(Press-News.org) CHICAGO — In examining why some advanced melanoma patients respond so well to the experimental immunotherapy MK-3475, while others have a less robust response, researchers at Mayo Clinic in Florida found that the size of tumors before treatment was the strongest variable.
MULTIMEDIA ALERT: Video and audio are available for download on the Mayo Clinic News Network.
They say their findings, being presented June 2 at the 50th annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), offered several clinical insights that could lead to different treatment strategies and perhaps influence staging of advanced melanoma.
"This was the first robust assessment to determine the impact of baseline tumor size on clinical endpoints in patients with metastatic melanoma — in particular — those receiving MK-3475. Our findings suggest the location of spread is less important than the amount of tumor that is present before treatment," says the study's lead investigator, Richard W. Joseph, M.D., an oncologist at Mayo Clinic in Florida.
Metastatic melanoma is currently staged primarily according to where the cancer has spread — Stage IVa if melanoma has spread to distant skin, Stage IVb if the cancer has reached the lungs, and Stage IVc when melanoma has spread to other organs, such as the liver or bones. In general, prognosis for Stage IVa is best and for Stage IVc is worst.
"The traditional staging system does not account for the total volume of disease or baseline tumor burden," Dr. Joseph says. "For instance, a Stage IVb patient with metastases only to the lung would be expected to have a better prognosis than a patient with Stage IVc. However, a patient with a large volume of disease in the lung may, in fact, have a worse prognosis than someone with a small volume of disease in the liver," Dr. Joseph says.
"That is not to say this drug doesn't work in patients with a large amount of disease. However, the efficacy is significantly less than in those with small volume disease," he says. "While this may seem intuitive, this was the first robust analysis of its kind."
The likely reason for this finding is that MK-3475 is a monoclonal antibody that stimulates the body's immune system response to the tumors, Dr. Joseph says. "But the immune system can get overwhelmed when there is too much tumor, and not work as effectively as possible," he says. "Some tumors have evolved to both evade and turn off nearby immune cells. MK-3475 provides a shield for the immune cells so that they can remain active when they reach the tumor."
The drug is also being investigated in lung, bladder and kidney cancer.
"The implications of these findings are that perhaps decreasing the baseline tumor size through surgery or other means and then treating with MK-3475 may be a more effective means of inducing long-lasting remissions," he says. Follow-up studies will be necessary to explore this strategy, he adds.
While Dr. Joseph led this study, he is a part of a team of international researchers studying the drug, which he says has offered patients with metastatic melanoma "truly impressive results." In a phase I clinical trial, overall survival one year after treatment was 81 percent.
"In the past, immunotherapies were associated with relatively high toxicities and provided meaningful clinical benefit to the minority of patients. MK-3475 and other drugs like it are revolutionizing the way we treat metastatic melanoma by benefitting a much larger segment of the population as well as having very few side effects," says Dr. Joseph.
MK-3475 is on the Food and Drug Administration's list of priority reviews.
Dr. Joseph and Mayo Clinic in Florida have currently enrolled an additional 20 patients since the clinical trial was re-opened in April through an expanded access program for qualifying patients.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by Merck.
About Mayo Clinic
Recognizing 150 years of serving humanity in 2014, Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit worldwide leader in medical care, research and education for people from all walks of life. For more information, visit 150years.mayoclinic.org, MayoClinic.org or newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org.
About Mayo Clinic Cancer Center
As a leading institution funded by the National Cancer Institute, Mayo Clinic Cancer Center conducts basic, clinical and population science research, translating discoveries into improved methods for prevention, diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. For information on cancer clinical trials, call 507-538-7623
Tumor size is defining factor to response from promising melanoma drug
2014-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Anti-diabetic drug slows aging and lengthens lifespan
2014-06-02
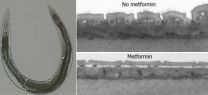
A study by Belgian doctoral researcher Wouter De Haes (KU Leuven) and colleagues provides new evidence that metformin, the world's most widely used anti-diabetic drug, slows ageing and increases lifespan.
In experiments reported in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers tease out the mechanism behind metformin's age-slowing effects: the drug causes an increase in the number of toxic oxygen molecules released in the cell and this, surprisingly, increases cell robustness and longevity in the long term.
Mitochondria – the energy factories ...
Marijuana shows potential in treating autoimmune disease
2014-06-02
A team of University of South Carolina researchers led by Mitzi Nagarkatti, Prakash Nagarkatti and Xiaoming Yang have discovered a novel pathway through which marijuana can suppress the body's immune functions. Their research has been published online in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Marijuana is the most frequently used illicit drug in the United States, but as more states legalize the drug for medical and even recreational purposes, research studies like this one are discovering new and innovative potential health applications for the federal Schedule I drug. ...
Shape matters...
2014-06-02
Which look bigger, packages of complicated shape or packages of simple shape? Some prior research shows that complex packages appear larger than simple packages of equal volume, while other research has shown the opposite - that simple packages look bigger than the more complex. US researchers, writing in the International Journal of Management Practice believe they have resolved this dilemma.
Lawrence Garber of Elon University in North Carolina and Eva Hyatt and Ünal Boya of Appalachian State University report that human beings are just not very good at estimating the ...
Carnegie Mellon researchers discover social integration improves lung function in elderly
2014-06-02
PITTSBURGH—It is well established that being involved in more social roles, such as being married, having close friends, close family members, and belonging to social and religious groups, leads to better mental and physical health. However, why social integration — the total number of social roles in which a person participates — influences health and longevity has not been clear.
New research led by Carnegie Mellon University shows for the first time that social integration impacts pulmonary function in the elderly. Lung function, which decreases with age, is an important ...
Study suggests fast food cues hurt ability to savor experience
2014-06-02
Toronto – Want to be able to smell the roses?
You might consider buying into a neighbourhood where there are more sit-down restaurants than fast-food outlets, suggests a new paper from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management.
The paper looks at how exposure to fast food can push us to be more impatient and that this can undermine our ability to smell the preverbal roses.
One study, surveyed a few hundred respondents throughout the US on their ability to savor a variety of realistic, enjoyable experiences such as discovering a beautiful waterfall on ...
Gene therapy combined with IMRT found to reduce recurrence for select prostate cancer patients
2014-06-02
Fairfax, Va., June 2, 2014—Combining oncolytic adenovirus-mediated cytotoxic gene therapy (OAMCGT) with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) reduces the risk of having a positive prostate biopsy two years after treatment in intermediate-risk prostate cancer without affecting patients' quality of life, according to a study published in the June 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Previous prospective ...
How Thomas Edison laid the foundation for the modern lab (video)
2014-06-02
WASHINGTON, June 2, 2014 — Thomas Edison is hands-down one of the greatest inventors in history. He also had a love of chemistry that banished him to the basement as a kid. This week, the Reactions team went behind the scenes at the Thomas Edison National Historical Park to see how Edison's love of chemistry fueled his world-changing inventions. Recently named a National Historic Chemical Landmark, the complex is home to more than 400,000 artifacts (which we definitely weren't allowed to touch) and is considered the template for modern research-and-development labs everywhere. ...
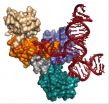
Scientists capture most detailed images yet of humans' tiny cellular machines
2014-06-02
MADISON, Wis. — A grandfather clock is, on its surface, a simple yet elegant machine. Tall and stately, its job is to steadily tick away the time. But a look inside reveals a much more intricate dance of parts, from precisely-fitted gears to cable-embraced pulleys and bobbing levers.
Like exploring the inner workings of a clock, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers is digging into the inner workings of the tiny cellular machines called spliceosomes, which help make all of the proteins our bodies need to function. In a recent study published in the journal ...
Computer scientists develop tool to make the Internet of Things safer
2014-06-02
Computer scientists at the University of California, San Diego, have developed a tool that allows hardware designers and system builders to test security- a first for the field. One of the tool's potential uses is described in the May-June issue of IEEE Micro magazine.
"The stakes in hardware security are high", said Ryan Kastner, a professor of computer science at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego.
There is a big push to create the so-called Internet of Things, where all devices are connected and communicate with one another. As a result, embedded ...
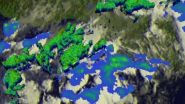
NASA's TRMM satellite sees Eastern Pacific tropical cyclone forming
2014-06-02
VIDEO:
This 3-D animated fly-by of developing tropical low pressure System 93E on June 2 revealed the highest thunderstorms (in red) as it continues to develop.
Click here for more information.
There's a new tropical low pressure area brewing in the Eastern Pacific and NASA's TRMM satellite flew overhead and got a read on its rainfall rates and cloud heights.
The eastern Pacific Ocean has become active on cue with the start of the hurricane season in that area. Only a few days ...