(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – Not all cancer cells are created equal – some stay put in the primary tumor, while others move and invade elsewhere. A major goal for cancer research is predicting which cells will metastasize, and why.
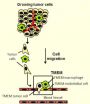
A Cornell cancer research team is taking a new approach to screening for these dangerous cells, using a microfluidic device they invented that isolates only the most aggressive, metastatic cells.
"The approach we've taken is a reverse approach from what is conventionally done," said Cynthia Reinhart-King, associate professor of biomedical engineering and senior author of the recently published Technology Journal paper describing the research. "Instead of looking at what molecules are being expressed by the tumor, we're looking for the phenotype – that is, the behavior – of individual cells first. Then we can determine what molecules are causing that behavior."
Typically, searching for biomarkers of metastasis has focused on screening for certain molecules or genes expressed by large numbers of migrating cancer cells. The problem is that it's easy to miss subtle differences in the tiny subpopulations of cells that are the most aggressive.
Taking, for example, 100 tumors and seeking out molecular biomarkers for metastasis, one particular molecule might be identified as being "upregulated" in those tumors, Reinhart-King said. But it's not the whole tumor expressing that particular molecule – some cells express the biomarker and some do not.
The researchers decided to first sort cells with the most aggressive behavior, and analyze only them for molecular changes. Their innovation is a microfluidic device that contains side channels to wash out the less aggressive cells, while herding the more aggressive ones into a separate channel.
For their proof-of-concept, the researchers screened for cells with migratory responses to Epidermal Growth Factor, for which the receptor is known to be present in most human cancers and is tightly linked to poor prognosis.
"The thing we're most excited about, in addition to the physical device, is the conceptual framework we're using by trying to shift gears and screen for cells that are causing the worst parts of the disease," Reinhart-King said. The device could also be used in other applications of tissue engineering, inflammation and wound healing.
INFORMATION: END
New device isolates most aggressive cancer cells
2014-06-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Many breast cancer patients don't get treatment for heart problems
2014-06-03
Only a third of older breast cancer patients saw a cardiologist within 90 days of developing heart problems, in a study presented at the American Heart Association's Quality of Care and Outcomes Research 2014 Scientific Sessions.
Breast cancer patients with heart problems who saw a cardiologist were more likely to receive standard therapy for their heart failure than those who did not see a heart specialist, the study found.
"The majority of older women who develop heart problems after their breast cancer therapy aren't treated by a cardiologist, and they had lower ...
Community program helps lower blood pressure among minorities
2014-06-03
Minorities at a higher risk of developing hypertension used a community-based program to significantly lower their blood pressure, researchers said at the American Heart Association's Quality of Care and Outcomes Research 2014 Scientific Sessions.
Minorities at a higher risk of developing hypertension used a community-based program to significantly lower their blood pressure, researchers said at the American Heart Association's Quality of Care and Outcomes Research 2014 Scientific Sessions.
Researchers assessed the use of the American Heart Association's Check. Change. ...
Implanted heart device linked to increased survival
2014-06-03
DURHAM, N.C. -- Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) are associated with improved survival among heart failure patients whose left ventricles only pump 30 to 35 percent of blood out of the heart with each contraction, according to a study from the Duke Clinical Research Institute.
The findings, published in the June 4 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association, support existing recommendations to implant ICDs in patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) – a measurement of how much blood is squeezed out of the heart – of 35 percent ...
High risk of recurrence of 2 life-threatening adverse drug reactions
2014-06-03
Individuals who are hospitalized for the skin conditions of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis appear to have a high risk of recurrence, according to a study in the June 4 issue of JAMA.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are life-threatening conditions that develop primarily as responses to drugs, and result in extensive epidermal detachment (upper layers of the skin detach from the lower layers). Recurrence has been reported in isolated cases, and the overall risk of recurrence has been unknown, according to background ...
Outcomes for older adults with pneumonia who receive treatment including azithromycin
2014-06-03
In a study that included nearly 65,000 older patients hospitalized with pneumonia, treatment that included azithromycin compared with other antibiotics was associated with a significantly lower risk of death and a slightly increased risk of heart attack, according to a study in the June 4 issue of JAMA.
Pneumonia and influenza together are the eighth leading cause of death and the leading causes of infectious death in the United States. Although clinical practice guidelines recommend combination therapy with macrolides (a class of antibiotics), including azithromycin, ...
Preventive placement of ICDs for less severe heart failure may improve survival
2014-06-03
An examination of the benefit of preventive placement of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) in patients with a less severe level of heart failure, a group not well represented in clinical trials, finds significantly better survival at three years than that of similar patients with no ICD, according to a study in the June 4 issue of JAMA.
Although clinical trials have established the ICD as the best currently available therapy to prevent sudden cardiac death in patients with heart failure, some uncertainties remain regarding preventive use of ICDs in patients ...
Study: New test predicts if breast cancer will spread
2014-06-03
June 3, 2014 – BRONX, NY – The study was led by researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI)─designated Albert Einstein Cancer Center of Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University and Montefiore Einstein Center for Cancer Care and was published online today in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI).
"Tests assessing metastatic risk can help doctors identify which patients should receive aggressive therapy and which patients should be spared," said Thomas Rohan, M.D., Ph.D., the lead and corresponding author of the study and professor ...
Deeper than ancestry.com, 'EvoCor' identifies gene relationships
2014-06-03
A frontier lies deep within our cells.
Our bodies are as vast as oceans and space, composed of a dizzying number of different types of cells. Exploration reaches far, yet the genes that make each cell and tissue unique have remained largely obscure.
That's changing with the help of a team led by Gregorio Valdez, an assistant professor at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute.
Valdez and his team designed a search engine – called EvoCor – that identifies genes that are functionally linked.
The name, a portmanteau of "evolution" and "correlation," points to ...
New definition of kidney disease for clinical trials could lead to new treatments
2014-06-03
A new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health suggests that new therapies for kidney disease could be developed more quickly by revising the definition of kidney disease progression used during clinical trials. If adopted, the new definition could shorten the length of some clinical trials and also potentially encourage more clinical trials in kidney disease. The findings will be published in the June 3, 2014 online edition of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a worldwide public health ...
2-D transistors promise a faster electronics future
2014-06-03
Faster electronic device architectures are in the offing with the unveiling of the world's first fully two-dimensional field-effect transistor (FET) by researchers with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab). Unlike conventional FETs made from silicon, these 2D FETs suffer no performance drop-off under high voltages and provide high electron mobility, even when scaled to a monolayer in thickness.
Ali Javey, a faculty scientist in Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and a UC Berkeley professor of electrical engineering and computer science, led ...