(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered a relationship between climate change and ocean currents over the past six million years after analysing an area of the Atlantic near the Strait of Gibraltar, according to research published today (Friday, 13 June) in the journal Science.
An expedition of scientists, jointly led by Dr Javier Hernandez-Molina, from the Department of Earth Sciences at Royal Holloway, University of London, examined core samples from the seabed off the coast of Spain and Portugal which provided proof of shifts of climate change over millions of years.
The team also discovered new evidence of a deep-earth tectonic pulse in the region, as well as thick layers of sand within mountains of mud in a vast sheet, spreading out nearly 100km into the Atlantic from the Gibraltar gateway. The quantity of sand is far more than was expected and has been caused by the strength, speed and long duration of bottom currents flowing through the Strait of Gibraltar from the Mediterranean.
"The sediments we examined show various shifts of climate change over millions of years", Dr Hernandez-Molina said. "In addition, our findings could herald a significant shift in future targets for oil and gas exploration in deep-water settings. The thickness, extent and properties of these sands make them an ideal target in places where they are buried deep enough to allow for the trapping of hydrocarbons. The sand is especially clean and well sorted and therefore very porous and permeable."
The expedition, carrying an international team of 35 scientists from 14 countries, recovered 5km of core samples from an area along the Gulf of Cadiz and west of Portugal.
The research found that a powerful cascade of Mediterranean water spilling into the Atlantic was scouring the rocky seafloor, carving deep-sea channels and building up mountains of mud. This is due to Mediterranean water being saltier than the Atlantic and therefore denser, causing it to plunge downwards.
Dr Hernandez-Molina added: "We set out to understand how the Strait of Gibraltar acted first as a barrier and then a gateway over the past six million years. The fascinating results we came back with have hugely increased our understanding of the Mediterranean Outflow Water (MOW) that flows through the Gibraltar gateway and have led to some key discoveries about the relationship between climatic shifts, deep-water circulation and plate tectonic events over a huge timescale."
INFORMATION:
Scientists discover link between climate change and ocean currents over 6 million years
2014-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Habitat fragmentation increases vulnerability to disease in wild plants
2014-06-12
Proximity to other meadows increases disease resistance in wild meadow plants, according to a study led by Anna-Liisa Laine at the University of Helsinki. The results of the study, analysing the epidemiological dynamics of a fungal pathogen in the archipelago of Finland, will be published in Science on 13 June 2014.
The study surveyed more than 4,000 Plantago lanceolata meadows and their infection status by a powdery mildew fungus in the Åland archipelago of Finland. The surveys have continued since 2001, resulting in one of the world's largest databases on disease dynamics ...
Quantum computation: Fragile yet error-free
2014-06-12
This news release is available in German and Spanish. Even computers are error-prone. The slightest disturbances may alter saved information and falsify the results of calculations. To overcome these problems, computers use specific routines to continuously detect and correct errors. This also holds true for a future quantum computer, which will require procedures for error correction as well: "Quantum phenomena are extremely fragile and error-prone. Errors can spread rapidly and severely disturb the computer," says Thomas Monz, member of Rainer Blatt's research group ...
Movies with gory and disgusting scenes more likely to capture and engage audience
2014-06-12
Washington, DC (June 12, 2014) – We know it too well. We are watching a horror film and the antagonist is about to maim a character; we ball up, get ready for the shot and instead of turning away, we lean forward in the chair, then flinch and cover our eyes – Jason strikes again! But what is going on in our body that drives us to this reaction, and why do we engage in it so readily? Recent research published in the Journal of Communication found that people exposed to core disgusts (blood, guts, body products) showed higher levels of attention the more disgusting the content ...
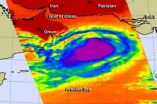
NASA takes Tropical Cyclone Nanuak's temperature
2014-06-12
Tropical Cyclone Nanauk is holding its own for now as it moves through the Arabian Sea. NASA's Aqua satellite took its cloud top temperatures to determine its health.
In terms of infrared data viewing tropical cyclones, those with the coldest cloud top temperatures indicate that a storm is the most healthy, most robust and powerful. That's because thunderstorms that have strong uplift are pushed to the top of the troposphere where temperatures are bitter cold. Infrared data, such as that collected from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard ...
Findings point toward one of first therapies for Lou Gehrig's disease
2014-06-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers have determined that a copper compound known for decades may form the basis for a therapy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Lou Gehrig's disease.
In a new study just published in the Journal of Neuroscience, scientists from Australia, the United States (Oregon), and the United Kingdom showed in laboratory animal tests that oral intake of this compound significantly extended the lifespan and improved the locomotor function of transgenic mice that are genetically engineered to develop this debilitating and terminal disease.
In humans, ...
Scientists identify Deepwater Horizon Oil on shore even years later, after most has degraded
2014-06-12
Years after the 2010 Deepwater Horizon Oil spill, oil continues to wash ashore as oil-soaked "sand patties," persists in salt marshes abutting the Gulf of Mexico, and questions remain about how much oil has been deposited on the seafloor. Scientists from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences have developed a unique way to fingerprint oil, even after most of it has degraded, and to assess how it changes over time. Researchers refined methods typically used to identify the source of oil spills and adapted them for application on a ...
Anti-dsDNA, surface-expressed TLR4 and endosomal TLR9 cooperate to exacerbate lupus
2014-06-12
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complicated multifactorial autoimmune disease influenced by many genetic and environmental factors. The hallmark of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the presence of high levels of anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody (anti-dsDNA) in sera. In addition, greater infection rates are found in SLE patients and higher morbidity and mortality usually come from bacterial infections. Deciphering interactions between the susceptibility genes and the environmental factors for lupus complex traits is challenging and has resulted in only ...
Protein anchors help keep embryonic development 'just right'
2014-06-12
The "Goldilocks effect" in fruit fly embryos may be more intricate than previously thought. It's been known that specific proteins, called histones, must exist within a certain range—if there are too few, a fruit fly's DNA is damaged; if there are too many, the cell dies. Now research out of the University of Rochester shows that different types of histone proteins also need to exist in specific proportions. The work further shows that cellular storage facilities keep over-produced histones in reserve until they are needed.
Associate Professor of Biology Michael Welte ...
Penn study describes new models for testing Parkinson's disease immune-based drugs
2014-06-12
PHILADELPHIA - Using powerful, newly developed cell culture and mouse models of sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD), a team of researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, has demonstrated that immunotherapy with specifically targeted antibodies may block the development and spread of PD pathology in the brain. By intercepting the distorted and misfolded alpha-synuclein (α-syn) proteins that enter and propagate in neurons, creating aggregates, the researchers prevented the development of pathology and also reversed some of the ...
Viral infections, including flu, could be inhibited by naturally occurring protein
2014-06-12
PITTSBURGH, June 12, 2014 – By boosting a protein that naturally exists in our cells, an international team of researchers led by the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute (UPCI), partner with UPMC CancerCenter, has found a potential way to enhance our ability to sense and inhibit viral infections.
The laboratory-based discovery, which could lead to more effective treatments for viruses ranging from hepatitis C to the flu, appears in the June 19 issue of the journal Immunity. The research is supported by the National Institutes of Health.
"Despite remarkable advances ...