(Press-News.org) SCOTTSDALE, Ariz. — June 5, 2014 — A clinical trial conducted by researchers at the Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center Clinical Trials, a partnership between Scottsdale Healthcare and the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), showed that a new drug called MM-398, given in combination with 5-flourouracil (5FU) and leucovorin, produced a significant overall survival rate in patients with advanced, previously-treated pancreatic cancer.
The NAPOLI-1 (NAnoliPOsomaL Irinotecan) Phase 3 study — a final confirmation of a drug's safety and effectiveness — was conducted among patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer who previously received gemcitibine, which has been the standard-of-care therapy for such patients.
The study, sponsored by Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, evaluated 417 patients enrolled at more than 100 sites in North America, South America, Europe, Asia and Australia, including patients at the Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center at Scottsdale Healthcare. Merrimack expects to submit a New Drug Application this year to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the MM-398 combination regimen.
"This demonstration of a survival benefit from the MM-398 plus 5-FU and leucovorin combination is particularly important given that we have very few treatment options for patients in this tough clinical setting," said Dr. Daniel D. Von Hoff, MD, FACP, global principal investigator of the NAPOLI-1 study, Chief Scientific Officer for Scottsdale Healthcare's Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center Clinical Trials and Physician-In-Chief and Distinguished Professor at TGen. "The results of the NAPOLI-1 study are important because of the critical need to help patients with this devastating illness and move forward towards FDA approval."
The combination of MM-398 with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and leucovorin achieved an overall survival of 6.1 months, a 1.9 month improvement over the 4.2 month survival demonstrated by the control arm of 5-FU and leucovorin alone.
Each year in the U.S., nearly 46,000 people are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, and more than 39,000 patients die, making it the fourth leading cause of cancer death. Only about 1 in 4 patients survive more than one year after diagnosis, and only 6 percent survivor more than five years.
Symptoms of pancreatic cancer usually do not appear until the cancer is in its late stages, making it difficult to treat. Once the disease spreads to other parts of the body, most patients are not candidates for surgery and receive chemotherapy as their primary treatment.
This study will be presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology World Conference on Gastrointestinal Cancer being held June 25-28 in Barcelona, Spain.
INFORMATION:
Patients seeking information about research studies may contact the Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center Clinical Trials at Scottsdale Healthcare at 480-323-1339 or toll free at 1-877-273-3713 or e-mail: clinicaltrials@shc.org.
About the Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center at Scottsdale Healthcare
The Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center at Scottsdale Healthcare in Scottsdale, Ariz. offers comprehensive cancer treatment and research through clinical trials, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and support services in collaboration with leading scientific researchers and community oncologists. The Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center at Scottsdale Healthcare, Scottsdale Healthcare Research Institute, Scottsdale Healthcare Osborn Medical Center, Scottsdale Healthcare Shea Medical Center and Scottsdale Healthcare Thompson Peak Hospital and related entities are affiliates of the non-profit Scottsdale Lincoln Health Network. For more information, visit http://www.shc.org.
Press Contact:
Alice Giedraitis
Virginia G. Piper Cancer Center at Scottsdale Healthcare
480-323-1386
agiedraitis@shc.org
About TGen
Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) is a Phoenix, Arizona-based non-profit organization dedicated to conducting groundbreaking research with life changing results. TGen is focused on helping patients with cancer, neurological disorders and diabetes, through cutting edge translational research (the process of rapidly moving research towards patient benefit). TGen physicians and scientists work to unravel the genetic components of both common and rare complex diseases in adults and children. Working with collaborators in the scientific and medical communities literally worldwide, TGen makes a substantial contribution to help our patients through efficiency and effectiveness of the translational process. For more information, visit: http://www.tgen.org.
Press Contact:
Steve Yozwiak
TGen Senior Science Writer
602-343-8704
syozwiak@tgen.org
New therapy for pancreatic cancer patients shows promising results
TGen-Scottsdale Healthcare lead international clinical trials in advance of FDA application for NAPOLI-1
2014-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Team finds on-off switch to burning stored fat
2014-06-05
SAN ANTONIO, Texas (June 5, 2014) — Scientists this week reported that a molecular pathway called mTORC1 controls the conversion of unhealthy white fat into beige fat, an appealing target for increasing energy expenditure and reducing obesity. The team, led by researchers from the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, also found that a protein, Grb10, serves as the on-off switch for mTORC1 signaling and the "beigeing" of fat.
The finding could inform development of novel diabetes and obesity drugs, the scientists said. The ...
How do phytoplankton survive a scarcity of a critical nutrient?
2014-06-05
Phytoplankton—tiny, photosynthetic organisms—are essential to life on Earth, supplying us with roughly half the oxygen we breathe. Like all other life forms, phytoplankton require the element phosphorus to carry out critical cellular activity, but in some parts of the world's ocean, P is in limited supply. How do phytoplankton survive when phosphorus is difficult to find?
Phytoplankton can alter their biochemical make-up according to the availability of nutrients in the water. When phosphorus (P) is particularly abundant in the water, phytoplankton produce and store ...
Stimulating a protein in skin cells could improve psoriasis symptoms
2014-06-05
Psoriasis is a common, long-lasting disease that causes itchy or sore patches of thick, red skin with silvery scales. Environmental contaminants can trigger psoriasis and other autoimmune disorders, and it is thought that a protein called the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), which senses environmental toxins, could play a role. A study published by Cell Press on June 5 in the journal Immunity shows that the severity of inflammation associated with psoriasis is unexpectedly suppressed by AhR. The findings suggest that stimulation of AhR could improve symptoms and may represent ...
Neurons transplanted into Parkinson's-affected brains appear healthy after 14 years
2014-06-05
When transplanted into the midbrains of adult patients with Parkinson's disease, dopamine neurons derived from fetal tissue can remain healthy for many years. The findings reported in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports on June 5th suggest that transplanted neurons don't degenerate over time as some had suggested and feared they would, which provides further rationale for pursuing stem cells as a source for transplant-ready dopamine neurons, according to the researchers.
"Our findings show a robust expression of dopamine transporters and a lack of abnormal mitochondrial ...
Activating the immune system could treat obesity and diabetes
2014-06-05
Obesity is a worldwide epidemic that is causing alarming rates of diabetes and cardiovascular disease, but currently there is a lack of effective drug treatments. Two unrelated studies published by Cell Press June 5th in the journal Cell reveal an important role for immune pathways in activating good types body fat, called brown and beige fat, which burn stored calories, reduce weight, and improve metabolic health. The findings could pave the way for much-needed treatments for obesity and related metabolic diseases.
"The idea that metabolic health can be improved by activation ...
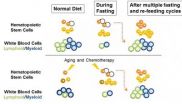
Fasting may help protect against immune-related effects of chemotherapy and aging
2014-06-05
While chemotherapy can save lives, it can also cause many side effects, including the depletion of immune cells. Also, even in the absence of chemotherapy, normal aging takes a heavy toll on the immune system, leading to immune deficiencies and a higher risk of developing leukemia and a variety of malignancies with age. Now researchers reporting in the June 5th issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Stem Cell have found that a simple dietary intervention—periodic fasting—may combat both chemotherapy-induced and aging-related changes in immune cell function by replenishing ...
Outcomes of a 2-year national rare disease gene discovery project
2014-06-05
OTTAWA, ON – June 5, 2014 – As part of the Finding of Rare Disease Genes (FORGE) research project, Canadian researchers have developed an expertise in understanding the underlying biology of rare childhood disorders. The first public commentary of this nationwide study is available today in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
"When we launched this project, we predicted we might explain, or solve, 50 disorders; we've almost tripled that goal," said Dr. Kym Boycott, lead investigator of FORGE and clinician scientist at the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario ...
First 3-D pterosaur eggs found with their parents
2014-06-05
Researchers have discovered the first three-dimensionally preserved pterosaur eggs in China. The eggs were found among dozens, if not hundreds, of pterosaur fossils, representing a new genus and species (Hamipterus tianshanensis). The discovery, described in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on June 5, reveals that the pterosaurs—flying reptiles with wingspans ranging from 25 cm to 12 m—lived together in gregarious colonies.
Xiaolin Wang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology says it was most exciting to find ...
McLean Hospital researchers see promise in transplanted fetal stem cells for Parkinson's
2014-06-05
BELMONT, MA -- Researchers at Harvard-affiliated McLean Hospital have found that fetal dopamine cells transplanted into the brains of patients with Parkinson's disease were able to remain healthy and functional for up to 14 years, a finding that could lead to new and better therapies for the illness.
The discovery, reported in the June 5, 2014 issue of the journal Cell Reports, could pave the way for researchers to begin transplanting dopamine neurons taken from stem cells grown in laboratories, a way to get treatments to many more patients in an easier fashion.
"We ...
Fasting triggers stem cell regeneration of damaged, old immune system
2014-06-05
In the first evidence of a natural intervention triggering stem cell-based regeneration of an organ or system, a study in the June 5 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Stem Cell shows that cycles of prolonged fasting not only protect against immune system damage — a major side effect of chemotherapy — but also induce immune system regeneration, shifting stem cells from a dormant state to a state of self-renewal.
In both mice and a Phase 1 human clinical trial, long periods of not eating significantly lowered white blood cell counts. In mice, fasting cycles then "flipped ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
[Press-News.org] New therapy for pancreatic cancer patients shows promising resultsTGen-Scottsdale Healthcare lead international clinical trials in advance of FDA application for NAPOLI-1