(Press-News.org) Fairfax, Va., June 2, 2014—Combining oncolytic adenovirus-mediated cytotoxic gene therapy (OAMCGT) with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) reduces the risk of having a positive prostate biopsy two years after treatment in intermediate-risk prostate cancer without affecting patients' quality of life, according to a study published in the June 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Previous prospective clinical trials in prostate cancer have shown that increasing the standard radiation dose of 70 Gy by 10 to 15 percent improves the biochemical disease-free survival in some prognostic risk groups; however, more than 25 percent of men with intermediate- or high-risk disease develop prostate-specific antigen (PSA) progression within 10 years, suggesting that radiation doses higher than 80 Gy may be necessary. This prospective randomized phase II trial examines the use of OAMCGT to improve the effectiveness of IMRT without increasing the radiation dose in intermediate-risk prostate cancer.
Based on encouraging results from a prior phase I trial, 44 patients were enrolled in this randomized phase II trial from January 2008 to July 2010. Patients were randomized to receive either OAMCGT with IMRT (21) or IMRT alone (23), and outcomes were focused on toxicity, quality of life and prostate biopsy findings at two years post-treatment. Eligible patients had newly diagnosed, clinically localized, intermediate-risk prostate cancer, defined as clinical stage T1/T2 with a Gleason score of 7 or a PSA of 10 to 20 ng/ml. Patients with a Gleason score of 5/6, a PSA END
Gene therapy combined with IMRT found to reduce recurrence for select prostate cancer patients
Quality of life and toxicity measures also favorable
2014-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How Thomas Edison laid the foundation for the modern lab (video)
2014-06-02
WASHINGTON, June 2, 2014 — Thomas Edison is hands-down one of the greatest inventors in history. He also had a love of chemistry that banished him to the basement as a kid. This week, the Reactions team went behind the scenes at the Thomas Edison National Historical Park to see how Edison's love of chemistry fueled his world-changing inventions. Recently named a National Historic Chemical Landmark, the complex is home to more than 400,000 artifacts (which we definitely weren't allowed to touch) and is considered the template for modern research-and-development labs everywhere. ...
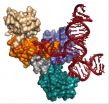
Scientists capture most detailed images yet of humans' tiny cellular machines
2014-06-02
MADISON, Wis. — A grandfather clock is, on its surface, a simple yet elegant machine. Tall and stately, its job is to steadily tick away the time. But a look inside reveals a much more intricate dance of parts, from precisely-fitted gears to cable-embraced pulleys and bobbing levers.
Like exploring the inner workings of a clock, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers is digging into the inner workings of the tiny cellular machines called spliceosomes, which help make all of the proteins our bodies need to function. In a recent study published in the journal ...
Computer scientists develop tool to make the Internet of Things safer
2014-06-02
Computer scientists at the University of California, San Diego, have developed a tool that allows hardware designers and system builders to test security- a first for the field. One of the tool's potential uses is described in the May-June issue of IEEE Micro magazine.
"The stakes in hardware security are high", said Ryan Kastner, a professor of computer science at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego.
There is a big push to create the so-called Internet of Things, where all devices are connected and communicate with one another. As a result, embedded ...
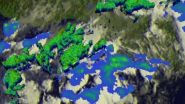
NASA's TRMM satellite sees Eastern Pacific tropical cyclone forming
2014-06-02
VIDEO:
This 3-D animated fly-by of developing tropical low pressure System 93E on June 2 revealed the highest thunderstorms (in red) as it continues to develop.
Click here for more information.
There's a new tropical low pressure area brewing in the Eastern Pacific and NASA's TRMM satellite flew overhead and got a read on its rainfall rates and cloud heights.
The eastern Pacific Ocean has become active on cue with the start of the hurricane season in that area. Only a few days ...
Laser device can detect alcohol in cars, say authors in Journal of Applied Remote Sensing
2014-06-02
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA — A new open-access article in the Journal of Applied Remote Sensing is garnering attention for research that could aid in the campaign to prevent drunk driving: a device that can detect alcohol in cars. The Journal of Applied Remote Sensing is published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.
The article "Stand-off detection of alcohol in car cabins," by Jarosław Młyńczak, Jan Kubicki, and Krzysztof Kopczyński of the Military University of Technology in Warsaw, details experiments using an external ...
Solving the puzzle of ice age climates
2014-06-02
The paleoclimate record for the last ice age — a time 21,000 years ago called the "Last Glacial Maximum" (LGM) — tells of a cold Earth whose northern continents were covered by vast ice sheets. Chemical traces from plankton fossils in deep-sea sediments reveal rearranged ocean water masses, as well as extended sea ice coverage off Antarctica. Air bubbles in ice cores show that carbon dioxide in the atmosphere was far below levels seen before the Industrial Revolution.
While ice ages are set into motion by Earth's slow wobbles in its transit around the sun, researchers ...
Seniors who exercise regularly experience less physical decline as they age
2014-06-02
COLUMBIA, Mo. –The majority of adults aged 65 and older remains inactive and fails to meet recommended physical activity guidelines, previous research has shown. However, these studies have not represented elders living in retirement communities who may have more access to recreational activities and exercise equipment. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri found that older adults in retirement communities who reported more exercise experienced less physical decline than their peers who reported less exercise, although many adults — even those who exercised — did ...
CDC report: Patients harmed after health-care providers steal patients' drugs
2014-06-02
Rochester, MN, June 2, 2014 – When prescription medicines are stolen or used illegally, it is called drug diversion. One aspect of drug diversion that is not well recognized involves health care providers who steal controlled substances for their personal use. A report authored by experts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) --published today in Mayo Clinic Proceedings -- outlines outbreaks of infections that have occurred as a result of health care providers stealing or tampering with their patients' medications. These outbreaks revealed gaps in prevention, ...
Rensselaer researchers predict the electrical response of metals to extreme pressures
2014-06-02
Troy, N.Y. – Research published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences makes it possible to predict how subjecting metals to severe pressure can lower their electrical resistance, a finding that could have applications in computer chips and other materials that could benefit from specific electrical resistance.
The semiconductor industry has long manipulated materials like silicon through the use of pressure, a strategy known as "strain engineering," to improve the performance of transistors. But as the speed of transistors has increased, the limited ...
Study shows impact of tart cherries on inflammation and oxidative stress after cycling
2014-06-02
Cyclists who drank Montmorency tart cherry juice concentrate before a three-day simulated race experienced less inflammation and oxidative stress compared to those who drank another beverage, according to a recent U.K. study published in the journal Nutrients.
A research team led by Dr. Glyn Howatson with PhD student Phillip Bell at Northumbria University gave 16 well-trained, male cyclists about 1 ounce (30 ml) of Montmorency tart cherry juice concentrate mixed with water (equivalent to 90 whole Montmorency tart cherries per serving), or a calorie-matched placebo, twice ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
[Press-News.org] Gene therapy combined with IMRT found to reduce recurrence for select prostate cancer patientsQuality of life and toxicity measures also favorable