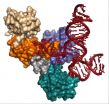
(Press-News.org) Scientists at New York University and the University of Melbourne have developed a method using DNA origami to turn one-dimensional nano materials into two dimensions. Their breakthrough, published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Nanotechnology, offers the potential to enhance fiber optics and electronic devices by reducing their size and increasing their speed.
"We can now take linear nano-materials and direct how they are organized in two dimensions, using a DNA origami platform to create any number of shapes," explains NYU Chemistry Professor Nadrian Seeman, the paper's senior author, who founded and developed the field of DNA nanotechnology, now pursued by laboratories around the globe, three decades ago.
Seeman's collaborator, Sally Gras, an associate professor at the University of Melbourne, says, "We brought together two of life's building blocks, DNA and protein, in an exciting new way. We are growing protein fibers within a DNA origami structure."
DNA origami employs approximately two hundred short DNA strands to direct longer strands in forming specific shapes. In their work, the scientists sought to create, and then manipulate the shape of, amyloid fibrils—rods of aggregated proteins, or peptides, that match the strength of spider's silk.
To do so, they engineered a collection of 20 DNA double helices to form a nanotube big enough (15 to 20 nanometers—just over one-billionth of a meter—in diameter) to house the fibrils.
The platform builds the fibrils by combining the properties of the nanotube with a synthetic peptide fragment that is placed inside the cylinder. The resulting fibril-filled nanotubes can then be organized into two-dimensional structures through a series of DNA-DNA hybridization interactions.
"Fibrils are remarkably strong and, as such, are a good barometer for this method's ability to form two-dimensional structures," observes Seeman. "If we can manipulate the orientations of fibrils, we can do the same with other linear materials in the future."
Seeman points to the promise of creating two-dimensional shapes on the nanoscale.
"If we can make smaller and stronger materials in electronics and photonics, we have the potential to improve consumer products," Seeman says. "For instance, when components are smaller, it means the signals they transmit don't need to go as far, which increases their operating speed. That's why small is so exciting—you can make better structures on the tiniest chemical scales."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by grants from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, part of the National Institutes of Health (GM-29554), the National Science Foundation (CMMI-1120890, CCF-1117210), the Army Research Office (MURI W911NF-11-1-0024), the Office of Naval Research (N000141110729, N000140911118), an Australian Nanotechnology Network Overseas Travel Fellowship, a Melbourne Abroad Travelling Scholarship, the Bio21 Institute and Particulate Fluids Processing Centre. The work was carried out, in part, at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials, Brookhaven National Laboratory, which is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences.
Nano-platform ready: Scientists use DNA origami to create 2-D structures
2014-06-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists capture most detailed images yet of tiny cellular machines
2014-06-03
MADISON, Wis. — A grandfather clock is, on its surface, a simple yet elegant machine. Tall and stately, its job is to steadily tick away the time. But a look inside reveals a much more intricate dance of parts, from precisely-fitted gears to cable-embraced pulleys and bobbing levers.
Like exploring the inner workings of a clock, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers is digging into the inner workings of the tiny cellular machines called spliceosomes, which help make all of the proteins our bodies need to function. In a recent study published in the journal ...
Preventive services by medical and dental providers and treatment outcomes
2014-06-03
Alexandria, Va., USA – The International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR) have published a paper titled "Preventive Services by Medical and Dental Providers and Treatment Outcomes." Nearly all state Medicaid programs reimburse non-dental primary care providers (nDPCPs) for providing preventive oral health services to young children; yet, little is known about how treatment outcomes compare to children visiting dentists. This study compared the association between the provider of preventive services (nDPCP, dentist or both) to Medicaid-enrolled children ...
New Ichthyosaur graveyard found
2014-06-03
Boulder, Colo., USA – In a new study published in the Geological Society of America Bulletin, geoscientists Wolfgang Stinnesbeck of the University of Heidelberg and colleagues document the discovery of forty-six ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaurs (marine reptiles). These specimens were discovered in the vicinity of the Tyndall Glacier in the Torres del Paine National Park of southern Chile. Among them are numerous articulated and virtually complete skeletons of adults, pregnant females, and juveniles.
Preservation is excellent and occasionally includes soft tissue and embryos. ...
Miniature digital zenith telescope for astronomy and geoscience
2014-06-03
As a kind of ground-based optical astrometric instrument, zenith telescope observes stars near zenith, which substantially reduces the influence of normal atmospheric refraction. Its high-precision observations can be used to calculate astronomical latitude and longitude, which are mainly applied in mobile measurement for deflection of the vertical, long-term measurement for the variations of the vertical, and related researches of astronomical seismology. Utilizing CCD camera, high-precision tiltmeter and other new technologies and devices, Chinese researchers have successfully ...
Image release: A violent, complex scene of colliding galaxy clusters
2014-06-03
Astronomers using the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) and the Chandra X-Ray Observatory have produced a spectacular image revealing new details of violent collisions involving at least four clusters of galaxies. Combined with an earlier image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST), the new observations show a complex region more than 5 billion light-years from Earth where the collisions are triggering a host of phenomena that scientists still are working to understand.
The HST image forms the background of this composite, with the X-ray emission detected by Chandra ...
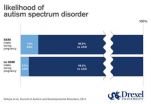
In utero exposure to antidepressants may influence autism risk
2014-06-03
PHILADELPHIA (June 2, 2014) – A new study from researchers at Drexel University adds evidence that using common antidepressant medications during pregnancy may contribute to a higher risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in children, although this risk is still very small.
Results from past studies of prenatal use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and ASD risk have not been consistent. An ongoing challenge in this line of research is trying to tease apart potential effects of the medication on risk from the effects associated with the condition for ...
Breaking down barriers
2014-06-03
The Gobi-Steppe Ecosystem is world renowned for its populations of migratory ungulates, which cover great distances in search of forage. Researchers at the Research Institute of Wildlife Ecology at Vetmeduni Vienna have documented, that in just one year an individual wild ass can range over an area of 70,000 km2. "Wild asses and gazelles have to be permanently on the move and travel very long distances to find enough food. Rainfall is highly variable in this region. As a consequence pastures are patchy and unpredictable in space and time," explains Petra Kaczensky, one ...
Lasers and night-vision technology help improve imaging of hidden lymphatic system
2014-06-03
VIDEO:
This is a movie illustrating the lack of lymphatic flow in the lower leg of a subject with lymphedema.
Click here for more information.
WASHINGTON, June 3, 2014—The human lymphatic system is an important but poorly understood circulatory system consisting of tiny vessels spread throughout the body. This "drainage" network helps guard against infections and prevents swelling, which occasionally happens when disease or trauma interrupts normal lymphatic function. Chronic ...
Security guard industry lacks standards, training
2014-06-03
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Despite playing a more important role in the wake of 9/11, the security guard industry remains plagued by inadequate training and standards in many states, indicates new research by Michigan State University criminologists.
Formal training of the nation's 1 million-plus private security officers is widely neglected, a surprising finding when contrasted with other private occupations such as paramedics, childcare workers and even cosmetologists, said Mahesh Nalla, lead investigator and MSU professor of criminal justice.
By and large, security ...
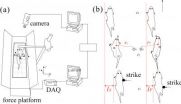
Balancing strategy to lateral impact in a rat Rattus norregicus
2014-06-03
The balancing strategy to lateral impact in a rat is closely related to the striked position of the body. The research result can be inspired to improve the robustness of bionic robot. This was found by Dr. JI Aihong and his group from Institute of Bio-inspired Structure and Surface Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics. This work, entitled "Balancing strategy to lateral impact in a rat Rattus norregicus", was published in Chinese Science Bulletin (In Chinese),2014, Vol 59(13) issue.
The center of mass(COM) of animal's body always falls ...