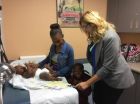
(Press-News.org) CHICAGO --- In low-income and minority communities where colonoscopies may be prohibitively expensive for many residents, less-invasive, more frequent testing combined with automated reminders, can yield dramatic improvements in colorectal cancer (CRC) screening rates, according to a new Northwestern Medicine® study.
The study found that community health center patients who received follow-up -– that is, outreach by mail, automated telephone and text messages, and calls by a health center staff member if no response was given in three months -- were more than twice as likely to complete an at-home colon cancer screening test. This was true even though most patients in the study were poor, uninsured, had limited English proficiency and a low understanding of health information.
The study will be published in JAMA Internal Medicine June 16.
"With electronic health records, we can set up inexpensive systems to remind patients to do annual home colon cancer screening tests and achieve a very high success rate," said the study's author David Baker, M.D. "We can achieve success even for patients with multiple financial, literacy and cultural barriers to CRC screening."
Baker is chief of internal medicine and geriatrics and the Michael A. Gertz Professor of Medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. He also is a physician at Northwestern Memorial Hospital.
CRC is the third most common cancer for both men and women and the second-leading cancer killer in the United States. Screening and early treatment can be extremely successful in preventing CRC deaths; approximately 90 percent of people with CRC that is found early and treated appropriately are still alive five years later.
In the U.S., the majority of CRC screening is done by colonoscopy, even though the procedure is expensive and invasive, and several safe and effective recommended alternatives exist. In this study, Baker's team used fecal occult blood testing (FOBT), which can be completed at home with a single stool sample. FOBT must be conducted annually to catch colon cancer before it is too advanced to cure.
Prior to the study, it was not known whether patients would adhere to an annual at-home testing schedule for CRC.
Baker and his colleagues identified 450 patients who received their care through a network of community health centers in Chicago. The overwhelming majority of the patients studied were uninsured Latino women and all had had a negative result with a previous at-home FOBT.
Patients were divided into two groups, a usual care group and an intervention group. Usual care included computerized reminders, standing orders to give patients home tests and provider feedback. The intervention group received usual care plus the following: a mailed reminder letter; a free home test with low-literacy instructions and a postage-paid return envelope; automated phone and text messages reminding them that a home test was being mailed to them and they were due for screening; automated phone and text reminders two weeks later for those who did not return the home test; and personal outreach from a trained professional after three months if a test was not completed.
The researchers found that the intervention was very successful, with 82.2 percent of the patients in the intervention group completing the FOBT within six months of the screening due date compared to 37.3 percent of the patients in the usual care group.
"This intervention greatly increased adherence to annual colorectal cancer screening," Baker said. "It is possible to improve annual screening for vulnerable populations with relatively low-cost strategies, and we know that earlier detection of cancer through screening will save lives."
The next step in this work is for Baker's team is to work with community health centers that want to implement similar outreach programs to improve CRC screening rates. Baker noted that he has already spoken to health centers in the Midwest and Pacific Northwest, and has provided them with materials.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) grant number HS021141.
NORTHWESTERN NEWS: http://www.northwestern.edu/newscenter/
Outreach doubles colon cancer screening in low-income communities
Minority residents respond to follow-up to complete at-home screening test
2014-06-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Penn anesthesiologists identify top 5 practices that could be avoided
2014-06-16
(PHILADELPHIA) – A team of researchers led by Penn Medicine anesthesiologists have pinpointed the "top five" most common perioperative procedures that are supported by the least amount of clinical evidence, in an effort to direct providers to make more cost-effective treatment decisions. Their findings are published in the current issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
The team surveyed anesthesiologists, many of them in academic practice, to identify the most common activities that should be questioned in the field, using practice parameters developed by the American Society ...
In military personnel, no difference between blast and nonblast-related concussions
2014-06-16
Explosions are the most common cause of traumatic brain injuries in veterans returning from Iraq and Afghanistan. A new study shows that military personnel with mild brain trauma related to such blasts had outcomes similar to those with mild brain injury from other causes, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
However, nearly 80 percent of patients in both categories of brain trauma suffered moderate to severe overall disability within a year after injury.
The analysis appears June 16 in JAMA Neurology.
"We are interested ...
How to prevent disparities in colon cancer screening
2014-06-16
SEATTLE—People living in poverty are less likely to be screened regularly for colorectal cancer—and more likely to develop the disease and die from it. How to end these disparities—and raise screening rates, lower disease rates, and prevent deaths? A promising way is to mail fecal immunochemical tests (a newer kind of stool test) to populations, Beverly B. Green, MD, MPH, and Gloria D. Coronado, PhD, wrote in the June 17 JAMA Internal Medicine.
Dr. Green is a Group Health physician and an associate investigator at Group Health Research Institute. Dr. Coronado is a senior ...
When patients wish for a miracle, tool helps medical staff say 'amen'
2014-06-16
Cancer clinicians and a chaplain at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center have developed a new tool to help doctors, nurses and other health care providers talk to dying patients and families who are, literally, praying for a miracle.
The AMEN (Affirm, Meet, Educate, No matter what) protocol, a script that can be used by medical staff, offers a way to negotiate these challenging conversations to affirm or acknowledge a patient's hope, share the patient's wish with others, continue to educate the patient and family about medical issues, and assure them that their health ...
Redesigning the well-child checkup
2014-06-16
Well-child visits are the foundation of pediatric primary care in the U.S. Accounting for more than one-third of all outpatient visits for infants and toddlers, the appointments are intended to give doctors the opportunity to identify health, social, developmental and behavioral issues that could have a long-term impact on children's lives.
However, several studies have shown that the current system of well-child care leaves room for improvement. One major concern is that well-child care guidelines issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics call for physicians to provide ...
Many bodies prompt stem cells to change
2014-06-16
HOUSTON – (June 16, 2014) – How does a stem cell decide what path to take? In a way, it's up to the wisdom of the crowd.
The DNA in a pluripotent stem cell is bombarded with waves of proteins whose ebb and flow nudge the cell toward becoming blood, bone, skin or organs. A new theory by scientists at Rice University shows the cell's journey is neither a simple step-by-step process nor all random.
Theoretical biologist Peter Wolynes and postdoctoral fellow Bin Zhang set out to create a mathematical tool to analyze large, realistic gene networks. As a bonus, their open-access ...
Researchers create better methods to detect E. coli
2014-06-16
MANHATTAN, KANSAS — Kansas State University diagnosticians are helping the cattle industry save millions of dollars each year by developing earlier and accurate detection of E. coli.
Lance Noll, master's student in veterinary biomedical science, Greensburg; T.G. Nagaraja, university distinguished professor of diagnostic medicine and pathobiology; and Jianfa Bai, assistant professor in the Kansas State Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, are leading a project to improve techniques for detecting pathogenic Shiga toxin-producing E. coli O157:H7. A U.S. Department of Agriculture ...
Getting rid of old mitochondria
2014-06-16
It's broadly assumed that cells degrade and recycle their own old or damaged organelles, but researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and Kennedy Krieger Institute have discovered that some neurons transfer unwanted mitochondria – the tiny power plants inside cells – to supporting glial cells called astrocytes for disposal.
The findings, published in the June 17 online Early Edition of PNAS, suggest some basic biology may need revising, but they also have potential implications for improving ...
Discovery of Earth's northernmost perennial spring
2014-06-16
Boulder, Colo., USA – A Canadian team lead by Stephen Grasby reports the discovery of the highest latitude perennial spring known in the world. This high-volume spring demonstrates that deep groundwater circulation through the cryosphere occurs, and can form gullies in a region of extreme low temperatures and with morphology remarkably similar to those on Mars. The 2009 discovery raises many new questions because it remains uncertain how such a high-volume spring can originate in a polar desert environment.
Grasby and colleagues encountered the northernmost perennial ...
Pathological gambling runs in families
2014-06-16
A study by University of Iowa researchers confirms that pathological gambling runs in families and shows that first-degree relatives of pathological gamblers are eight times more likely to develop this problem in their lifetime than relatives of people without pathological gambling.
"Our work clearly shows that pathological gambling runs in families at a rate higher than for many other behavioral and psychiatric disorders," says Donald W. Black, MD, professor of psychiatry in the UI Carver College of Medicine. "I think clinicians and health care providers should be alerted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Outreach doubles colon cancer screening in low-income communitiesMinority residents respond to follow-up to complete at-home screening test