(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
Imagine a tower builds itself into the desired structure only by choosing the appropriate bricks. Absurd – and however, in the nano world this is reality: There an unordered crowd of components can initiate the formation of an ordered structure – a process known as self-assembly. The physicists Christos Likos (University of Vienna), Emanuela Bianchi and Gerhard Kahl (both Vienna University of Technology) investigate how they can control the ordering of such self-assembling structures and found out how to switch the assembly process on and off. The results are now published in the high-impact journal Nano Letters.
Materials with specific properties at the nano- and micro-scale level are heavily sought after due to the broad spectrum of applications in electronics, photovoltaics and biomimetic material synthesis. For many of these applications, mesoscopic crystalline structures are often needed and hence scientists have to deal with the challenge of developing reliable, efficient and cheap methods to produce target structures with specific symmetries and physical properties. Nowadays, rather than relying on externally-controlled tools, most of the fabrication methods are based on the self-assembly of carefully chosen/synthesized base units. The macroscopic counterpart would correspond to building a tower or a bridge just by choosing the appropriate bricks and letting them self-organize into the desired structure.
In the vast realm of functional nano- and micro-scale materials, the realization of mono- and bi-layer assemblies on surfaces is of paramount relevance. Low-dimensional systems with well-defined features have indeed applications as e.g. antireflection coatings, biosensors, data-storage, optical and photovoltaic devices, or catalysts. The properties of these materials strongly depend on a delicate balance between the properties of the assembling units and those of the underlying surface.
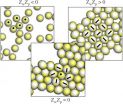
In our contribution we focused on nano-units with a complicated surface pattern, consisting of regions with different surface charge. The investigated units are mostly negatively charged with the exception of the positively charged polar regions on the top and at the bottom of the particles. Similar non-homogeneously charged units appear either in biosystems, e.g. viral capsids and proteins, or in experimentally synthesized systems, e.g. virus-like nano-particles, spotted vesicles and nano-cubes covered with specific metals.
In the up-coming paper we focused on the self-assembly of the described heterogeneously charged particles in the vicinity of a homogeneously charged substrate. Our computer simulations showed how complex structures at the nano-scale level can spontaneously emerge and how it is possible to reliably control the ordering of the particles into specific, quasi two-dimensional aggregates. Depending on different parameters, such as the particle/wall charge and the extension of the charged regions on the particle surface, our units can form surface layers with different densities (and possibly different responses to external stimuli): sometimes particles assemble into close-packed, hexagonally ordered crystalline aggregates, sometimes they form open, square-like layers, sometimes they do not assemble at all. Our work was able to investigate the variety of the self-assembled structures offered by the chosen bricks and to characterise the specific collective behaviors occurring on tuning the relevant parameters of these systems. Moreover and most importantly, we showed that upon subtle changes of either the pH of the solution or of the electrical charge of the substrate, it is possible to reversibly switch the assembly process on and off as well as to induce a transformation from a one specific spatial/orientational arrangement to another.
INFORMATION:
Publication in Nano Letters:
Emanuela Bianchi, Christos N. Likos und Gerhard Kahl: Tunable Assembly of Heterogeneously Charged Colloids. In: Nano Letters (2014).
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl500934v
The University of Vienna, founded in 1365, is one of the oldest and largest universities in Europe. About 9,500 employees, 6,700 of who are academic employees, work at 15 faculties and four centres. This makes the University of Vienna Austria's largest research and education institution. About 92,000 national and international students are currently enrolled at the University of Vienna. With more than 180 degree programmes, the University offers the most diverse range of studies in Austria. The University of Vienna is also a major provider of continuing education. In 2015, the Alma Mater Rudolphina Vindobonensis celebrates its 650th Anniversary. http://www.univie.ac.at
Nano world: Where towers construct themselves
How physicists get control on the self-assembly process
2014-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Physicist builds useful light source from harmonic generation
2014-06-02
MANHATTAN, KANSAS — A Kansas State University physicist's proposal may lead to a new way of creating tabletop light sources in the laboratory.
Cheng Jin, research associate in physics; Chii-Dong Lin, university distinguished professor of physics; and collaborators are developing a way to greatly enhance the generation of high-order harmonics to create powerful small tabletop light sources that are important to science and technology.
The researchers are building theoretical framework and providing experimental guidance in the area of strong-field physics. The work is ...
CU Denver study shows public health often ignored in transportation policy
2014-06-02
DENVER (June 2, 2014) – A new study from the University of Colorado Denver shows public health issues are often ignored in many transportation projects, especially when major roads are built through lower-income neighborhoods.
Air pollution, crime and numerous traffic hazards, the study said, point to a serious and persistent gap between public health and planning.
"The public health effects of heavy traffic are broad," said study author Carolyn McAndrews, PhD, assistant professor at the CU Denver College of Architecture and Planning, one of the largest schools of its ...
Surgeons report fewer postoperative blood clots using risk-based preventive measures
2014-06-02
Chicago (June 2, 2014): Surgery patients are much less likely to get a blood clot in the lower extremities or lungs if they receive preventive treatment based on their individual clotting risk, in addition to walking soon after the operation. Results from a surgical quality improvement study, appearing in the June issue of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons, indicate that the odds of this common and potentially life-threatening postoperative complication steadily declined after the implementation of a multicomponent prevention program in a hospital's department ...
Study links evening blue light exposure to increased hunger
2014-06-02
DARIEN, IL – A new study suggests that blue-enriched light exposure immediately before and during the evening meal may increase hunger and alter metabolism.
Results show that blue-enriched light exposure, compared with dim light exposure, was associated with an increase in hunger that began 15 minutes after light onset and was still present almost two hours after the meal. Blue light exposure also decreased sleepiness and resulted in higher measures of insulin resistance.
"It was very interesting to observe that a single three-hour exposure to blue-enriched light in ...
Astronomers find a new type of planet: The 'mega-Earth'
2014-06-02
Astronomers announced today that they have discovered a new type of planet - a rocky world weighing 17 times as much as Earth. Theorists believed such a world couldn't form because anything so hefty would grab hydrogen gas as it grew and become a Jupiter-like gas giant. This planet, though, is all solids and much bigger than previously discovered "super-Earths," making it a "mega-Earth."
"We were very surprised when we realized what we had found," says astronomer Xavier Dumusque of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), who led the data analysis and made ...
'Neapolitan' exoplanets come in three flavors
2014-06-02
The planets of our solar system come in two basic flavors, like vanilla and chocolate ice cream. We have small, rocky terrestrials like Earth and Mars, and large gas giants like Neptune and Jupiter. We're missing the astronomical equivalent of strawberry ice cream - planets between about one and four times the size of Earth. NASA's Kepler mission has discovered that these types of planets are very common around other stars.
New research following up on the Kepler discoveries shows that alien worlds, or exoplanets, can be divided into three groups - terrestrials, gas giants, ...
Harsh space weather may doom potential life on red-dwarf planets
2014-06-02
Life in the universe might be even rarer than we thought. Recently, astronomers looking for potentially habitable worlds have targeted red dwarf stars because they are the most common type of star, comprising 80 percent of the stars in the universe. But a new study shows that harsh space weather might strip the atmosphere of any rocky planet orbiting in a red dwarf's habitable zone.
"A red-dwarf planet faces an extreme space environment, in addition to other stresses like tidal locking," says Ofer Cohen of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA).
Cohen ...
Because you can't eat just one: Star will swallow two planets
2014-06-02
Two worlds orbiting a distant star are about to become a snack of cosmic proportions. Astronomers announced today that the planets Kepler-56b and Kepler-56c will be swallowed by their star in a short time by astronomical standards. Their ends will come in 130 million and 155 million years, respectively.
"As far as we know, this is the first time two known exoplanets in a single system have a predicted 'time of death,'" says lead author Gongjie Li of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA).
She presented her research today in a press conference at a meeting ...
Long-term results encouraging for combination immunotherapy for advanced melanoma
2014-06-02
New Haven, CT — The first long-term follow-up results from a phase 1b immunotherapy trial combining drugs for advanced melanoma patients has shown encouraging results — long-lasting with high survival rates — researchers report. First author Mario Sznol, M.D., professor of medical oncology at Yale Cancer Center, is presenting the updated data at the 2014 annual conference of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in Chicago.
Sznol, clinical research leader of the melanoma research program at Yale Cancer Center, was the senior author on the original study of ...
Does your stomach bacteria protect you from obesity?
2014-06-02
The germ Helicobacter pylori is the cause of most stomach ulcers, but new research in Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics suggests that treating the bacteria is linked to weight gain.
It is estimated that 50% of the global population may be infected with H. pylori; however, only 20% of infected people experience symptoms. New evidence suggests that patients treated for the infection developed significant weight gain compared to subjects with untreated H. pylori colonization.
By reviewing data taken from forty-nine studies with data from ten European countries, Japan, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Nano world: Where towers construct themselvesHow physicists get control on the self-assembly process