(Press-News.org) Researchers have provided the first functional analysis of a member of a family of transporter proteins implicated in diabetes, obesity, and lifespan. The study appears in the June issue of The Journal of General Physiology.
Members of the SLC13 transporter family play a key role in the regulation of fat storage, insulin resistance, and other processes. Some SLC13 transporters mediate the transport of Krebs cycle intermediates—compounds essential for the body's metabolic activity—across the cell membrane. Previous studies have shown that loss of one member of this family protects mice against obesity and insulin resistance, and loss of another results in reduced fat storage and extended lifespan in fruit flies. These findings hint at the therapeutic potential of targeting these transporters to combat metabolic disease, obesity, diabetes, and other conditions.
A recently obtained high-resolution structure of VcINDY—a member of the SLC13 family found in the bacteria that causes cholera—has provided key structural insights, but understanding how these transporters function at the cellular level remains a mystery. To find out more, researchers from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) reconstituted VcINDY into small synthetic vesicles called liposomes that allowed them to monitor its activity in isolation. Led by Joseph Mindell, the team was thereby able to analyze the properties of VcINDY as a transporter and provide a model that lays the groundwork for future studies of SLC13 transporters, potentially providing the key that will enable researchers to unlock their therapeutic potential.
INFORMATION:
Mulligan, C., et al. 2014. J. Gen. Physiol. doi:10.1085/jgp.201311141
About The Journal of General Physiology
Founded in 1918, The Journal of General Physiology (JGP) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editor. JGP content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit http://www.jgp.org.
Research reported in the press release was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institutes of Health.
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of SLC13 transporters
2014-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Penn team links placental marker of prenatal stress to brain mitochondrial dysfunction
2014-06-18
When a woman experiences a stressful event early in pregnancy, the risk of her child developing autism spectrum disorders or schizophrenia increases. Yet how maternal stress is transmitted to the brain of the developing fetus, leading to these problems in neurodevelopment, is poorly understood.
New findings by University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine scientists suggest that an enzyme found in the placenta is likely playing an important role. This enzyme, O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine transferase, or OGT, translates maternal stress into a reprogramming ...
Study examines how brain 'reboots' itself to consciousness after anesthesia
2014-06-18
One of the great mysteries of anesthesia is how patients can be temporarily rendered completely unresponsive during surgery and then wake up again, with their memories and skills intact.
A new study by Dr. Andrew Hudson, an assistant professor in anesthesiology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, and colleagues provides important clues about the processes used by structurally normal brains to navigate from unconsciousness back to consciousness. Their findings are currently available in the early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of ...
Scripps Florida scientists pinpoint how genetic mutation causes early brain damage
2014-06-18
JUPITER, FL, June 18, 2014 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have shed light on how a specific kind of genetic mutation can cause damage during early brain development that results in lifelong learning and behavioral disabilities. The work suggests new possibilities for therapeutic intervention.
The study, which focuses on the role of a gene known as Syngap1, was published June 18, 2014, online ahead of print by the journal Neuron. In humans, mutations in Syngap1 are known to cause devastating forms of intellectual disability ...
Blocking brain's 'internal marijuana' may trigger early Alzheimer's deficits, study shows
2014-06-18
A new study led by investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine has implicated the blocking of endocannabinoids — signaling substances that are the brain's internal versions of the psychoactive chemicals in marijuana and hashish — in the early pathology of Alzheimer's disease.
A substance called A-beta — strongly suspected to play a key role in Alzheimer's because it's the chief constituent of the hallmark clumps dotting the brains of people with Alzheimer's — may, in the disease's earliest stages, impair learning and memory by blocking the natural, beneficial ...
Groundbreaking model explains how the brain learns to ignore familiar stimuli
2014-06-18
Dublin, June 18th, 2014 – A neuroscientist from Trinity College Dublin has proposed a new, ground-breaking explanation for the fundamental process of 'habituation', which has never been completely understood by neuroscientists.
Typically, our response to a stimulus is reduced over time if we are repeatedly exposed to it. This process of habituation enables organisms to identify and selectively ignore irrelevant, familiar objects and events that they encounter again and again. Habituation therefore allows the brain to selectively engage with new stimuli, or those that ...
Fight-or-flight chemical prepares cells to shift brain from subdued to alert
2014-06-18
A new study from The Johns Hopkins University shows that the brain cells surrounding a mouse's neurons do much more than fill space. According to the researchers, the cells, called astrocytes because of their star-shaped appearance, can monitor and respond to nearby neural activity, but only after being activated by the fight-or-flight chemical norepinephrine. Because astrocytes can alter the activity of neurons, the findings suggest that astrocytes may help control the brain's ability to focus.
The study involved observing the cells in the brains of living, active mice ...
Modeling how neurons work together
2014-06-18
A newly-developed, highly accurate representation of the way in which neurons behave when performing movements such as reaching could not only enhance understanding of the complex dynamics at work in the brain, but aid in the development of robotic limbs which are capable of more complex and natural movements.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge, working in collaboration with the University of Oxford and the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), have developed a new model of a neural network, offering a novel theory of how neurons work together when ...
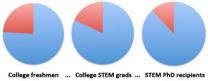
Stem pipeline problems to aid STEM diversity
2014-06-18
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Decades of effort to increase the number of minority students entering the metaphorical science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) pipeline, haven't changed this fact: Traditionally underrepresented groups remain underrepresented. In a new paper in the journal BioScience, two Brown University biologists analyze the pipeline's flawed flow and propose four research-based ideas to ensure that more students emerge from the far end with Ph.D.s and STEM careers.
Senior author Andrew G. Campbell, associate professor of biology, said ...
Nanoparticles from dietary supplement drinks likely to reach environment, say scientists
2014-06-18
Nanoparticles are becoming ubiquitous in food packaging, personal care products and are even being added to food directly. But the health and environmental effects of these tiny additives have remained largely unknown. A new study now suggests that nanomaterials in food and drinks could interfere with digestive cells and lead to the release of the potentially harmful substances to the environment. The report on dietary supplement drinks containing nanoparticles was published in the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Robert Reed and colleagues note that food ...
BU-lead study shows surprising spread of spring leaf-out times
2014-06-18
(Boston) – Despite conventional wisdom among gardeners, foresters and botanists that woody plants all "leaf out" at about the same time each spring, a new study organized by a Boston University biologist found a surprisingly wide span of as much as three months in leaf-out times. Significantly, observations the past two springs of 1,597 woody plants in eight botanical gardens in the U.S., Canada, Germany and China suggest that species differences in leaf-out times could impact the length of the growing season and the activities of birds, insect and other animals and therefore ...