(Press-News.org) Everything we know nowadays about novel materials and the underlying processes in them we also know thanks to studies at contemporary synchrotron facilities like BESSY II. Here, relativistic electrons in a storage ring are employed to generate very brilliant and partly coherent light pulses from the THz to the X-ray regime in undulators and other devices. However, most of the techniques used at synchrotrons are very "photon hungry" and demand brighter and brighter light pulses to conduct innovative experiments. The general greed for stronger light pulses does, however, not really meet the requirements of one of the most important techniques in material science: photoelectron spectroscopy. Physicists and chemists have been using it for decades to study molecules, gases and surfaces of solids. However, if too many photons hit a surface at the same time, space charge effects deteriorate the results. Owing to these limits, certain material parameters stay hidden in such cases. Thus, a tailored temporal pattern of x-ray pulses is mandatory to move things forward in surface physics at Synchrotrons.
Scientists from HZB's Institute for Methods and Instrumentation in Synchrotron Radiation Research and the Accelerator Department have now jointly solved the gordic knot as they published in the renowned journal Nature Communications. Their novel method is capable of picking single pulses out of a conventional pulse train as usually emitted from Synchrotron facilities. They managed to apply this for the first time to time-of-flight electron spectroscopy based on modern instruments as developed within a joint Lab with Uppsala University, Sweden.
Picking single pulses out of a pulse train
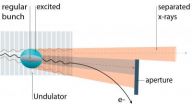
The pulse picking technique is based on a quasi resonant magnetic excitation of transverse oscillations in one specific relativistic electron bunch that – like all others – generates a radiation cone within an undulator. The selective excitation leads to an enlargement of the radiation cone. Employing a detour ("bump") in the electron beam path, the regular radiation and the radiation from the excited electrons can be easily separated and only pulses from the latter arrive – once per revolution - at the experiment. Thus, the arrival time of the pulses is now perfectly accommodated for modern high resolution time-of-flight spectrometers.
Users will be able to examine band structures with higher precision
"The development of the Pulse Picking by Resonant Excitation (PPRE) was science driven by our user community working with single bunch techniques. They demand more beamtime to improve studies on e.g. graphene, topological insulators and other "hot topics" in material science like the current debates about high Tc-Superconductors, magnetic ordering phenomena and catalytic surface effects for energy storage. Moreover, with pulse picking techniques at hand, we are now well prepared for our future light source with variable pulse lengths: BESSY-VSR, where users will appreciate pulse selection on demand to readily switch from high brightness to ultrashort pulses according to their individual needs" says Karsten Holldack, corresponding author of the paper.
First tests successful
The researchers have proven the workability of their method with ARTOF-time-of-flight spectrometers at different undulators and beamlines as well as in BESSY II's regular user mode. "Here we could certainly benefit from long year experiences with emittance manipulation", says Dr. P. Kuske acting as head of the accelerator part of the team. Thanks to accelerator developments in the past, we are capable of even picking ultrashort pulses out of the bunch trains in low-alpha operation, a special operation mode of BESSY II. At last, the users can, already right now, individually switch - within minutes – between high static flux and the single pulse without touching any settings at their instruments and the sample.
INFORMATION:
The work has now been published on May 30th 2014 in Nature Communications: Single Bunch X-ray Pulses on Demand from a Multibunch Synchrotron Radiation Source, K. Holldack et al. DOI 10.1038/ncomms5010
X-ray pulses on demand from electron storage rings
2014-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Glow-in-the-dark tool lets scientists find diseased bats
2014-05-29
Scientists working to understand the devastating bat disease known as white-nose syndrome (WNS) now have a new, non-lethal tool to identify bats with WNS lesions —ultraviolet, or UV, light.
If long-wave UV light is directed at the wings of bats with white-nose syndrome, it produces a distinctive orange-yellow fluorescence. This orange-yellow glow corresponds directly with microscopic skin lesions that are the current "gold standard" for diagnosing white-nose syndrome in bats.
"When we first saw this fluorescence of a bat wing in a cave, we knew we were on to something," ...
Police reform law underenforced by Department of Justice
2014-05-29
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A law designed to combat police misconduct is hamstrung by limited resources, a lack of transparency and "political spillover" at the U.S. Department of Justice, says a recently published empirical study by Stephen Rushin, a law professor at the University of Illinois and expert in criminal law and policing.
In 1994, Congress passed 42 U.S.C. Section 14141 as part of the Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act, granting the U.S. attorney general the power to initiate structural reform litigation against local police departments engaged in a pattern ...
Powerful tool combs family genomes to find shared variations causing disease
2014-05-29
(SALT LAKE CITY)—Scientists at the University of Utah (U of U), the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and colleagues have developed a powerful tool called pVAAST that combines linkage analysis with case control association to help researchers and clinicians identify disease-causing mutations in families faster and more precisely than ever before.
In a study in Nature Biotechnology, the researchers describe cases in which pVAAST (the pedigree Variant Annotation, Analysis and Search Tool) identified mutations in two families with separate diseases ...
Ecosystem services: Looking forward to mid-century
2014-05-29
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — As population grows, society needs more — more energy, more food, more paper, more housing, more of nearly everything. Meeting those needs can lead to changes in how land is used.
Native grasslands, forests and wetlands may be converted into croplands, tree plantations, residential areas and commercial developments. Those conversions can, in turn, diminish the health of natural ecosystems and their ability to provide an array of valuable services, such as clean air and water, wildlife and opportunities for recreation, to name a few.
In two ...
Study: Baltimore hookah bars contain elevated levels of carbon monoxide and air nicotine
2014-05-29
Smoking waterpipes, or hookahs, creates hazardous concentrations of indoor air pollution and poses increased risk from diminished air quality for both employees and patrons of waterpipe bars, according to a new study from the Institute for Global Tobacco Control at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. In an analysis of air quality in seven Baltimore waterpipe bars, researchers found that airborne particulate matter and carbon monoxide exceeded concentrations previously measured in public places that allowed cigarette smoking and that air nicotine was markedly ...
Solar panel manufacturing is greener in Europe than China, study says
2014-05-29
Solar panels made in China have a higher overall carbon footprint and are likely to use substantially more energy during manufacturing than those made in Europe, said a new study from Northwestern University and the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory. The report compared energy and greenhouse gas emissions that go into the manufacturing process of solar panels in Europe and China.
"We estimated that a solar panel's carbon footprint is about twice as high when made in China and used in Europe, compared to those locally made and used in Europe," said ...
Study links unexpected death of a loved one with onset of psychiatric disorders
2014-05-29
May 29, 2014 -- The sudden loss of a loved one can trigger a variety of psychiatric disorders in people with no history of mental illness, according to researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health and colleagues at Columbia's School of Social Work and Harvard Medical School. While previous studies have suggested there is a link between sudden bereavement and an onset of common psychiatric disorders, this is the first study to show the association of acute bereavement and mania in a large population sample. Findings are published online in the American ...
Domestication of dogs may explain mammoth kill sites and success of early modern humans
2014-05-29
A new analysis of European archaeological sites containing large numbers of dead mammoths and dwellings built with mammoth bones has led Penn State Professor Emerita Pat Shipman to formulate a new interpretation of how these sites were formed. She suggests that their abrupt appearance may have been due to early modern humans working with the earliest domestic dogs to kill the now-extinct mammoth -- a now-extinct animal distantly related to the modern-day elephant. Shipman's analysis also provides a way to test the predictions of her new hypothesis. Advance publication of ...
NASA widens 2014 hurricane research mission
2014-05-29
VIDEO:
During this year's Atlantic hurricane season, NASA is redoubling its efforts to probe the inner workings of hurricanes and tropical storms with two unmanned Global Hawk aircraft flying over storms...
Click here for more information.
During this year's Atlantic hurricane season, NASA is redoubling its efforts to probe the inner workings of hurricanes and tropical storms with two unmanned Global Hawk aircraft flying over storms and two new space-based missions.
NASA's ...
Mechanisms of ibrutinib resistance identified in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
2014-05-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study has discovered how resistance develops in patients taking ibrutinib, a new and highly effective drug for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
The study was published in the New England Journal of Medicine and led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James). It identifies gene mutations that cause ibrutinib resistance in CLL patients.
"Knowledge of these mutations is the first step in the development of ...