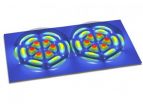
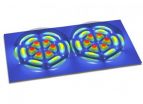
(Press-News.org) Scientists at the University of Bonn and the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada) have developed a novel camera system which can see around the corner without using a mirror. Using diffusely reflected light, it reconstructs the shape of objects outside of the field of view. The researchers will be reporting their results at the international Conference for Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) from June 24-27 in Columbus (Ohio, USA).
A laser shines on the wall; a camera watches the scene. Nothing more than white ingrain wallpaper with a bright spot of light can be seen through the lens. A computer records these initially unremarkable images and as the data is processed further, little by little, the outlines of an object appear on a screen. Yet, this object is behind a partition and the camera cannot possibly have seen it – we have apparently looked around the corner. A magic trick? "No," says Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias B. Hullin from the Institute of Computer Science II at the University of Bonn. "This is an actual reconstruction from diffusely scattered light. Our camera, combined with a mathematical procedure, enables us to virtually transform this wall into a mirror."
Scattered light is used as a source of information
The laser dot on the wall is by itself a source of scattered light, which serves as the crucial source of information. Some of this light, in a roundabout way, falls back onto the wall and finally into the camera. "We are recording a kind of light echo, that is, time-resolved data, from which we can reconstruct the object," explains the Bonn computer scientist. "Part of the light has also come into contact with the unknown object and it thus brings valuable information with it about its shape and appearance." To be able to measure such echoes, a special camera system is required which Prof. Hullin has developed together with his colleagues at the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada) and further refined after his return to Bonn. In contrast to conventional cameras, it records not just the direction from which the light is coming but also how long it took the light to get from the source to the camera.
The technical complexity for this is comparatively low – suitable image sensors came onto the mass market long ago. They are mainly found in depth image cameras as they are used, for instance, as video game controllers or for range measurements in the automotive field. The actual challenge is to elicit the desired information from such time-of-flight measurements. Hullin compares the situation to a room which reverberates so greatly that one can no longer have a conversation with one's partner. "In principle, we are measuring nothing other than the sum of numerous light reflections which reached the camera through many different paths and which are superimposed on each other on the image sensor."
This problem, known as multipath interference, has been giving engineers headaches for a long time. Traditionally, one would attempt to remove the undesired multipath scatter and only use the direct portion of the signal. Based on an advanced mathematical model, Hullin and his colleagues, however, developed a method which can obtain the desired information exclusively from what would usually be considered noise rather than signal. Since multipath light also originates from objects which are not at all in the field of view, the researchers can thus make visible what is virtually invisible.
Minimal technical complexity and intelligent programming
"The accuracy of our method has its limits, of course," says Prof. Hullin – the results are still limited to rough outlines. However, the researchers assume that based on the rapid development of technical components and mathematical models, an even higher resolution can be achieved soon. Together with his colleagues, he will present the method at the international Conference for Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) from June 24 to 27 in Columbus (Ohio, USA). The new technology is received with great interest – Hullin hopes that similar approaches can be used, for example, in telecommunications, remote sensing and medical imaging.
INFORMATION:
Publication: Felix Heide, Lei Xiao, Wolfgang Heidrich und Matthias B. Hullin, "Diffuse Mirrors: 3D Reconstruction from Diffuse Indirect Illumination Using Inexpensive Time-of-Flight Sensors". Internet: http://cg.cs.uni-bonn.de/multipath/
A podcast on this topic is available at: http://youtu.be/af6rhRPPwRs
Contact information:
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias B. Hullin
Institute of Computer Science II
University of Bonn
Tel. ++49-(0)228-7354169
E-Mail: hullin@cs.uni-bonn.de
With light echoes, the invisible becomes visible
Researchers at the University of Bonn and from Vancouver have developed a camera that can see around the corner
2014-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Three parents and a baby
2014-06-17
Mitochondria are cell organelles located within animal and human cells. They produce energy for the organism, possess their own genetic material - mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) - and are transmitted exclusively by the mother. Depending on their activity and tasks, different numbers of mitochondria are present in a cell - usually a few hundred to a thousand per body cell.
Inherited mitochondrial disorders or so-called mitochondropathies occur in about one of 10,000 humans throughout the world. Diseases such as diabetes, stroke, cardiac defects, epilepsy, or muscle weakness ...
Chemical pollution of European waters is stronger than anticipated
2014-06-17
This news release is available in German.
Substantial improvements in freshwater quality by 2015 have been a declared objective of the EU member states, manifesting itself by the requirements of the Water Framework Directive (WFD). A recent study conducted by the Institute for Environmental Sciences Landau together with the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) and fellow scientists from France (University of Lorraine and EDF) and Switzerland (Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology - EAWAG) shows that this target is unlikely to be ...
Social inequality intensifies amongst low-scoring pupils
2014-06-17
Children's marks at school influence the likelihood of them abandoning their studies, but the effect varies according to their social background: among students with poor marks, those from a higher social class have more opportunities to raise their marks than children of low-skilled workers. This is according to a study carried out by researchers from the National University of Distance Learning (UNED) and the European University Institute.
"The study deals with dissociating the effect of the marks (considered the 'primary source' of educational results) from other processes ...
Strange physics turns off laser
2014-06-17
Inspired by anomalies that arise in certain mathematical equations, researchers have demonstrated a laser system that paradoxically turns off when more power is added rather than becoming continuously brighter.
The finding by a team of researchers at Vienna University of Technology and Princeton University, could lead to new ways to manipulate the interaction of electronics and light, an important tool in modern communications networks and high-speed information processing.
The researchers published their results June 13 in the journal Nature Communications (Ref. 1).
Their ...
Study: In wild yak society, moms are the real climbers
2014-06-17
NEW YORK (June 17, 2014) – A new study led by the Wildlife Conservation Society says that in wild yak societies, it's the mothers that are the real climbers. The study found that mothers with young venture on steeper terrain and slightly higher elevation than either males or females without young.
The authors of the study expect that this strategy is an adaptive way to avoid predators and to access more nutritious food. Wild yaks are an endangered species occurring only on the Tibetan Plateau and closely related to North American bison.
The study, which appears in ...
Promising T cell therapy
2014-06-17
This news release is available in German. The cells of the human immune system are created from special stem cells in the bone marrow. In diseases affecting the bone marrow, such as leukemia, the degenerate cells must be destroyed using radiation or chemotherapy. Subsequently, the hematopoietic system has to be replaced with stem cells from the blood of a healthy donor. Because of the resulting temporary weakening of the immune system, patients are more exposed to viruses that would normally be warded off.
The cytomegalovirus (CMV), which can cause serious damage to ...
Laser physics upside down
2014-06-17
This news release is available in German.
Sound waves fade, water waves ebb, light waves are dissipated by a wall. The absorption of waves is a very common phenomenon. But only recently have physicists realized that amazing new possibilities are opened up, when this energy loss, rather than being seen as an annoying nuisance, is actually considered a desired effect. At the Vienna University of Technology, a system of two coupled lasers has been created, in which wave dissipation leads to a behaviour completely contrary to intuition: additional energy can switch it ...
Research at Granada finds that the eye's optical quality deteriorates after alcohol consumption
2014-06-17
A study conducted by the University of Granada has scientifically proven that alcohol consumption markedly impairs night-vision because it increases the perception of halos—luminous circles—and other visual night-time disturbances. Moreover, this deterioration of vision is significantly greater in subjects with breath alcohol content in excess of 0.25mg/litre—the legal limit for driving in Spain and other countries and, also, that recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Researchers from the Laboratory of Vision Sciences and Applications conclude that alcohol ...
Does the moon affect our sleep?
2014-06-17
Popular beliefs about the influence of the moon on humans widely exist. Many people report sleeplessness around the time of full moon. In contrast to earlier studies, scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry in Munich did not observe any correlation between human sleep and the lunar phases. The researchers analyzed preexisting data of a large cohort of volunteers and their sleep nights. Further identification of mostly unpublished null findings suggests that the conflicting results of previous studies might be due to a publication bias.
For centuries, people ...
How does a tree know it's time to grow again?
2014-06-17
Winter takes its toll on living things. To protect themselves from the elements, bears hibernate, and trees go dormant. Biologists have observed what happens when trees become dormant, but up to now, they haven't understood the underlying genetic mechanisms that enable them to start growing again.
Led by molecular geneticists from Michigan Technological University a gene has been identified and characterized that tells a poplar tree when winter ends and a spring growing season begins. Victor Busov, a professor in Michigan Tech's School of Forest Resources and Environmental ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] With light echoes, the invisible becomes visibleResearchers at the University of Bonn and from Vancouver have developed a camera that can see around the corner