(Press-News.org) Biomedical engineering researchers have developed daisy-shaped, nanoscale structures that are made predominantly of anti-cancer drugs and are capable of introducing a "cocktail" of multiple drugs into cancer cells. The researchers are all part the joint biomedical engineering program at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
"We found that this technique was much better than conventional drug-delivery techniques at inhibiting the growth of lung cancer tumors in mice," says Dr. Zhen Gu, senior author of the paper and an assistant professor in the joint biomedical engineering program. "And based on in vitro tests in nine different cell lines, the technique is also promising for use against leukemia, breast, prostate, liver, ovarian and brain cancers."
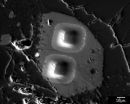
To make the "nanodaisies," the researchers begin with a solution that contains a polymer called polyethylene glycol (PEG). The PEG forms long strands that have much shorter strands branching off to either side. Researchers directly link the anti-cancer drug camptothecin (CPT) onto the shorter strands and introduce the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin (Dox) into the solution.
PEG is hydrophilic, meaning it likes water. CPT and Dox are hydrophobic, meaning they don't like water. As a result, the CPT and Dox cluster together in the solution, wrapping the PEG around themselves. This results in a daisy-shaped drug cocktail, only 50 nanometers in diameter, which can be injected into a cancer patient.
Once injected, the nanodaisies float through the bloodstream until they are absorbed by cancer cells. In fact, one of the reasons the researchers chose to use PEG is because it has chemical properties that prolong the life of the drugs in the bloodstream.
Once in a cancer cell, the drugs are released. "Both drugs attack the cell's nucleus, but via different mechanisms," says Dr. Wanyi Tai, lead author and a former postdoctoral researcher in Gu's lab.
"Combined, the drugs are more effective than either drug is by itself," Gu says. "We are very optimistic about this technique and are hoping to begin pre-clinical testing in the near future."
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Folding Graft Copolymer with Pedant Drug Segment for Co-Delivery of Anticancer Drugs," is published online in the journal Biomaterials. Co-authors include Dr. Ran Mo, a current postdoctoral researcher in the program, and Yue Lu and Tianyue Jiang, who are both Ph.D. students in the program. The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health under grant 1UL1TR001111 and funding from NC State and UNC-Chapel Hill.
'Nanodaisies' deliver drug cocktail to cancer cells
2014-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Marathon runners' times develop in a U shape
2014-05-28
Spanish researchers have demonstrated that the relationship between marathon running times and the age of the athlete is U-shaped. The work shows the unusual fact that it takes an 18-year-old athlete the same amount of time to finish a marathon as a 55- or 60-year-old runner.
The 42,195 metres that are nowadays known as the marathon were run for the first time at the London Olympic Games of 1908. Since then, many athletes have completed this race and there has also been numerous scientific studies conducted on endurance runners.
Up to now, the majority of these works ...
International research group documents unique songbird diversity of the Eastern Himalayas
2014-05-28
The Eastern Himalayas are home to more than 360 different songbird species, most of which are to be found nowhere else on the planet. This makes the region extending from eastern Nepal to the borderlands of China, India, and Myanmar unique and one of the most important hot spots for biological diversity in the western hemisphere. A recent research paper describes how this impressive bird community came about millions of years ago, emphasizing both the uniqueness and biological significance of this remote area. "As the Himalayan mountain range was formed, a profusion of ...
Sneaky bacteria change key protein's shape to escape detection
2014-05-28
Every once in a while in the U.S., bacterial meningitis seems to crop up out of nowhere, claiming a young life. Part of the disease's danger is the ability of the bacteria to evade the body's immune system, but scientists are now figuring out how the pathogen hides in plain sight. Their findings, which could help defeat these bacteria and others like it, appear in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Linda Columbus and colleagues explain that the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis, one cause of meningitis, and its cousin Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is responsible ...
Artificial lung the size of a sugar cube
2014-05-28
This news release is available in German.
Lung cancer is a serious condition. Once patients are diagnosed with it, chemotherapy is often their only hope. But nobody can accurately predict whether or not this treatment will help. To start with, not all patients respond to a course of chemotherapy in exactly the same way. And then there's the fact that the systems drug companies use to test new medications leave a lot to be desired. "Animal models may be the best we have at the moment, but all the same, 75 percent of the drugs deemed beneficial when tested on animals ...
Water in moon rocks provides clues and questions about lunar history
2014-05-28
A recent review of hundreds of chemical analyses of Moon rocks indicates that the amount of water in the Moon's interior varies regionally – revealing clues about how water originated and was redistributed in the Moon. These discoveries provide a new tool to unravel the processes involved in the formation of the Moon, how the lunar crust cooled, and its impact history.
This is not liquid water, but water trapped in volcanic glasses or chemically bound in mineral grains inside lunar rocks. Rocks originating from some areas in the lunar interior contain much more water ...
Ultraviolet cleaning reduces hospital superbugs by 20 percent: Study
2014-05-28
Washington, DC, May 27, 2014 – Healthcare-associated vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile (CD), and other multidrug-resistant organisms (MDRO) were decreased among patients after adding ultraviolet environmental disinfection (UVD) to the cleaning regimen, according to a study published in the June issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
In this retrospective study led by the ...
What can plants reveal about gene flow? That it's an important evolutionary force
2014-05-28
A plant breeder discovers his experimental crops have been "contaminated" with genes from a neighboring field. New nasty weeds sometimes evolve directly from natural crosses between domesticated species and their wild relatives. A rare plant is threatened due to its small population size and restricted range. What do all these situations have in common? They illustrate the important role of gene flow among populations and its potential consequences. Although gene flow was recognized by a few scientists as a significant evolutionary force as early as the 1940s, its relative ...
In Africa, STI testing could boost HIV prevention
2014-05-28
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To maximize HIV prevention efforts in South Africa and perhaps the broader region, public health officials should consider testing for other sexually transmitted infections when they test for HIV, according to a new paper in the journal Sexually Transmitted Infections.
STIs can make HIV easier to transmit even after antiretroviral therapy has begun, so rooting out STI co-infections in patients should improve HIV prevention. The new study led by Brown University public health researchers emphasizes that sooner is indeed better than ...
Variety in diet can hamper microbial diversity in the gut
2014-05-28
AUSTIN, Texas — Scientists from The University of Texas at Austin and five other institutions have discovered that the more diverse the diet of a fish, the less diverse are the microbes living in its gut. If the effect is confirmed in humans, it could mean that the combinations of foods people eat can influence the diversity of their gut microbes.
The research could have implications for how probiotics and diet are used to treat diseases associated with the bacteria in human digestive systems.
A large body of research has shown that the human microbiome, the collection ...
Melting Arctic opens new passages for invasive species
2014-05-28
For the first time in roughly 2 million years, melting Arctic sea ice is connecting the north Pacific and north Atlantic oceans. The newly opened passages leave both coasts and Arctic waters vulnerable to a large wave of invasive species, biologists from the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center assert in a commentary published May 28 in Nature Climate Change.
Two new shipping routes have opened in the Arctic: the Northwest Passage through Canada, and the Northern Sea Route, a 3000-mile stretch along the coasts of Russia and Norway connecting the Barents and Bering ...