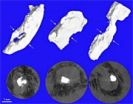
(Press-News.org) Hollow capsules that have a selectively permeable shell are promising candidates as tiny containers for molecules, particles or bubbles, and are becoming increasingly important in a wide variety of applications. But making these kinds of capsules with more than one kind of substance on their shells has been challenging – until now.
In a article in the latest edition of Nature Communications, NTNU researcher Jon Otto Fossum and Paul Dommersnes from the University of Paris, Diderot, were part of a team that showed that both Janus and more advanced patchy capsules can be assembled by combining electro-coalescence and electro-hydrodynamic flow in leaky dielectric emulsion drops. This technique can be used with any type of insulating or weakly conductive particles.
Their work is the realization of one possible direction foreseen by the same researchers in a publication in Nature Communications in 2013.
Hollow capsules with two or more substances on their surface are able to organize themselves in specific ways, which means they could be used to grow human skin or other body tissues, or to make porous tissues and composites. They can also be used to transport a variety of substances and release them in specific environments.
Janus capsules, named for the two-faced Roman god, have just two different substances in their shells. They are a sub-group of patchy capsules, which can have more than two different substances in their shells. The researchers were able to make both Janus capsules, with two different substances, and patchy capsules, which had stripes or flecks on them.
Janus and patchy capsules are distinct from Janus and patchy particles, which are solid. These capsules combine the characteristics of Janus or patchy particles, and those of capsules such as colloidosomes.
The different characteristics on the shells of the capsules make them attractive to each other in different ways, depending on the composition of the capsule shells, which means they can create scaffolds suitable for biomedical applications, for assembling electric circuits or optical structures such as photonic crystals, and as vehicles for liquid or molecular transport.
The researchers foresee that their route for designing patchy capsules will facilitate the foundation for many advanced applications, for example, by using microfluidic methods.
INFORMATION:
The article "Electroformation of Janus and patchy capsules" is in Nature Communications 5:3945 (2014), DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4945.
It is open access and can be viewed at:
http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2014/140523/ncomms4945/full/ncomms4945.html
Breakthrough method for making Janus or patchy capsules
Tiny capsules with different substances on their surface could be useful in medicine and materials technology
2014-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Straw from oilseed as a new source of biofuels
2014-05-23
The bright yellow fields of oilseed rape are a familiar sight at this time of year, but for scientists what lies beneath is just as exciting.
Researchers at the Institute of Food Research are looking at how to turn straw from oilseed rape into biofuel. Preliminary findings are pointing at ways the process could be made more efficient, as well as how the straw itself could be improved.
Straw from crops such as wheat, barley, oats and oilseed rape is seen as a potential source of biomass for second generation biofuel production. Currently the UK produces around 12 million ...
Tiny muscles help bats fine-tune flight, stiffen wing skin
2014-05-23
VIDEO:
As bats fly the air pushes their compliant skin around. A new study provides evidence that they control wing stiffness and shape using muscles embedded in their skin.
Click here for more information.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study of bats reveals a capability within their wondrous wings that may help them fine-tune their flight.
Bats employ a network of nearly hair-thin muscles embedded in the membrane of their inherently floppy wing skin to adjust ...
NASA sees first tropical depression of Eastern Pacific hurricane season
2014-05-23
One week after the official start of hurricane season in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, the first tropical depression was born hundreds of miles southwest of Mexico. NASA's TRMM satellite and NOAA's GOES-West satellites provided looks inside and outside of the depression's clouds. Hurricane season in the Eastern Pacific began officially on May 15.
On May 21 at 22:59 UTC (6:59 p.m. EDT) the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over System 92E, which was what Tropical Depression 1E (TD1E) was called before it organized into a depression. TRMM's Precipitation ...
Supernova caught in the act by palomar transient factory
2014-05-23
Supernovae—stellar explosions—are incredibly energetic, dynamic events. It is easy to imagine that they are uncommon, but the universe is a big place and supernovae are actually fairly routine. The problem with observing supernovae is knowing just when and where one is occurring and being able to point a world-class telescope at it in the hours immediately afterward, when precious data about the supernova's progenitor star is available. Fortunately the intermediate Palomar Transient Factory (iPTF) operated by Caltech scans the sky constantly in search of dramatic astrophysical ...
Mapping atherosclerotic arteries: Combined approach developed
2014-05-23
A new method allows calcified and constricted blood vessels to be visualized with micrometer precision, and can be used to design containers for targeted drug delivery. Within the project "NO-stress", materials scientists from the Medical Faculty of the University of Basel combined cutting-edge-imaging techniques to visualize and quantify the constrictions caused by atherosclerosis.
Cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, are associated with plaque formation and the most prevalent cause of death worldwide. Unlike vessels and other soft tissues, the plaque ...
Risk is much more than a game
2014-05-23
Wildfires and flooding affect many more people in the USA than earthquakes and landslide and yet the dread, the perceived risk, of the latter two is much greater than for those hazards that are more frequent and cause greater loss of life. Research published in the International Journal of Risk Assessment and Management, suggests that a new paradigm for risk assessment is needed so that mitigation plans in the face of natural disasters can be framed appropriately by policy makers and those in the emergency services.
Maura Knutson (nee Hurley) and Ross Corotis of the University ...
The protective milk shot
2014-05-23
Antibodies against C. suis are transferred via the sow's very first milk to the piglets immediately after birth. This was discovered by veterinarian and parasitologist Lukas Schwarz and his colleagues in 2013. These findings prompted the researchers at the Institute for Parasitology to look for a way to increase the level of these antibodies in sows. The ultimate goal was to provide the piglets with as much antibodies as possible via their mother's milk during the first few days of life.
Piglets from infected mothers are healthier
The idea paid off. Piglets from infected ...
Nature inspires drones of the future
2014-05-23
Researchers have been taking tips from nature to build the next generation of flying robots.
Based on the mechanisms adopted by birds, bats, insects and snakes, 14 distinguished research teams have developed solutions to some of the common problems that drones could be faced with when navigating through an urban environment and performing novel tasks for the benefit of society.
Whether this is avoiding obstacles, picking up and delivering items or improving the take-off and landing on tricky surfaces, it is hoped the solutions can lead to the deployment of drones in ...
Rapid evolution aids spread of exotic plant species
2014-05-23
A team of Belgian biologists led by researchers at KU Leuven has provided the first genetic evidence that rapid evolution can help non-native plant species spread in new environments. Using samples of centuries-old herbaria and DNA analysis, the researchers reconstructed the genetic adaptations undergone by the Pyrenean rocket prior to its rapid spread in Belgium.
The Pyrenean rocket (Sisymbrium austriacum subsp. chrysanthum) is a plant that grows in the mountains of southern Europe and is particularly prevalent in the Pyrenees. The species was first reported in Belgium ...
Lack of plant diversity spurs cankerworm damage in cities
2014-05-23
Research from North Carolina State University finds that a lack of plant diversity is a key contributor to the widespread defoliation caused by cankerworms in cities, and highlights the role that increasing diversity can play in limiting future damage.
Fall cankerworms (Alsophila pometaria) are caterpillars that are native to the eastern United States and hatch in early spring. The cankerworms defoliate trees and other plants, eating new leaves as they emerge – which is both unsightly and can ultimately kill the plants.
"We see cankerworms doing more damage to trees ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough method for making Janus or patchy capsulesTiny capsules with different substances on their surface could be useful in medicine and materials technology