cancer Center and other institutions have shown in clinical trials that the malaria drug hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) blocked autophagy in a host of aggressive cancers—glioblastoma, melanoma, lymphoma and myeloma, renal and colon cancers—and in some cases helped stabilize disease. Autophagy—an essential process cancer cells need to fuel their growth—is a key troublemaker spurring tumor growth. Block this pathway, many preclinical studies suggest, and anti-cancer agents such as chemotherapy ...
Yale Cancer Center studies find lifestyle changes improve biomarkers for breast cancer recurrence and mortality
2014-05-22
New Haven, CT – A pair of Yale Cancer Center interventional studies involving breast cancer survivors found that lifestyle changes in the form of healthy eating and regular exercise can decrease biomarkers related to breast cancer recurrence and mortality. The abstracts are scheduled to be presented at the 2014 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology in Chicago May 30-June 3rd.
"The findings of both studies support a growing body of research that suggests lifestyle interventions lower biomarkers associated with breast cancer recurrence and mortality, ...
Repeated sexual assault victims report more psychological problems than previously thought
2014-05-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. – According to recent studies, one in five adult women and one in 100 adult men have reported being raped. The prevalence increases to two in five among women and one in five among men who report experiencing other forms of sexual violence, such as repeated unwanted sexual contact and sexual coercion. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have determined that those victims who are repeatedly assaulted, but not necessarily violently raped, show greater levels of psycho-behavioral consequences than earlier thought. The researchers suggest that understanding ...
Male and female sex cell determination requires lifelong maintenance and protection
2014-05-22
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (May 22, 2014) – The way in which the sex of an organism is determined may require lifelong maintenance, finds new research from the University of Minnesota. According to the study published today in the journal Developmental Cell, sex-specific transcription factors perform lifelong work to maintain sexual determination and protect against reprogramming of cells from one sex to the other.
Previous research at the University of Minnesota's Department of Genetics, Cell Biology, and Development showed sex determination is not permanent. Using a mouse ...
Study shows how common obesity gene contributes to weight gain
2014-05-22
NEW YORK, NY (May 22, 2014) — Researchers have discovered how a gene commonly linked to obesity—FTO—contributes to weight gain. The study shows that variations in FTO indirectly affect the function of the primary cilium, a little-understood hair-like appendage on brain and other cells. Specific abnormalities of cilium molecules, in turn, increase body weight, in some instances, by affecting the function of receptors for leptin, a hormone that suppresses appetite. The findings, made in mice, suggest that it might be possible to modify obesity through interventions that alter ...
Scientific collections play vital role in conservation biology
2014-05-22
Scientists from the California Academy of Sciences and more than 60 other international research institutions spanning six continents have responded to a recent paper in Science, which questioned current methods of scientific collecting and advocated the use of non-lethal alternatives. The response, led by Luiz Rocha, Ph.D., the Academy's Assistant Curator and Follett Chair of Ichthyology, and co-authored by such science luminaries as Harvard's E. O. Wilson and the Academy's Chief of Science and Sustainability, Margaret (Meg) Lowman, describes in detail the value that scientific ...
A glimpse into nature's looking glass -- to find the genetic code is reassigned
2014-05-22
In the Lewis Carroll classic, Through the Looking Glass, Humpty Dumpty states, "When I use a word, it means just what I choose it to mean—neither more nor less." In turn, Alice (of Wonderland fame) says, "The question is, whether you can make words mean so many different things." All organisms on Earth use a genetic code, which is the language in which the building plans for proteins are specified in their DNA. It has long been assumed that there is only one such "canonical" code, so each word means the same thing to every organism. While a few examples of organisms ...
RI Hospital researcher and colleagues discover protein that may lead to malaria vaccine
2014-05-22
VIDEO:
Jonathan Kurtis, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Center for International Health Research at Rhode Island Hospital, talks about the latest findings in their research to find a vaccine for malaria,...
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – Rhode Island Hospital researchers have discovered a protein that is essential for malaria-causing parasites to escape from inside red blood cells. Antibodies to this protein trap the parasite inside these red blood cells. This ...
Growing inequalities make science more of a 'winner takes all' field
2014-05-22
ANN ARBOR—As new research documents growing inequalities in health and wealth, the gap between "haves" and "have-nots" is growing in the field of scientific research itself, says University of Michigan sociologist Yu Xie.
"It's surprising that more attention has not been paid to the large, changing inequalities in the world of scientific research, given the preoccupation with rising social and economic inequality in many countries," said Xie, research professor at the U-M Institute for Social Research and professor of sociology, statistics and public policy.
The forces ...
Fruit flies show mark of intelligence in thinking before they act
2014-05-22
Fruit flies 'think' before they act, a study by researchers from the University of Oxford's Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour suggests. The neuroscientists showed that fruit flies take longer to make more difficult decisions.
In experiments asking fruit flies to distinguish between ever closer concentrations of an odour, the researchers found that the flies don't act instinctively or impulsively. Instead they appear to accumulate information before committing to a choice.
Gathering information before making a decision has been considered a sign of higher intelligence, ...