(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR – With precarious particles called polaritons that straddle the worlds of light and matter, University of Michigan researchers have demonstrated a new, practical and potentially more efficient way to make a coherent laser-like beam.
They have made what's believed to be the first polariton laser that is fueled by electrical current as opposed to light, and also works at room temperature, rather than way below zero.
Those attributes make the device the most real-world ready of the handful of polariton lasers ever developed. It represents a milestone like none the field has seen since the invention of the most common type of laser – the semiconductor diode – in the early 1960s, the researchers say. While the first lasers were made in the 1950s, it wasn't until the semiconductor version, fueled by electricity rather than light, that the technology took off.
This work could advance efforts to put lasers on computer circuits to replace wire connections, leading to smaller and more powerful electronics. It may also have applications in medical devices and treatments and more.
The researchers didn't develop it with a specific use in mind. They point out that when conventional lasers were introduced, no one envisioned how ubiquitous they would become. Today they're used in the fiber-optic communication that makes the Internet and cable television possible. They are also in DVD players, eye surgery tools, robotics sensors and defense technologies, for example.
A polariton is part light and part matter. Polariton lasers harness these particles to emit light. They are predicted to be more energy efficient than traditional lasers. The new prototype requires 250 times less electricity to operate than its conventional counterpart made of the same material.
"This is big," said Pallab Bhattacharya, the Charles M. Vest Distinguished University Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and the James R. Mellor Professor of Engineering at U-M. "For the past 50 years, we have relied on lasers to make coherent light and now we have something else based on a totally new principle."
Bhattacharya's system isn't technically a laser. The term was initially an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Polariton lasers don't stimulate radiation emission. They stimulate scattering of polaritons.
In a typical laser, light--or more often electrical current-- is pumped into a material called a gain medium that's designed to amplify the signal. Before the pumping begins, most of the electrons in the gain medium are in their least energetic state, also known as the ground state. Once the light or current hits them, the electrons absorb that energy and move to a higher-energy state. At some point, more electrons are high-energy than are low-energy and the device is said to have achieved a "population inversion." Now any light or current that goes in has the opposite effect on the excited electrons. It kicks them down to the ground state and releases pent-up light in the process.
Polariton lasers don't rely on these population inversions, so they don't need a lot of start-up energy to excite electrons and then knock them back down. "The threshold current can be very small, which is an extremely attractive feature," Bhattacharya said.
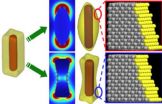
He and his team paired the right material – the hard, transparent semiconductor gallium nitride – with a unique design to maintain the controlled circumstances that encourage polaritons to form and then emit light.
How it works
A polariton is a combination of a photon or light particle and an exciton – an electron-hole pair. The electron is negatively charged and the hole is technically the absence of an electron, but it behaves as if it were positively charged. Excitons will only fuse with light particles under just the right conditions. Too much light or electrical current will cause the excitons to break down too early. But with just enough, polaritons will form and then bounce around the system until they come to rest at their lowest energy level in what Bhattacharya describes as a coherent pool. There, the polaritons decay and in the process, release a beam of single-colored light.
The beam they demonstrated was ultraviolet and very low power – less than a millionth of a watt. For context, the laser in a CD player is about one-thousandth of a watt.
"We're thrilled," said Thomas Frost, a doctoral student in electrical and computer engineering. "This is the first really practical polariton laser that could be used on chip for real applications."
The design the team used helped them achieve the beam with an electrical rather than light input signal. Getting the electrical current into the system requires electrodes sandwiching the gallium nitride and several layers of mirrors to render the electrical signal useable. Other groups' approaches put the electrodes outside the mirrors. Bhattacharya said it was tough to get the signal strong enough under those circumstances. So he deconstructed the sandwich. He put the mirrors on the sides of the gallium nitride and left the electrodes on the top and bottom.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Room Temperature Electrically Injected Polariton Laser," will be published online in Physical Review Letters on June 10. The work was funded by the National Science Foundation.
A new way to make laser-like beams using 250x less power
2014-06-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New species of ancient chirping giant pill-millipedes from Madagascar already threatened
2014-06-06
An international team of researchers comprised of Thomas Wesener, Museum Koenig, Bonn, Daniel Le, Field Museum, Chicago and Stephanie Loria, American Museum of Natural History, New York, discovered seven new species of chirping giant pill-millipedes on Madagascar. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The species discovered all belong to the genus Sphaeromimus, which is Latin for 'small ball animal'. However, the designation 'small' is not always true for the members of the genus as one of the newly discovered species surprises with a size larger ...
Probiotics prevent deadly complications of liver disease
2014-06-06
Bethesda, MD (June 6, 2014) — Probiotics are effective in preventing hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis of the liver, according to a new study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatic encephalopathy is a deterioration of brain function that is a serious complication of liver disease.
"This rigorous new research finds that probiotics modify the gut microbiota to prevent hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis of the liver," said David W. Victor III, ...
Shatterproof screens that save smartphones
2014-06-06
University of Akron polymer scientists have developed a transparent electrode that could change the face of smartphones, literally, by making their displays shatterproof.
In a recently published scientific paper, researchers demonstrated how a transparent layer of electrodes on a polymer surface could be extraordinarily tough and flexible, withstanding repeated scotch tape peeling and bending tests. This could revolutionize and replace conventional touchscreens, according to Yu Zhu, UA assistant professor of polymer science. Currently used coatings made of indium tin ...
Breakthrough study solves plant sex mystery
2014-06-06
A team of biologists from the University of Leicester has solved a mystery surrounding how plants have sex.
The researchers have discovered a pair of proteins made by flowering plants that are vital for the production of the sperm present within each pollen grain.
Scientists already knew that flowering plants, in contrast to animals, require not one, but two sperm cells for successful fertilisation: one to join with the egg cell to produce the embryo and one to join with a second cell to produce the nutrient-rich endosperm inside the seed.
The mystery of this 'double ...
Method of nickel-carbon heterofullerenes synthesis presented
2014-06-06
Scientists from several British, Spanish and Russian research centers (MIPT, Institute for Spectroscopy RAS, Kurchatov Institute and Kintech Lab Ltd) have come up with a method of synthesizing a new type of nickel-carbon compound. The article titled Formation of nickel-carbon heterofullerenes under electron irradiation has been published by Dalton Transactions and is available as a pre-print at arxiv.org. The first author of the article is Alexander Sinitsa, an MIPT student, and the leading author is Andrey Popov (Institute for Spectroscopy RAS, 1989 MIPT graduate).
Heterofullerenes ...
Mitochondrial DNA of first Near Eastern farmers is sequenced for the first time
2014-06-06
The mitochondrial DNA of the first Near Eastern farmers has been sequenced for the first time. In the research, published in the journal PLOS Genetics, experts analysed samples from three sites located in the birthplace of Neolithic agricultural practices: the Middle Euphrates basin and the oasis of Damascus, located in today's Syria and date at about 8,000 BC.
The paper is signed by Daniel Turbón and Alejandro Pérez Pérez, from the Department of Animal Biology of the University of Barcelona (UB); Eva Fernández, from Liverpool John Moores University; Cristina Gamba, Eduardo ...
Herpesviruses undercover
2014-06-06
This news release is available in German.
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), a gammaherpesvirus that can cause multiple forms of cancer, establishes lifelong infections within the body. To do so the virus has to find a way to modulate the immune system of its host.
„Intruders are usually fought off immediately by an antiviral immune response that is triggered by sensors including the toll-like receptors (TLR)," says HZI researcher Dr. Kendra Bussey, author of the study that was published in the "Journal of Virology". Toll-like receptors detect ...
Opening a wide window on the nano-world of surface catalysis
2014-06-06
Surface catalysts are notoriously difficult to study mechanistically, but scientists at the University of South Carolina and Rice University have shown how to get real-time reaction information from Ag nanocatalysts that have long frustrated attempts to describe their kinetic behavior in detail.
The key to the team's success was bridging a size gap that had represented a wide chasm to researchers in the past. To be effective as nanocatalysts, noble metals such as Au, Pt, Pd and Ag typically must be nanoparticles smaller than 5 nm, says Hui Wang, an assistant professor ...
Exotic particle confirmed
2014-06-06
This news release is available in French. For decades, physicists have searched in vain for exotic bound states comprising more than three quarks. Experiments performed at Jülich's accelerator COSY have now shown that, in fact, such complex particles do exist in nature. This discovery by the WASA-at-COSY collaboration has been published in the journal Physical Review Letters. The measurements confirm results from 2011, when the more than 120 scientists from eight countries discovered for the first time strong indications for the existence of an exotic dibaryon made ...
Early exposure to certain bacteria may protect toddlers from wheezing
2014-06-06
WHAT: Research funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) suggests that exposure to specific combinations of allergens and bacteria within the first year of life may protect children from wheezing and allergic disease. These observations come from the Urban Environment and Childhood Asthma (URECA) study, which aims to identify factors responsible for asthma development in children from inner-city settings, where the disease is more prevalent and severe. Since 2005, the URECA study has enrolled 560 children from four cities—Baltimore, Boston, New York and St. Louis. ...