(Press-News.org) Researchers from the Department of Cell Biology, Physiology and Immunology at Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), in collaboration with researchers from the Institute of Microelectronics of Barcelona (IMB-CNM) of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), have developed an identification system for oocytes and embryos in which each can be individually tagged using silicon barcodes. Researchers are now working to perfect the system and soon will test it with human oocytes and embryos.
The research, published online in Human Reproduction, represents a first step towards designing a direct labelling system of oocytes and embryos. The objective was to develop a system which minimises risks when identifying female gametes and embryos during in vitro fertilisation and embryo transfer procedures, to reduce the phases of the clinical process requiring control and supervision by two embryologists.
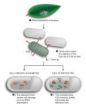
Microscopic silicon codes, fabricated using microelectronic techniques, were employed in the research. In previous tests, researchers verified the innocuousness of silicon particles in human cells, particularly in macrophages. In the present study, the codes were microinjected into the perivitelline space of mouse embryos, located between the cell membrane and the zona pellucida, a cover which surrounds the plasma membrane of the embryo. Since the embryo exits the zona pellucida before its implantation in the uterus, this approximation should allow the embryo to free itself of the identification codes when leaving the zona pellucida.
This research shows that labelled embryos develop normally in culture up to the blastocyst stage, the phase of development which precedes implantation. Researchers also studied the retention of the codes throughout the culture process, the easiness in reading the codes in a standard microscope, and their elimination when embryos free themselves from the zona pellucida. The research also verified the efficacy of the system when freezing and thawing the embryos.
To make the system more viable, researchers are now working on improving the embryo's process of freeing itself from the identification code. This is the only stage of the research which presented limitations. They are currently studying whether the modification of the codes' surface could allow their direct attachment to the outer side of the zona pellucida, avoiding their microinjection into the perivitelline space. They also aim to develop an automatic code reading system.
Researchers recently received authorisation from the Department of Health of the Government of Catalonia to begin testing the system with human oocytes and embryos from several fertility clinics in Spain.
INFORMATION:
The research was carried out with the participation of Elena Ibáñez, Sergi Novo, Leonardo Barrios, Josep Santaló and Carme Nogués from the UAB Department of Cell Biology, Physiology and Immunology; and Rodrigo Gómez-Martínez, Marta Duch, Jaume Esteve and José Antonio Plaza from the Institute of Microelectronics of Barcelona, a CSIC member centre, at the UAB Research Park.
Reference article: A Novel Embryo Identification System by Direct Tagging Using Silicon-Based Barcodes. Novo, S., Barrios, L., Santaló, J., Gómez-Martínez, R., Duch, M., Esteve, J., Plaza, J.A., Nogués, C., Ibáñez, E. Human Reproduction. doi:10.1093/humrep/deq309
Researchers insert identification codes into mouse embryos
In a study to improve traceability of reproductive material
2010-11-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Laboratory studies show promise for new multiple sclerosis treatment
2010-11-19
Successfully treating and reversing the effects of multiple sclerosis, or MS, may one day be possible using a drug originally developed to treat chronic pain, according to Distinguished Professor Linda Watkins of the University of Colorado at Boulder.
Watkins and her colleagues in CU-Boulder's department of psychology and neuroscience discovered that a single injection of a compound called ATL313 -- an anti-inflammatory drug being developed to treat chronic pain -- stopped the progression of MS-caused paralysis in rats for weeks at a time.
Lisa Loram, a senior research ...
Bacteria use 'toxic darts' to disable each other, according to UCSB scientists
2010-11-19
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– In nature, it's a dog-eat-dog world, even in the realm of bacteria. Competing bacteria use "toxic darts" to disable each other, according to a new study by UC Santa Barbara biologists. Their research is published in the journal Nature.
"The discovery of toxic darts could eventually lead to new ways to control disease-causing pathogens," said Stephanie K. Aoki, first author and postdoctoral fellow in UCSB's Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology (MCDB). "This is important because resistance to antibiotics is on the rise."
Second ...
Wellness programs provide high returns, research reveals
2010-11-19
Employee wellness programs have often been viewed as a nice extra, not a strategic imperative. But the data demonstrate otherwise, according to a team of researchers led by Leonard L. Berry of Texas A&M University, Ann M. Mirabito of Baylor University and William B. Baun of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Their research shows that the return on investment on comprehensive, well-run employee wellness programs is impressive — sometimes as high as six to one.
The findings are compiled in a comprehensive piece in the December issue of Harvard Business ...
Spacecraft flew through 'snowstorm' on encounter with comet Hartley 2
2010-11-19
COLLEGE PARK, Md. -- On its recent trip by comet Hartley 2, the Deep Impact spacecraft took the first pictures of, and flew through, a storm of fluffy particles of water ice being spewed out by carbon dioxide jets coming from the rough ends of the comet. The resulting images and data shed new light on the nature and composition of comets, according to the University of Maryland-led EPOXI science team, which today announced its latest findings and released the first images of this comet created snowstorm. See images at: http://epoxi.umd.edu/index.shtml
"When we visited ...
Latest American Chemical Society podcast: New water filter kills disease-causing bacteria
2010-11-19
WASHINGTON, Nov. 18, 2010 — The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS) award-winning podcast series, "Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions," focuses on development and successful initial tests of an inexpensive new filtering technology that kills up to 98 percent of disease-causing bacteria in water in just seconds without clogging.
The technology could aid many of the almost one billion people lacking access to clean, safe drinking water. A report on the work appears in the American Chemical Society's monthly journal Nano Letters.
Most water purifiers ...
Researchers identify PTSD measures for use in traumatic brain injury research
2010-11-19
(Boston) - Five U.S. federal agencies recently cosponsored a set of expert work groups to formulate common data elements for research related to psychological adjustment and traumatic brain injury (TBI). Danny G. Kaloupek, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at Boston University School of Medicine, chaired the work group on posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Dr. Kaloupek's work at the National Center for PTSD at VA Boston Healthcare helped to guide identification of key PTSD-related characteristics and evidence-based measures that might ...
Taking a break from osteoporosis drugs can protect bones
2010-11-19
MAYWOOD, Ill. -- Taking time off from certain osteoporosis drugs may be beneficial to bone health, according to a study conducted at Loyola University Health System. Researchers found that bone density remained stable for three years in patients who took a drug holiday from bisphosphonates, a popular class of osteoporosis drugs that can cause fractures in the thigh bones and tissue decay in the jaw bone.
"These drugs are potentially harmful when taken for long durations, yet little has been known until now about the length of time osteoporosis patients should go without ...
Al Jazeera helps shape political identity of Arabs, study finds
2010-11-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Residents of the Middle East who are heavy viewers of Arab television news networks like Al Jazeera are more likely to view their primary identity as that of Muslims, rather than as citizens of their own country, a new study suggests.
Because networks like Al Jazeera are transnational – focusing on events of interest across the region rather than those in any one country – they may encourage viewers to see themselves in broader terms than simply residents of a particular nation, the researchers said.
"The goal of these relatively new networks is not ...
Culturally sensitive treatment model helps bring depressed Chinese immigrants into treatment
2010-11-19
A treatment model designed to accommodate the beliefs and concerns of Chinese immigrants appears to significantly improve the recognition and treatment of major depression in this typically underserved group. In a report in the December American Journal of Public Health, a Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) research team describes how their model for screening and assessing patients for depression in a primary care setting increased the percentage of depressed patients entering treatment nearly sevenfold.
"Ours is the first study to incorporate a culturally sensitive ...
What factors contribute to the success or failure of software firms?
2010-11-19
PITTSBURGH—Throughout the 1990s and 2000s, news about 20-somethings becoming billionaires from the sale of their software companies flooded the media, giving the impression that a good idea was all it took to succeed in the software industry. Jennifer Shang, an associate professor of business management in the Joseph M. Katz Graduate School of Business, along with colleagues Shanling Li of McGill University and Sandra Slaughter of the Georgia Institute of Technology, investigated what caused software companies to succeed or fail. Their research study, titled "Why Do Software ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Researchers insert identification codes into mouse embryosIn a study to improve traceability of reproductive material