(Press-News.org) The number of deaths involving commonly prescribed painkillers is higher than the number of deaths by overdose from heroin and cocaine combined, according to researchers at McGill University. In a first-of-its-kind review of existing research, the McGill team has put the spotlight on a major public health problem: the dramatic increase in deaths due to prescribed painkillers, which were involved in more than 16,000 deaths in 2010 in the U.S. alone. Currently, the US and Canada rank #1 and #2 in per capita opioid consumption.
"Prescription painkiller overdoses have received a lot of attention in editorials and the popular press, but we wanted to find out what solid evidence is out there," says Nicholas King, of the Biomedical Ethics Unit in the Faculty of Medicine. In an effort to identify and summarize available evidence, King and his team conducted a systematic review of existing literature, comprehensively surveying the scientific literature and including only reports with quantitative evidence.
"We also wanted to find out why thousands of people in the U.S and Canada are dying from prescription painkillers every year, and why these rates have climbed steadily during the past two decades," says Nicholas King, of the Biomedical Ethics Unit in the Faculty of Medicine. "We found evidence for at least 17 different determinants of increasing opioid-related mortality, mainly, dramatically increased prescription and sales of opioids; increased use of strong, long-acting opioids like Oxycontin and methadone; combined use of opioids and other (licit and illicit) drugs and alcohol; and social and demographic factors."
"We found little evidence that Internet sales of pharmaceuticals and errors by doctors and patients--factors commonly cited in the media -- have played a significant role," Prof. King adds.
The findings point to a complicated "epidemic" in which physicians, users, the health care system, and the social environment all play a role, according to the researchers.
"Our work provides a reliable summary of the possible causes of the epidemic of opioid overdoses, which should be useful for clinicians and policy makers in North America in figuring out what further research needs to be done, and what strategies might or might not be useful in reducing future mortality," says King. "And as efforts are made to increase access to prescription opioids outside of North America, our findings might be useful in preventing other countries from following the same path as the U.S. and Canada."
The results of this research are published in the American Journal of Public Health, http://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/abs/10.2105/AJPH.2014.301966
INFORMATION:
Contact:
Cynthia Lee
cynthia.lee@mcgill.ca
Relations avec les médias | Media Relations
Université McGill | McGill University
T. 514.398.6754
http://www.mcgill.ca/newsroom/
http://twitter.com/#!/McGilluMedia
Death by prescription painkiller
First major review provides evidence of sharp increase in deaths from painkillers in US and Canada and leading causes
2014-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Former athletes finish first in race for top jobs
2014-06-17
ITHACA, N.Y. – Whether you were a quarterback or point guard, past participation in competitive team sports marks you as a winner in the competition for better jobs, according to a new Cornell University study.
"Participation in competitive youth sports 'spills over' to occupationally advantageous traits that persist across a person's life," says Kevin M. Kniffin, postdoctoral research associate at Cornell's Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management and lead researcher.
Research by Kniffen and his co-authors, published online this week in the Journal of Leadership ...
3-D breast imaging could revolutionize cancer screening
2014-06-17
Leesburg, VA, June 17, 2014—In community-based radiology practice, mammography screening with 3D digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) yielded lower recall rates, an increased overall cancer detection rate, and an increased detection rate for invasive cancer compared with 2D digital mammography (DM).
In the largest report to date, researchers at Washington Radiology Associates, PC, with offices in Washington, DC; Virginia; and Maryland, conducted a study of more than 59,000 patients. The results were striking: an increase in the detection rate for cancer overall of 28.6% ...
Hyperthyroidism patients more likely to take extended sick leave than healthy peers
2014-06-17
Washington, DC—People who have hyperthyroidism are more likely to take sick leave for extended periods than their healthy colleagues, particularly in the first year after diagnosis, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive. The thyroid, which is located in the front of the neck, secretes hormones that regulate how the body uses energy, consumes oxygen and produces heat.
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, ...
Pitt psychology researchers explore how engineers create
2014-06-17
PITTSBURGH—Simply put, engineers make things. But is finding that "new" invention a massive mental leap from point A to point B, or are there scores of unnoticed intermediate steps in between?
The University of Pittsburgh's Joel Chan and Christian Schunn say that not enough has been done to understand how engineers create. Understanding the process, they say, may provide a road map for speeding up innovation.
Chan, a graduate student in psychology in Pitt's Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, and his mentor Schunn, a professor of psychology as well as a ...
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value
2014-06-17
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value among patients, new study says
TORONTO, June 17, 2014—Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling tests heightened their perceived importance among patients with early breast cancer who were deciding whether to have chemotherapy, a new study says.
Gene expression profiling tests, such as Oncotype Dx, analyze the patterns of 21 different genes within cancer cells to help predict how likely it is that a women's cancer will recur within 10 years after initial treatment and how beneficial ...
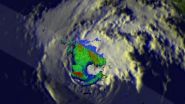
TRMM eyes rainfall in dissipating former Hurricane Cristina
2014-06-17
VIDEO:
On June 14, NASA's TRMM satellite found rain falling at a rate of almost 97 mm (about 3.8 inches) per hour in the northwestern side of Cristina's eye wall where...
Click here for more information.
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over a dissipating former Hurricane Cristina and found it still contained heavy rain as it rapidly weakened.
Hurricane Cristina had sustained winds of over 130 ...
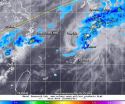
Tropical depression Hagibis gets a second chance
2014-06-17
Tropical Depression Hagibis appeared out for the count when it made landfall along southeastern China on June 16, but moved back into the South China Sea where it regenerated and sped northeast through the East China Sea. The next day, the TRMM satellite noticed power had come back to Hagibis in the form of some moderate rainfall in the depression's northeastern quadrant.
On June 17 at 10:30 UTC (6:30 a.m. EDT) the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over the regenerated Hagibis and the Precipitation Radar instrument gathered data on the storm's ...
Sleep education program spurs preschoolers to snooze 30 minutes longer at night
2014-06-17
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Taking part in an educational sleep program resulted in a 30-minute average increase in sleep duration at a one-month follow-up for preschoolers, according to a new study from the University of Michigan.
In the study, published in the journal SLEEP, families in two Head Start programs participated in the Sweet Dreamzzz Early Childhood Sleep Education Program™. The Detroit-area nonprofit organization, Sweet Dreamzzz, Inc. developed the program and offers it for free when funding allows. Head Start programs aim to give preschool opportunities to low-income ...
Dynamic spectroscopy duo
2014-06-17
From allowing our eyes to see, to enabling green plants to harvest energy from the sun, photochemical reactions – reactions triggered by light – are both ubiquitous and critical to nature. Photochemical reactions also play essential roles in high technology, from the creation of new nanomaterials to the development of more efficient solar energy systems. Using photochemical reactions to our best advantage requires a deep understanding of the interplay between the electrons and atomic nuclei within a molecular system after that system has been excited by light.
A major ...
Why species matter
2014-06-17
UC Santa Barbara doctoral candidate Caitlin Fong travels to French Polynesia often but not for vacation. She goes there to study a coral reef ecosystem influenced by human impacts such as overfishing and nutrient pollution.
Her work focuses not only on biological changes but also methods scientists use to determine within-group group responses to ecological processes. The findings are published in ESA Ecology, a journal of the Ecological Society of America.
Fong and Peggy Fong, a professor in UCLA's Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, conducted a study assessing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] Death by prescription painkillerFirst major review provides evidence of sharp increase in deaths from painkillers in US and Canada and leading causes