(Press-News.org) E-cigarettes, also known as vaping pens or e-hookas, are commonly advertised on Twitter and the tweets often link to commercial websites promoting e-cig use, according to University of Illinois at Chicago researchers.
The study, published as a special supplement in the July 2014 issue of Tobacco Control released online June 16, has implications for future FDA regulations on the marketing of e-cigarettes and related products.
"There's this whole wild west of social media platforms – Facebook, Twitter and Instagram – and the FDA has no way to track what's happening in those platforms," said Jidong Huang, senior research scientist at UIC's Institute for Health Research and Policy and lead author of the study.
While advertising for conventional cigarettes has long been prohibited, e-cigarettes are advertised routinely in traditional media (print, television and radio) and social media.
The researchers collected tweets and metadata related to e-cigarettes during a two month period in 2012. Using novel statistical methodology and carefully chosen keywords, they captured more than 70,000 tweets related to e-cigs.
Among those 70,000 tweets, nearly 90 percent were commercial tweets and only 10 percent were 'organic,' or individual consumer opinions. Fully 94 percent of the commercial tweets included a website link, while only 11 percent of the organic tweets did.
Of the commercial tweets, 11 percent mentioned quitting smoking, and more than one-third offered coupons or discounts to purchase e-cig products.
Although only 11 percent of commercial tweets referenced smoking cessation, the absolute number is significant, Huang said, if considered over longer timeframes than the two months of the study.
Twitter is the second-largest search engine after Google.
"If kids or youth search for 'vaping pen' or 'e-cig' on Twitter, they will get links to commercial sites where they can purchase these items," said Huang. Unlike Facebook and some other platforms where one can set privacy controls, all information on Twitter is accessible to anyone.
Previous research has demonstrated rapid growth in use and awareness of e-cigarettes among adults and youth in recent years. However, there is limited evidence related to the products' long-term health impact, efficacy in smoking cessation — or role as a "gateway" to other tobacco products.
"We know very little about what these products are made of and what kind of chemicals are in the e-juice," Huang said.
The study did not look at who was exposed to the messages, but it is known that Twitter users are primarily young adults (30 percent ages 18-29) and African American (27 percent) or Latino (28 percent).
"Given the substantial youth presence on social media, the marketing of e-cigarettes on those platforms may entice non-smokers – youth in particular – to experiment with and initiate e-cigarette use," write the authors.
INFORMATION:
Huang's coauthors are Rachel Kornfield, Glen Szcypka and Sherry Emery, all of UIC.
E-cigs heavily marketed on Twitter, study finds
2014-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Soft-drink tax worth its weight in lost kilos
2014-06-17
A tax on sweetened soft drinks could be an effective weapon in the war against obesity, generating weight losses of up to 3.64 kilograms as individuals reduce their consumption.
Researchers from Monash University, Imperial College London and University of York and Lancaster University, England have estimated the extent to which drinking habits would change if beverages such as carbonated non-diet soft drinks; cordials and fruit drinks were taxed.
Lead author Dr Anurag Sharma, of the Centre for Health Economics at Monash University, said such a tax could have important ...
Solar photons drive water off the moon
2014-06-17
Water is thought to be embedded in the moon's rocks or, if cold enough, "stuck" on their surfaces. It's predominantly found at the poles. But scientists probably won't find it intact on the sunlit side.
New research at the Georgia Institute of Technology indicates that ultraviolet photons emitted by the sun likely cause H2O molecules to either quickly desorb or break apart. The fragments of water may remain on the lunar surface, but the presence of useful amounts of water on the sunward side is not likely.
The Georgia Tech team built an ultra-high vacuum system that ...
Researchers identify new compound to treat depression
2014-06-17
There is new hope for people suffering from depression. Researchers have identified a compound, hydroxynorketamine (HNK), that may treat symptoms of depression just as effectively and rapidly as ketamine, without the unwanted side effects associated with the psychoactive drug, according to a study in the July issue of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®). Interestingly, use of HNK may also serve as a future therapeutic approach for treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, ...
Surgical patients more likely to follow medication instructions
2014-06-17
A study in the July issue of Anesthesiology revealed that patients who receive a simple, multicolor, standardized medication instruction sheet before surgery are more likely to comply with their physician's instructions and experience a significantly shorter post-op stay in recovery. These findings are important because surgical patients often fail to follow their doctor's medication instructions for preexisting conditions such as diabetes and hypertension on the day they are having surgery – a costly mistake that can lead to surgery cancellation, complications and longer ...
References resources find their place among open access and Google, study finds
2014-06-17
Los Angeles, CA (June 17, 2014) How do open access sources, tightened budgets, and competition from popular technologies affect how librarians perceive and employ reference resources? How do librarians expect to utilize reference in the future? "The State of Reference Collections," a new SAGE white paper out today, finds that though the definition of reference is changing, this is in part because reference resources now look and feel like other information sources and because other information resources perform the traditional purpose of reference – answering research ...
Study links APC gene to learning and autistic-like disabilities
2014-06-17
BOSTON (June 17, 2014, 4:00 a.m. EDT) — Autistic-like behaviors and decreased cognitive ability may be associated with disruption of the function of the Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC) gene. When Tufts researchers deleted the gene from select neurons in the developing mouse brain, the mice showed reduced social behavior, increased repetitive behavior, and impaired learning and memory formation, similar to behaviors seen in individuals with autism and intellectual disabilities. This study is the first to evaluate how the loss of APC from nerve cells in the forebrain affects ...
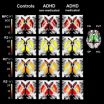
MRI technique may help prevent ADHD misdiagnosis
2014-06-17
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Brain iron levels offer a potential biomarker in the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and may help physicians and parents make better informed treatment decisions, according to new research published online in the journal Radiology.
ADHD is a common disorder in children and adolescents that can continue into adulthood. Symptoms include hyperactivity and difficulty staying focused, paying attention and controlling behavior. The American Psychiatric Association reports that ADHD affects 3 to 7 percent of school-age children.
Psychostimulant ...
Fecal transplants restore healthy bacteria and gut functions
2014-06-17
Fecal microbiota transplantation --- the process of delivering stool bacteria from a healthy donor to a patient suffering from intestinal infection with the bacterium Clostridium difficile --- works by restoring healthy bacteria and functioning to the recipient's gut, according to a study published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
The study provides insight into the structural and potential metabolic changes that occur following fecal transplant, says senior author Vincent B. Young, MD, PhD, an associate professor ...
Combining treatments boosts some smokers' ability to quit
2014-06-17
DURHAM, N.C. -- Combining two smoking cessation therapies is more effective than using just one for male and highly nicotine-dependent smokers who weren't initially helped by the nicotine patch, according to researchers at Duke Medicine.
The findings, published online June 17, 2014, in the American Journal of Psychiatry, also support using an adaptive treatment model to determine which smokers are likely to succeed in quitting with nicotine replacement alone before trying additional therapies.
"The findings offer a potential practical treatment approach that can identify ...
Minimizing belief in free will may lessen support for criminal punishment
2014-06-17
Exposure to information that diminishes free will, including brain-based accounts of behavior, seems to decrease people's support for retributive punishment, according to research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
People who learned about neuroscientific research, either by reading a magazine article or through undergraduate coursework, proposed less severe punishment for a hypothetical criminal than did their peers. The findings suggest that they did so because they saw the criminal as less blameworthy.
"There ...