(Press-News.org) Solar panels made in China have a higher overall carbon footprint and are likely to use substantially more energy during manufacturing than those made in Europe, said a new study from Northwestern University and the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory. The report compared energy and greenhouse gas emissions that go into the manufacturing process of solar panels in Europe and China.
"We estimated that a solar panel's carbon footprint is about twice as high when made in China and used in Europe, compared to those locally made and used in Europe," said Fengqi You, assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering at Northwestern and corresponding author on the paper.
"While it might be an economically attractive option to move solar panel manufacturing from Europe to China, it is actually less sustainable from the life cycle energy and environmental perspective—especially under the motivation of using solar panels for a more sustainable future," he said.
The team performed a type of systematic evaluation called life cycle analysis to come up with these hard data. Life cycle analysis tallies up all the energy used to make a product—energy to mine raw materials, fuel to transport the materials and products, electricity to power the processing factory, and so forth. This provides a more accurate picture of the overall energy consumed and produced and the environmental impact of making and using a solar panel.
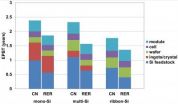
Assuming that a solar panel is made of silicon—by far the most common solar panel material—and is installed in sunny southern Europe, a solar panel made in China would take about 20 to 30 percent longer to produce enough energy to cancel out the energy used to make it. The carbon footprint is about twice as high.
The biggest reason is that China has fewer environmental and efficiency standards for its factories and plants and generates more electricity from coal and other non-renewable sources, the authors said.
"It takes a lot of energy to extract and process solar-grade silicon, and in China, that energy tends to come from dirtier and less efficient energy sources than it does in Europe," said Argonne scientist and co-author Seth Darling. "This gap will likely close over time as China strengthens environmental regulations."
The study did not include the energy cost of transporting a solar panel to its final destination. Transportation would magnify the difference even further if it—like 60 percent of all solar installations in 2012—went up in Germany or Italy, Darling said.
The team also compared the numbers for different types of silicon solar panels. Single-crystal solar panels are better at harvesting energy than other types, but take the longest to "pay back" the energy used to manufacture them because the process is more energy-intensive. Multicrystalline panels came next, followed by ribbon silicon panels, which are easiest to manufacture but least efficient—however, their payback time was fastest.
To encourage more sustainable production of solar cells, the authors suggest a break-even carbon tariff. "This would be based on the carbon footprint and energy efficiency difference between manufacturing regions, and would be a better market- and science-based solution than a solar panel tariff," said Dajun Yue, a Northwestern graduate student in You's research group and lead author on the paper.
"The break-even carbon tariff we calculated, which is at the range of €105-129 per ton of carbon dioxide, depending on the possible carbon tax to be imposed by these two regions in the near term, is close to the reported CO2 capture and sequestration cost," You said.
INFORMATION:
Funding for this research was provided by the Institute for Sustainability and Energy at Northwestern University. The research was performed in part at the Center for Nanoscale Materials, a U.S. Department of Energy user facility.
The paper, "Domestic and overseas manufacturing scenarios of silicon-based photovoltaics: Life cycle energy and environmental comparative analysis," is available online and will be printed in the July issue of the journal Solar Energy.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
The Center for Nanoscale Materials at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers (NSRCs), premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale, supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge and Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
Solar panel manufacturing is greener in Europe than China, study says
2014-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study links unexpected death of a loved one with onset of psychiatric disorders
2014-05-29
May 29, 2014 -- The sudden loss of a loved one can trigger a variety of psychiatric disorders in people with no history of mental illness, according to researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health and colleagues at Columbia's School of Social Work and Harvard Medical School. While previous studies have suggested there is a link between sudden bereavement and an onset of common psychiatric disorders, this is the first study to show the association of acute bereavement and mania in a large population sample. Findings are published online in the American ...
Domestication of dogs may explain mammoth kill sites and success of early modern humans
2014-05-29
A new analysis of European archaeological sites containing large numbers of dead mammoths and dwellings built with mammoth bones has led Penn State Professor Emerita Pat Shipman to formulate a new interpretation of how these sites were formed. She suggests that their abrupt appearance may have been due to early modern humans working with the earliest domestic dogs to kill the now-extinct mammoth -- a now-extinct animal distantly related to the modern-day elephant. Shipman's analysis also provides a way to test the predictions of her new hypothesis. Advance publication of ...
NASA widens 2014 hurricane research mission
2014-05-29
VIDEO:
During this year's Atlantic hurricane season, NASA is redoubling its efforts to probe the inner workings of hurricanes and tropical storms with two unmanned Global Hawk aircraft flying over storms...
Click here for more information.
During this year's Atlantic hurricane season, NASA is redoubling its efforts to probe the inner workings of hurricanes and tropical storms with two unmanned Global Hawk aircraft flying over storms and two new space-based missions.
NASA's ...
Mechanisms of ibrutinib resistance identified in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
2014-05-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study has discovered how resistance develops in patients taking ibrutinib, a new and highly effective drug for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine and led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James). It identifies gene mutations that cause ibrutinib resistance in CLL patients.
"Knowledge of these mutations is the first step in the development of ...
New tools help protect world's threatened species
2014-05-29
Athens, Ga. – New tools to collect and share information could help stem the loss of the world's threatened species, according to a paper published today in the journal Science. The study—by an international team of scientists that included John L. Gittleman, dean of the University of Georgia Odum School of Ecology—was led by Stuart L. Pimm of Duke University and Clinton N. Jenkins of the Instituto de Pesquisas Ecológicas in Brazil.
"As databases coalesce and policymakers have access to greater information, we see real and improving successes for conservation science," ...
Two GOES-R instruments complete spacecraft integration
2014-05-29
VIDEO:
In addition to monitoring weather on Earth, the GOES-R satellites will monitor weather in space caused by electromagnetic radiation and charged particles released from solar storms on the Sun. Many...
Click here for more information.
Two of the six instruments that will fly on NOAA's first Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite - R (GOES-R) satellite have completed integration with the spacecraft. The Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI) and Extreme Ultraviolet and ...
New report details more geoscience job opportunities than students
2014-05-29
Alexandria, Va. – In the American Geosciences Institute's newest Status of the Geoscience Workforce Report, released May 2014, jobs requiring training in the geosciences continue to be lucrative and in-demand. Even with increased enrollment and graduation from geoscience programs, the data still project a shortage of around 135,000 geoscientists needed in the workforce by the end of the decade.
"Industry has recognized, and is mitigating the upcoming shortage of skilled geoscientists in their employ, but the federal geoscience workforce is still demonstrably shrinking" ...
Study: Baltimore hookah bars contain elevated levels of carbon dioxide and air nicotine
2014-05-29
Smoking waterpipes, or hookahs, creates hazardous concentrations of indoor air pollution and poses increased risk from diminished air quality for both employees and patrons of waterpipe bars, according to a new study from the Institute for Global Tobacco Control at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. In an analysis of air quality in seven Baltimore waterpipe bars, researchers found that airborne particulate matter and carbon monoxide exceeded concentrations previously measured in public places that allowed cigarette smoking and that air nicotine was markedly ...
PCOS diagnosis tied to inflammation during pregnancy
2014-05-29
Washington, DC—Women who have polycystic ovary syndrome – the most common hormone disorder in women of reproductive age – are more likely to experience chronic low-grade inflammation during pregnancy than counterparts who do not have the condition, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is a leading cause of infertility. Symptoms can include irregular or absent menstrual periods, infertility, weight gain, acne, excess hair on the face and body, or thinning ...
Study finds mode of transportation affects how we feel
2014-05-29
What mode of transportation makes you happiest?
Clemson researchers investigated how emotions like happiness, pain, stress, sadness and fatigue vary during travel and by travel mode in a new study published in the journal Transportation.
Utilizing data from the American Time Use Survey, collected by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the researchers were able to determine the average mood felt by people during different types of travel.
"We found that people are in the best mood while they are bicycling compared to any other mode of transportation," said Eric Morris, ...