(Press-News.org) Obesity is a worldwide epidemic that is causing alarming rates of diabetes and cardiovascular disease, but currently there is a lack of effective drug treatments. Two unrelated studies published by Cell Press June 5th in the journal Cell reveal an important role for immune pathways in activating good types body fat, called brown and beige fat, which burn stored calories, reduce weight, and improve metabolic health. The findings could pave the way for much-needed treatments for obesity and related metabolic diseases.
"The idea that metabolic health can be improved by activation of immune cells in fat is pretty amazing," says senior study author Bruce Spiegelman of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School. "This research reveals an exciting new class of potential treatments that could one day be used for obesity-related disorders."
Human infants have large amounts of heat-generating brown fat to protect them from extreme cold, and scientists recently discovered that adult humans retain small amounts of brown fat consisting mainly of a subtype known as beige fat. Cold exposure or exercise can activate brown or beige fat, which burn stored calories and protect mammals from hypothermia, obesity, and metabolic problems. Despite their therapeutic potential for treating these conditions, relatively little was known about the molecular pathways that trigger the formation of these good types of fat.
To address this question in the new study, Spiegelman and Rajesh Rao of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School focused on a recently identified protein called PGC-1alpha4, which promotes muscle growth in response to resistance exercise. They discovered that PGC-1alpha4 stimulates the secretion of a newly identified hormone called meteorin-like (Metrnl), which is released into the bloodstream and produced in muscle tissue after exercise and in fat tissue after cold exposure in mice.
By converting energy-storing white fat to calorie-burning brown or beige fat, Metrnl increases energy expenditure and improves metabolic health in obese, diabetic mice. This hormone, which could potentially be suitable as a new therapy for obesity and diabetes, exerts these positive effects through activation of immune molecules called interleukin-4 and interleukin-13, as well as immune cells called macrophages located in fat tissue.
In another study published in the same issue, further light is shed on the question of immune responses and obesity by senior author Ajay Chawla of the University of California, San Francisco, who was motivated by his recent findings implicating the immune system in activating brown fat in response to cold environments. Chawla and his team have now revealed the circuit underlying beige fat activation in mice. They found that interleukin-4/13 signaling activated macrophages in white fat tissue, leading to the production of nervous system molecules required for converting white fat to beige fat. These findings reveal important new insights into how the immune system and nervous system work together to stimulate beige fat formation.
Moreover, the researchers found that mice with impaired signaling in this immune pathway produced less beige fat, showed lower energy expenditure, and were unable to maintain their body temperature in cold environments compared with normal mice. By contrast, treatment with interleukin-4 increased the formation of beige fat, reduced body weight, and improved metabolic health in obese mice.
"We were surprised by our observations that cold-induced recruitment of beige fat was almost entirely dependent on the immune system. This goes against the established dogma because nutrient and energy metabolism has largely been thought to be under the control of the brain and endocrine system," Chawla says. "Having identified the cellular and molecular pathway that regulates the development of beige fat, it is now possible to target any of its components to stimulate caloric expenditure and treat obesity."
INFORMATION:
Cell, Rao et al.: "Meteorin-like is a hormone that regulates immune-adipose interactions to increase beige fat thermogenesis."
Cell, Qiu et al.: "Eosinophils and type 2 cytokine signaling in macrophages orchestrate development of functional beige fat."
Activating the immune system could treat obesity and diabetes
2014-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fasting may help protect against immune-related effects of chemotherapy and aging
2014-06-05
While chemotherapy can save lives, it can also cause many side effects, including the depletion of immune cells. Also, even in the absence of chemotherapy, normal aging takes a heavy toll on the immune system, leading to immune deficiencies and a higher risk of developing leukemia and a variety of malignancies with age. Now researchers reporting in the June 5th issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Stem Cell have found that a simple dietary intervention—periodic fasting—may combat both chemotherapy-induced and aging-related changes in immune cell function by replenishing ...
Outcomes of a 2-year national rare disease gene discovery project
2014-06-05
OTTAWA, ON – June 5, 2014 – As part of the Finding of Rare Disease Genes (FORGE) research project, Canadian researchers have developed an expertise in understanding the underlying biology of rare childhood disorders. The first public commentary of this nationwide study is available today in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
"When we launched this project, we predicted we might explain, or solve, 50 disorders; we've almost tripled that goal," said Dr. Kym Boycott, lead investigator of FORGE and clinician scientist at the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario ...
First 3-D pterosaur eggs found with their parents
2014-06-05
Researchers have discovered the first three-dimensionally preserved pterosaur eggs in China. The eggs were found among dozens, if not hundreds, of pterosaur fossils, representing a new genus and species (Hamipterus tianshanensis). The discovery, described in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on June 5, reveals that the pterosaurs—flying reptiles with wingspans ranging from 25 cm to 12 m—lived together in gregarious colonies.
Xiaolin Wang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology says it was most exciting to find ...
McLean Hospital researchers see promise in transplanted fetal stem cells for Parkinson's
2014-06-05
BELMONT, MA -- Researchers at Harvard-affiliated McLean Hospital have found that fetal dopamine cells transplanted into the brains of patients with Parkinson's disease were able to remain healthy and functional for up to 14 years, a finding that could lead to new and better therapies for the illness.
The discovery, reported in the June 5, 2014 issue of the journal Cell Reports, could pave the way for researchers to begin transplanting dopamine neurons taken from stem cells grown in laboratories, a way to get treatments to many more patients in an easier fashion.
"We ...
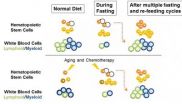
Fasting triggers stem cell regeneration of damaged, old immune system
2014-06-05
In the first evidence of a natural intervention triggering stem cell-based regeneration of an organ or system, a study in the June 5 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Stem Cell shows that cycles of prolonged fasting not only protect against immune system damage — a major side effect of chemotherapy — but also induce immune system regeneration, shifting stem cells from a dormant state to a state of self-renewal.
In both mice and a Phase 1 human clinical trial, long periods of not eating significantly lowered white blood cell counts. In mice, fasting cycles then "flipped ...
Immune system molecules may promote weight loss, UCSF study finds
2014-06-05
The calorie-burning triggered by cold temperatures can be achieved biochemically – without the chill – raising hopes for a weight-loss strategy focused on the immune system rather than the brain, according to a new study by UC San Francisco researchers.
The team determined that two signaling molecules secreted by cells of the immune system trigger the conversion of fat-storing white fat cells to fat-burning beige fat cells. Ajay Chawla, MD, PhD, an associate professor of medicine at the UCSF Cardiovascular Research Institute, led the study, published online June 5, 2014 ...
Scientists generate long-sought molecular map of critical genetic machinery
2014-06-05
LA JOLLA, CA—June 5, 2014—A team led by researchers at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) has used advanced electron microscopy techniques to determine the first accurate structural map of Mediator, one of the largest and most complex "molecular machines" in cells.
Mediator is crucial for the regulation of most genes' activity and works in the cells of all plants and animals. The mapping of its structure—which includes more than two dozen unique protein subunits—represents a significant advance in basic cell biology and should shed light on medical conditions involving ...
Diabetes care depends on how your doctor is paid
2014-06-05
TORONTO, June 5, 2014 – From 2006 to 2008, nearly 75 per cent of Ontarians with diabetes did not receive all of the tests recommended to properly monitor their disease. How their doctor was paid was one of the factors determining the care they received, according to a study by researchers at St. Michael's Hospital and the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES).
The study, published today in the Canadian Journal of Diabetes, found that patients who were not actively enrolled with a family doctor were least likely to receive optimum diabetes care. The researchers ...
New method reveals single protein interaction key to embryonic stem cell differentiation
2014-06-05
Proteins are responsible for the vast majority of the cellular functions that shape life, but like guests at a crowded dinner party, they interact transiently and in complex networks, making it difficult to determine which specific interactions are most important.
Now, researchers from the University of Chicago have pioneered a new technique to simplify the study of protein networks and identify the importance of individual protein interactions. By designing synthetic proteins that can only interact with a pre-determined partner, and introducing them into cells, the team ...
Research helps clarify how obesity leads to type 2 diabetes, cancer
2014-06-05
New findings about the biological links between obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes may also shed light on the connection between obesity and cancer, says a scientist at The University of Texas at Dallas.
In a study published online June 5 in the journal Cell, UT Dallas' Dr. Jung-whan (Jay) Kim and colleagues at the University of California, San Diego found that a protein called HIF-1 alpha plays a key role in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in obese mice.
The researchers genetically engineered mice to lack the HIF-1 alpha protein ...