(Press-News.org) Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a nanoshell to protect foreign enzymes used to starve cancer cells as part of chemotherapy. Their work is featured on the June 2014 cover of the journal Nano Letters.
Enzymes are naturally smart machines that are responsible for many complex functions and chemical reactions in biology. However, despite their huge potential, their use in medicine has been limited by the immune system, which is designed to attack foreign intruders. For example, doctors have long relied on an enzyme called asparaginase to starve cancer cells as a patient undergoes chemotherapy. But because asparaginase is derived from a nonhuman organism, E. Coli, it is quickly neutralized by the patient's immune system and sometimes produces an allergic reaction. In animal studies with asparaginase, and other therapeutic enzymes, the research team found that their porous hollow nanoshell effectively shielded enzymes from the immune system, giving them time to work.
Asparaginase works by reacting with amino acids that are an essential nutrient for cancer cells. The reaction depletes the amino acid, depriving the abnormal cells from the nutrients they need to proliferate.
"Ours is a pure engineering solution to a medical problem," said Inanc Ortac (Ph.D. '13), who developed the technology as part of his doctoral research in the laboratory of nanoengineering professor Sadik Esener at UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering.
The nanoshell acts like a filter in the bloodstream. The enzymes are loaded into the nanoparticle very efficiently through pores on its surface and later encapsulated with a shell of nanoporous silica. The shell's pores are too small for the enzyme to escape but big enough for diffusion of amino acids that feed cancer cells in and out of the particle. The enzymes remain trapped inside where they deplete any amino acids that enter.
"This is a platform technology that may find applications in many different fields. Our starting point was solving a problem for cancer therapeutics," said Ortac.
INFORMATION:
Ortac is currently serving as the chief technology officer of DevaCell, a local start-up which licensed the technology and is working to commercialize it under the name Synthetic Hollow Enzyme Loaded nanoShells or SHELS. Ortac, together with graduate student Ya-san Yeh, recently took the top prize at Research Expo 2014 at UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. Yeh discussed her role in the project in our video linked below. Ortac also won first place in the Collegiate Inventors Competition in 2012 and UC San Diego Entrepreneur Challenge in 2013 with a business plan based on the technology. Just recently, San Diego Business Journal recognized the researchers with the 2014 Innovation Award in Medical Research.
Nanoshell shields foreign enzymes used to starve cancer cells from immune system
2014-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gene 'switch' reverses cancer in common childhood leukaemia
2014-06-17
Melbourne researchers have shown a type of leukaemia can be successfully 'reversed' by coaxing the cancer cells back into normal development.
The discovery was made using a model of B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL), the most common cancer affecting children.
Researchers from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute showed that switching off a gene called Pax5 could cause cancer in a model of B-ALL, while restoring its function could 'cure' the disease.
Institute researchers Dr Ross Dickins and Ms Grace Liu led the study with institute colleagues and ...
E-cigs heavily marketed on Twitter, study finds
2014-06-17
E-cigarettes, also known as vaping pens or e-hookas, are commonly advertised on Twitter and the tweets often link to commercial websites promoting e-cig use, according to University of Illinois at Chicago researchers.
The study, published as a special supplement in the July 2014 issue of Tobacco Control released online June 16, has implications for future FDA regulations on the marketing of e-cigarettes and related products.
"There's this whole wild west of social media platforms – Facebook, Twitter and Instagram – and the FDA has no way to track what's happening in ...
Soft-drink tax worth its weight in lost kilos
2014-06-17
A tax on sweetened soft drinks could be an effective weapon in the war against obesity, generating weight losses of up to 3.64 kilograms as individuals reduce their consumption.
Researchers from Monash University, Imperial College London and University of York and Lancaster University, England have estimated the extent to which drinking habits would change if beverages such as carbonated non-diet soft drinks; cordials and fruit drinks were taxed.
Lead author Dr Anurag Sharma, of the Centre for Health Economics at Monash University, said such a tax could have important ...
Solar photons drive water off the moon
2014-06-17
Water is thought to be embedded in the moon's rocks or, if cold enough, "stuck" on their surfaces. It's predominantly found at the poles. But scientists probably won't find it intact on the sunlit side.
New research at the Georgia Institute of Technology indicates that ultraviolet photons emitted by the sun likely cause H2O molecules to either quickly desorb or break apart. The fragments of water may remain on the lunar surface, but the presence of useful amounts of water on the sunward side is not likely.
The Georgia Tech team built an ultra-high vacuum system that ...
Researchers identify new compound to treat depression
2014-06-17
There is new hope for people suffering from depression. Researchers have identified a compound, hydroxynorketamine (HNK), that may treat symptoms of depression just as effectively and rapidly as ketamine, without the unwanted side effects associated with the psychoactive drug, according to a study in the July issue of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®). Interestingly, use of HNK may also serve as a future therapeutic approach for treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, ...
Surgical patients more likely to follow medication instructions
2014-06-17
A study in the July issue of Anesthesiology revealed that patients who receive a simple, multicolor, standardized medication instruction sheet before surgery are more likely to comply with their physician's instructions and experience a significantly shorter post-op stay in recovery. These findings are important because surgical patients often fail to follow their doctor's medication instructions for preexisting conditions such as diabetes and hypertension on the day they are having surgery – a costly mistake that can lead to surgery cancellation, complications and longer ...
References resources find their place among open access and Google, study finds
2014-06-17
Los Angeles, CA (June 17, 2014) How do open access sources, tightened budgets, and competition from popular technologies affect how librarians perceive and employ reference resources? How do librarians expect to utilize reference in the future? "The State of Reference Collections," a new SAGE white paper out today, finds that though the definition of reference is changing, this is in part because reference resources now look and feel like other information sources and because other information resources perform the traditional purpose of reference – answering research ...
Study links APC gene to learning and autistic-like disabilities
2014-06-17
BOSTON (June 17, 2014, 4:00 a.m. EDT) — Autistic-like behaviors and decreased cognitive ability may be associated with disruption of the function of the Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC) gene. When Tufts researchers deleted the gene from select neurons in the developing mouse brain, the mice showed reduced social behavior, increased repetitive behavior, and impaired learning and memory formation, similar to behaviors seen in individuals with autism and intellectual disabilities. This study is the first to evaluate how the loss of APC from nerve cells in the forebrain affects ...
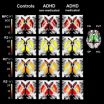
MRI technique may help prevent ADHD misdiagnosis
2014-06-17
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Brain iron levels offer a potential biomarker in the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and may help physicians and parents make better informed treatment decisions, according to new research published online in the journal Radiology.
ADHD is a common disorder in children and adolescents that can continue into adulthood. Symptoms include hyperactivity and difficulty staying focused, paying attention and controlling behavior. The American Psychiatric Association reports that ADHD affects 3 to 7 percent of school-age children.
Psychostimulant ...
Fecal transplants restore healthy bacteria and gut functions
2014-06-17
Fecal microbiota transplantation --- the process of delivering stool bacteria from a healthy donor to a patient suffering from intestinal infection with the bacterium Clostridium difficile --- works by restoring healthy bacteria and functioning to the recipient's gut, according to a study published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
The study provides insight into the structural and potential metabolic changes that occur following fecal transplant, says senior author Vincent B. Young, MD, PhD, an associate professor ...