(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, May 30, 2014—High throughput screening of compounds in live cells is a powerful approach for discovering new drugs, but the potential for cell toxicity must be considered. A novel technique that uses DNA-binding fluorescent dyes to evaluate the cytotoxicity of an experimental compound in real-time during screening, saving time and resources, is described in ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available on the ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies website.
Lucius Chiaraviglio and James Kirby, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, evaluated 19 fluorescent DNA-binding dyes and identified four dyes that were not harmful to cells and could not cross the cell membrane if a cell was viable. The authors demonstrated the ability to use these dyes to detect cell death during drug screening in the article "Evaluation of Impermeant, DNA-Binding Dye Fluorescence as a Real-Time Readout of Eukaryotic Cell Toxicity in a High Throughput Screening Format."
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Assay and Drug Development Technologies is an authoritative peer-reviewed journal published 10 times a year in print and online. It provides early-stage screening techniques and tools that enable identification and optimization of novel targets and lead compounds for new drug development. Complete tables of content and a complementary sample issue may be viewed on the ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers, is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many areas of science and biomedical research, including OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology and Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 80 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website.
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.
140 Huguenot St., New Rochelle, NY 10801-5215
http://www.liebertpub.com
Phone: (914) 740-2100
(800) M-LIEBERT
Fax: (914) 740-2101
DNA-binding fluorescent dyes detect real-time cell toxicity during drug screening
2014-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study explains how green tea could reduce pancreatic cancer risk
2014-05-30
LOS ANGELES – (May 30, 2014) – Green tea and its extracts have been widely touted as potential treatments for cancer, as well as several other diseases. But scientists have struggled to explain how the green tea and its extracts may work to reduce the risk of cancer or to slow the growth of cancer cells.
A study recently published online by the journal, Metabolomics, offers an explanation that researchers say could open a new area of cancer-fighting research. The study reports that EGCG, the active biologic constituent in green tea, changed the metabolism of pancreatic ...
Research shows overall survival benefit for patients with Stage III soft tissue sarcomas
2014-05-30
CHICAGO, IL (May 30, 2014)—Fox Chase Cancer Center researchers have carried out the first retrospective analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy's impact on overall survival in patients with stage III soft tissue sarcomas (STS), adjusted for socioeconomic status and other variables. The findings show that regardless of socioeconomic status and comorbidities, adjuvant chemotherapy improved survival by approximately 23 percent in stage III STS. Study leader Sujana Movva, MD, Medical Oncologist at Fox Chase, will present the findings the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Society ...
More patients with ovarian cancer are receiving chemotherapy before surgery
2014-05-30
CHICAGO, IL (May 30, 2014)—The use of chemotherapy before surgery to remove ovarian cancer has increased dramatically in recent decades, particularly among certain patients, according to a new analysis from Fox Chase Cancer Center that will be presented at the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Looking back at medical records from more than 58,000 women, Fox Chase's Angela Jain, MD, Medical Oncologist and co-investigator Elizabeth Handorf, PhD, member of the Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Facility, found that only 8.94% received chemotherapy ...
Compounds in saliva and common body proteins may fend off DNA-damaging chemicals
2014-05-30
A compound in saliva, along with common proteins in blood and muscle, may protect human cells from powerful toxins in tea, coffee and liquid smoke flavoring, according to results of a new study led by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The findings, reported online May 19 in Food and Chemical Toxicology, suggest that people naturally launch multiple defenses against plant chemicals called pyrogallol-like polyphenols or PLPs found in teas, coffees and liquid smoke flavoring. The presence of these defenses could help explain why PLPs are not crippling ...
New satellite animation shows the end of Hurricane Amanda
2014-05-30
VIDEO:
This animation of visible and infrared imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite shows the weakening of Hurricane Amanda from May 28 to its dissipation on May 30.
Click here for more information.
A new animation of visible and infrared imagery from NOAA's GOES-West satellite shows the weakening and dissipation of the Eastern Pacific Ocean's Hurricane Amanda. The animation that runs from from May 28 to May 30 was created at NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space ...
Hepatitis C reactivation doesn't worsen survival for HIV+ patients diagnosed with lymphoma
2014-05-30
CHICAGO, IL (May 30, 2014)—More than a quarter of HIV+ patients are also infected with the Hepatitis C virus (HCV), which may complicate treatment and care decisions after a cancer diagnosis. The specifics of those complications haven't been well-researched in the past. Results from a new Fox Chase Cancer Center study on this patient population may start filling in that gap.
Fox Chase Hematologist and Medical Oncologist Stefan K. Barta, MD, MS, MRCP – who led the study – analyzed data from HIV+ patients diagnosed with lymphoma, collected over 17 years, to better understand ...
Identification of central nervous system involvement for patients with AIDS-related lymphomas
2014-05-30
CHICAGO, IL (May 30, 2014)—Patients with AIDS-related lymphomas (ARL) may face an increased risk of central nervous system involvement (CNSi) compared to other lymphomas. The effect of CNSi on survival outcomes, however, hasn't been thoroughly examined until now.
In a new study led by Fox Chase Cancer Center Hematologist and Oncologist Stefan K. Barta, MD, MS, MRCP, researchers report that CNSi – identified at the time of an ARL diagnosis – does not appear to have an impact on overall survival. Dr. Barta's collaborators will present the findings at the 50th Annual Meeting ...
Moffitt Cancer Center instrumental in new clinical guidelines for cancer-related fatigue
2014-05-30
TAMPA, Fla. (May 30, 2014) – Fatigue is a debilitating problem for cancer patients undergoing treatment; however, it also poses a huge detriment after treatment and can significantly affect quality of life. Approximately 30 percent of cancer patients endure persistent fatigue for several years after treatment, according to an American Society of Clinical Oncology Expert Panel co-chaired by Paul Jacobsen, Ph.D., associate center director of Population Sciences at Moffitt Cancer Center.
ASCO created the panel to develop assessment, screening, and treatment guidelines for ...
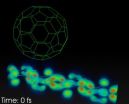
First real time movies of the light-to-current conversion in an organic solar cell
2014-05-30
VIDEO:
Real time quantum simulation of the conversion of light into current in an organic solar cell composed of a polymer chain, and a Fullerene buckyball. The movie lasts for about...
Click here for more information.
Photovoltaic cells directly convert sun light into electricity and hence are key technological devices to meet one of the challenges that mankind has to face in this century: a sustainable and clean production of renewable energy. Organic solar cells, using polymeric ...
Research details how developing neurons sense a chemical cue
2014-05-30
Symmetry is an inherent part of development. As an embryo, an organism's brain and spinal cord, like the rest of its body, organize themselves into left and right halves as they grow. But a certain set of nerve cells do something unusual: they cross from one side to the other. New research in mice delves into the details of the molecular interactions that help guide these neurons toward this anatomical boundary.
In an embryo, a neuron's branches, or axons, have special structures on their tips that sense chemical cues telling them where to grow. The new findings, by ...