(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
In addition to monitoring weather on Earth, the GOES-R satellites will monitor weather in space caused by electromagnetic radiation and charged particles released from solar storms on the Sun. Many...
Click here for more information.
Two of the six instruments that will fly on NOAA's first Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite - R (GOES-R) satellite have completed integration with the spacecraft. The Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI) and Extreme Ultraviolet and X-ray Irradiance Sensors (EXIS) were installed on the sun-pointing platform. They will observe the sun and space weather, including coronal mass ejections, solar flares and ion fluxes that can disrupt power grids, communication and navigation systems and create radiation hazards.
"This development highlights the forward progress underway to complete the installation of the space weather instrument suite onto the GOES-R spacecraft," said Pam Sullivan, GOES-R Flight Project Manager at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland. "It is critical we give our partners at NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center the tools they need to improve prediction capabilities and further our knowledge of space weather."
Understanding Space Weather
The space weather mission is an important part of not only the overall GOES-R Series Program, but also NOAA's National Weather Service (NWS), which is home to the Space Weather Prediction Center. Space weather describes the conditions in space that affect Earth and its technological systems. Space weather storms originate from the sun and occur in space near Earth or in the Earth's atmosphere. Space weather can be difficult to understand since it is unlike the weather we experience here on Earth. For example, one type of space weather, known as coronal mass ejections, can have changing polarities, which can make it more challenging to predict the impacts of the magnetic storm. Watch here to learn more about how space weather impacts our everyday lives. To help kids understand space weather, the GOES-R Program partnered with NASA to create materials available here for students and teachers.
Installation of the SUVI and EXIS instruments moves the program another step closer to the launch of the GOES-R satellite in early 2016. In addition to SUVI and EXIS, the Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) and the Space Environment In-Situ Suite (SEISS) were delivered for integration earlier this year and will be installed on the spacecraft in the coming months. The two remaining instruments that complete the GOES-R Series Program payload are the Magnetometer and Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM). Both instruments are scheduled for delivery later this year.
NOAA manages the GOES-R Series Program through an integrated NOAA-NASA office, staffed with personnel from both agencies and located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
INFORMATION:
For more information about NOAA's Satellite and Information Service visit:
http://www.nesdis.noaa.gov.
Two GOES-R instruments complete spacecraft integration
2014-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
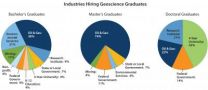
New report details more geoscience job opportunities than students
2014-05-29
Alexandria, Va. – In the American Geosciences Institute's newest Status of the Geoscience Workforce Report, released May 2014, jobs requiring training in the geosciences continue to be lucrative and in-demand. Even with increased enrollment and graduation from geoscience programs, the data still project a shortage of around 135,000 geoscientists needed in the workforce by the end of the decade.
"Industry has recognized, and is mitigating the upcoming shortage of skilled geoscientists in their employ, but the federal geoscience workforce is still demonstrably shrinking" ...
Study: Baltimore hookah bars contain elevated levels of carbon dioxide and air nicotine
2014-05-29
Smoking waterpipes, or hookahs, creates hazardous concentrations of indoor air pollution and poses increased risk from diminished air quality for both employees and patrons of waterpipe bars, according to a new study from the Institute for Global Tobacco Control at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. In an analysis of air quality in seven Baltimore waterpipe bars, researchers found that airborne particulate matter and carbon monoxide exceeded concentrations previously measured in public places that allowed cigarette smoking and that air nicotine was markedly ...
PCOS diagnosis tied to inflammation during pregnancy
2014-05-29
Washington, DC—Women who have polycystic ovary syndrome – the most common hormone disorder in women of reproductive age – are more likely to experience chronic low-grade inflammation during pregnancy than counterparts who do not have the condition, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is a leading cause of infertility. Symptoms can include irregular or absent menstrual periods, infertility, weight gain, acne, excess hair on the face and body, or thinning ...
Study finds mode of transportation affects how we feel
2014-05-29
What mode of transportation makes you happiest?
Clemson researchers investigated how emotions like happiness, pain, stress, sadness and fatigue vary during travel and by travel mode in a new study published in the journal Transportation.
Utilizing data from the American Time Use Survey, collected by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the researchers were able to determine the average mood felt by people during different types of travel.
"We found that people are in the best mood while they are bicycling compared to any other mode of transportation," said Eric Morris, ...
Study: New genes identified may unlock mystery of keloid development
2014-05-29
DETROIT – Researchers at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit have uncovered previously unidentified genes that may be responsible for keloid scarring, a discovery that could unlock the mystery of keloid development and provide insight for more effective treatment.
"Much of the uncertainty surrounding keloids is rooted in there being no known cause for their development," says study lead author Lamont R. Jones, M.D., vice chair, Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery at Henry Ford.
"But it is believed that keloids have a genetic component given the correlation ...
How breast cancer 'expresses itself'
2014-05-29
About one in eight women in the United States will contract breast cancer in her lifetime. Now new research from Tel Aviv University-affiliated researchers, in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University, has provided another tool to help women, clinicians, and scientists searching for a cure to the one of the most widespread yet incurable diseases on the planet.
Dr. Ella Evron and Dr. Ayelet Avraham of the TAU-affiliated Assaf Harofeh Medical Center, together with Prof. Saraswati Sukumar of Johns Hopkins, have found that "gene regulation," the process that shuts off ...
Cloud formation & rainfall affected by pollutant oxidation of biodiesel emissions
2014-05-29
A study into how organic molecules in the atmosphere affect cloud formation has found that a main component of biodiesel, methyl oleate, reacts with ozone surprisingly fast. This process may counterbalance the growth of water droplets resulting from emissions, which would in turn inhibit cloud formation and therefore affect the water cycle in a highly complex way.
The research, published in the journal Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, was performed by an international team of scientists working at the ILL (Institut Laue-Langevin) in Grenoble, France.
Methyl oleate ...
Lost in translation?
2014-05-29
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (May 29, 2014) – In any animal's lifecycle, the shift from egg cell to embryo is a critical juncture. This transition represents the formal initiation of development—a remarkably dynamic process that ultimately transforms a differentiated, committed oocyte to a totipotent cell capable of giving rise to any cell type in the body.
Induction of totipotency (as well as the pluripotency characteristic of embryonic stem cells) requires dramatic changes in gene expression. To date, investigations of such changes have largely focused on transcription, when DNA ...
There's more than one way to silence a cricket
2014-05-29
For most of us, crickets are probably most recognizable by the distinctive chirping sounds males make with their wings to lure females. But some crickets living on the islands of Hawaii have effectively lost their instruments and don't make their music anymore. Now researchers report in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on May 29 that crickets living on different islands quieted their wings in different ways at almost the same time.
"There is more than one way to silence a cricket," says Nathan Bailey of the University of St Andrews. "Evolution by natural selection ...
Melanoma of the eye caused by 2 gene mutations
2014-05-29
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a therapeutic target for treating the most common form of eye cancer in adults. They have also, in experiments with mice, been able to slow eye tumor growth with an existing FDA-approved drug.
The findings are published online in the May 29 issue of the journal Cancer Cell.
"The beauty of our study is its simplicity," said Kun-Liang Guan, PhD, professor of pharmacology at UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center and co-author of the study. "The genetics of this cancer are very simple ...