(Press-News.org) University of Adelaide research has for the first time confirmed that women who eat a poor diet before they become pregnant are around 50% more likely to have a preterm birth than those on a healthy diet.
Researchers at the University of Adelaide's Robinson Research Institute investigated the dietary patterns of more than 300 South Australian women to better understand their eating habits before pregnancy.
It's the first study of its kind to assess women's diet prior to conception and its association with outcomes at birth.
The results, published in The Journal of Nutrition, show that women who consistently ate a diet high in protein and fruit prior to becoming pregnant were less likely to have a preterm birth, while those who consistently ate high fat and sugar foods and takeaway were about 50% more likely to have a preterm birth.
"Preterm birth is a leading cause of infant disease and death and occurs in approximately one in 10 pregnancies globally. Anything we can do to better understand the conditions that lead to preterm birth will be important in helping to improve survival and long-term health outcomes for children," says the lead author of the paper, Dr Jessica Grieger, Posdoctoral Research Fellow with the Robinson Research Institute, based at the Lyell McEwin Hospital.
"In our study, women who ate protein-rich foods including lean meats, fish and chicken, as well as fruit, whole grains and vegetables, had significantly lower risk of preterm birth.
"On the other hand, women who consumed mainly discretionary foods, such as takeaway, potato chips, cakes, biscuits, and other foods high in saturated fat and sugar were more likely to have babies born preterm," Dr Grieger says.
"It is important to consume a healthy diet before as well as during pregnancy to support the best outcomes for the mum and baby," Dr Grieger says.
"Diet is an important risk factor that can be modified. It is never too late to make a positive change. We hope our work will help promote a healthy diet before and during pregnancy. This will help to reduce the number of neonatal deaths and improve the overall health of children," she says.
Dr Grieger will present her research findings at the upcoming SA Annual Scientific Meeting of the Australian Society for Medical Research during ASMR Medical Research Week on Wednesday 4 June.
INFORMATION:
Media contact:
Dr Jessica Grieger
Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Robinson Research Institute
The University of Adelaide
jessica.grieger@adelaide.edu.au
Poor diet before pregnancy is linked with preterm birth
2014-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An infrared NASA eye sees a weaker System 92B
2014-05-23
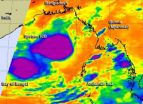
System 92B appears to have weakened in the last day as an infrared look at the tropical low pressure area's cloud temperatures have shown. NASA's AIRS instrument is an infrared "eye in the sky" that recently flew over the weaker tropical low pressure area.
On May 22 at 19:29 UTC/3:29 p.m. EDT, NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 92B and infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument and the SSMIS instrument saw patchy deep convection flaring and dissipating over the western portion of a low-level circulation center. Earlier on May 22, the areas ...
New drug for non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia passes early test
2014-05-23
A new chemotherapy drug being investigated for its potency against two types of cancer was found by scientists at Houston Methodist and seven other institutions to be effective in about one-third of the 58 patients who participated in a phase I study.
The drug, alisertib or MLN8237, inhibits the enzyme aurora A kinase, which is known to be very active during cell division. The present study, published in the journal Investigational New Drugs, looks at the safety, tolerability, and preliminary success of alisertib in treating non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic ...
Wound-healing role for microRNAs in colon offer new insight to inflammatory bowel diseases
2014-05-23
DALLAS – May 23, 2014 – A microRNA cluster believed to be important for suppressing colon cancer has been found to play a critical role in wound healing in the intestine, UT Southwestern cancer researchers have found.
The findings, first discovered in mice and later reproduced in human cells, could provide a fresh avenue for investigating chronic digestive diseases and for potentially repairing damage in these and other disease or injury settings.
"We identified a novel role for microRNAs in regulating wound healing in the intestine. This finding has important ...
Failed dwarf galaxy survives galactic collision thanks to full dark-matter jacket
2014-05-23
Like a bullet wrapped in a full metal jacket, a high-velocity hydrogen cloud hurtling toward the Milky Way appears to be encased in a shell of dark matter, according to a new analysis of data from the National Science Foundation's Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope (GBT). Astronomers believe that without this protective shell, the high-velocity cloud (HVC) known as the Smith Cloud would have disintegrated long ago when it first collided with the disk of our Galaxy.
If confirmed by further observations, a halo of dark matter could mean that the Smith Cloud is actually ...
Slide Fire update May 23, 2014
2014-05-23
The Slide Fire is located in Oak Creek Canyon just north of Slide Rock State Park and burning northward, up the canyon into places such as West Fork and Harding Point. Currently it has burned 7,500 acres and is 5% contained. The fire originated just about 4 to 5 miles north of Sedona, just north of Slide Rock State Park on May 20, and was human caused. Investigations regarding the cause are ongoing.
Crews made good progress overnight conducting burnout operations along the north and east flanks of the fire. Several small spot fires were contained through the evening ...
Personal judgments are swayed by group opinion, but only for 3 days
2014-05-23
We all want to feel like we're free-thinking individuals, but there's nothing like the power of social pressure to sway an opinion. New research suggests that people do change their own personal judgments so that they fall in line with the group norm, but the change only seems to last about 3 days. The research is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
This is a photo of a figure standing out from the crowd."Our findings suggest that exposure to others' opinions does indeed change our own private opinions — but it doesn't ...
Social marketing at the movies
2014-05-23
Word-of-mouth marketing is recognized as a powerful route from long-tail sales to blockbuster, whether one is talking about the latest fishy ice cream flavor or a Hollywood romantic comedy. In the age of social media and online networking sites, such as Twitter and Facebook, the potential for spreading the word could mean the difference between consumers seeing a product as the best thing since sliced bread or the most rotten of tomatoes.
Chong Oh, Assistant Professor of Computer Information Systems at Eastern Michigan University, in Ypsilanti, Michigan, USA, has analyzed ...
A new way to make sheets of graphene
2014-05-23
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Graphene's promise as a material for new kinds of electronic devices, among other uses, has led researchers around the world to study the material in search of new applications. But one of the biggest limitations to wider use of the strong, lightweight, highly conductive material has been the hurdle of fabrication on an industrial scale.
Initial work with the carbon material, which forms an atomic-scale mesh and is just a single atom thick, has relied on the use of tiny flakes, typically obtained by quickly removing a piece of sticky tape from a block ...
Breakthrough method for making Janus or patchy capsules
2014-05-23
Hollow capsules that have a selectively permeable shell are promising candidates as tiny containers for molecules, particles or bubbles, and are becoming increasingly important in a wide variety of applications. But making these kinds of capsules with more than one kind of substance on their shells has been challenging – until now.
In a article in the latest edition of Nature Communications, NTNU researcher Jon Otto Fossum and Paul Dommersnes from the University of Paris, Diderot, were part of a team that showed that both Janus and more advanced patchy capsules can ...
Straw from oilseed as a new source of biofuels
2014-05-23
The bright yellow fields of oilseed rape are a familiar sight at this time of year, but for scientists what lies beneath is just as exciting.
Researchers at the Institute of Food Research are looking at how to turn straw from oilseed rape into biofuel. Preliminary findings are pointing at ways the process could be made more efficient, as well as how the straw itself could be improved.
Straw from crops such as wheat, barley, oats and oilseed rape is seen as a potential source of biomass for second generation biofuel production. Currently the UK produces around 12 million ...