(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, June 19, 2014—Before they excise a tumor, surgeons need to determine exactly where the cancerous cells lie. Now, research published today in The Optical Society's (OSA) journal Optics Letters details a new technique that could give surgeons cheaper and more lightweight tools, such as goggles or hand-held devices, to identify tumors in real time in the operating room.
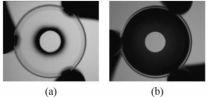
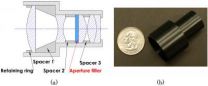
The new technology, developed by a team at the University of Arizona and Washington University in St. Louis, is a dual-mode imager that combines two systems—near-infrared fluorescent imaging to detect marked cancer cells and visible light reflectance imaging to see the contours of the tissue itself—into one small, lightweight package approximately the size of a quarter in diameter, just 25 millimeters across.
"Dual modality is the path forward because it has significant advantages over single modality," says author Rongguang Liang, associate professor of optical sciences at the University of Arizona.
Interest in multi-modal imaging technology has surged over the last 10 years, says Optics Letters topical editor Brian Applegate of Texas A&M University, who was not involved in the research. People have realized that in order to better diagnose diseases like cancer, he says, you need information from a variety of sources, whether it's fluorescence imaging, optical imaging or biochemical markers.
"By combining different modalities together, you get a much better picture of the tissue," which could help surgeons make sure they remove every last bit of the tumor and as small amount of healthy tissue as possible, Applegate says.
Currently, doctors can inject fluorescent dyes into a patient to help them pinpoint cancer cells. The dyes converge onto the diseased cells, and when doctors shine a light of a particular wavelength onto the cancerous area, the dye glows. In the case of a common dye called indocyanine green (ICG), it glows in near-infrared light. But because the human eye isn't sensitive to near-infrared light, surgeons have to use a special camera to see the glow and identify the tumor's precise location.
Surgeons also need to be able to see the surface of the tissue and the tumor underneath before cutting away, which requires visible light imaging. So researchers have been developing systems that can see in both fluorescent and visible light modes.
The trouble is that the two modes have opposing needs, which makes integration difficult. Because the fluorescent glow tends to be dim, a near-infrared light camera needs to have a wide aperture to collect as much fluorescent light as possible. But a camera with a large aperture has a low depth of field, which is the opposite of what's needed for visible-light imaging.
"The other solution is to put two different imaging systems together side by side," Liang says. "But that makes the device bulky, heavy and not easy to use."
To solve this problem, Liang's group and that of his colleagues, Samuel Achilefua and Viktor Gruev at Washington University in St. Louis, created the first-of-its-kind dual-mode imaging system that doesn't make any sacrifices.
The new system relies on a simple aperture filter that consists of a disk-shaped region in the middle and a ring-shaped area on the outside. The middle area lets in visible and near-infrared light but the outer ring only permits near-infrared light. When you place the filter in the imaging system, the aperture is wide enough to let in plenty of near-infrared light. But since visible light can't penetrate the outer ring, the visible-sensitive part of the filter has a small enough aperture that the depth of field is large.
Liang's team is now adapting its filter design for use in lightweight goggle-like devices that a surgeon can wear while operating. They are also developing a similar hand-held instrument.
INFORMATION:
Paper: "Dual-mode optical imaging system for fluorescence image-guided surgery," N. Zhu et al., Optics Letters, vol. 39, issue 13, pp. 3830-3832 (2014)
EDITOR'S NOTE: Images are available to members of the media upon request. Contact Lyndsay Meyer, lmeyer@osa.org.
About Optics Letters
Published by The Optical Society (OSA), Optics Letters offers rapid dissemination of new results in all areas of optics with short, original, peer-reviewed communications. Optics Letters covers the latest research in optical science, including optical measurements, optical components and devices, atmospheric optics, biomedical optics, Fourier optics, integrated optics, optical processing, optoelectronics, lasers, nonlinear optics, optical storage and holography, optical coherence, polarization, quantum electronics, ultrafast optical phenomena, photonic crystals, and fiber optics. This journal, edited by Xi-Cheng Zhang of the University of Rochester and published twice each month, is where readers look for the latest discoveries in optics. Visit http://www.OpticsInfoBase.org/OL.
About OSA
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional society for scientists, engineers, students and business leaders who fuel discoveries, shape real-world applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership programs, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of professionals in optics and photonics. For more information, visit http://www.osa.org.
A better imager for identifying tumors
Smaller, cheaper 2-mode imaging system could help surgeons see and remove cancer
2014-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Swiftly moving gas streamer eclipses supermassive black hole
2014-06-19
Astronomers have discovered strange and unexpected behaviour around the supermassive black hole at the heart of the galaxy NGC 5548. The international team of researchers detected a clumpy gas stream flowing quickly outwards and blocking 90 percent of the X-rays emitted by the black hole. This activity could provide insights into how supermassive black holes interact with their host galaxies.
The discovery of the unusual behaviour in NGC 5548 is the result of an intensive observing campaign using major ESA and NASA space observatories, including the NASA/ESA Hubble Space ...
LLNL, MIT researchers develop new ultralight, ultrastiff 3D printed materials
2014-06-19
LIVERMORE, Calif. – Imagine a material with the same weight and density as aerogel -- a material so light it's called 'frozen smoke' -- but with 10,000 times more stiffness. This material could have a profound impact on the aerospace and automotive industries as well as other applications where lightweight, high-stiffness and high-strength materials are needed.
Lawrence Livermore and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) researchers have developed a material with these properties using additive micro-manufacturing processes. The research team's findings are published ...
Kids with strong bonds to parents make better friends, can adapt in relationships
2014-06-19
URBANA, Ill. – What social skills does a three-year-old bring to interactions with a new peer partner? If he has strong bonds to his parents, the child is likely to be a positive, responsive playmate, and he'll be able to adapt to a difficult peer by asserting his needs, according to a new University of Illinois study published in Developmental Psychology.
"Securely attached children are more responsive to suggestions or requests made by a new peer partner. A child who has experienced a secure attachment relationship with caregivers is likely to come into a new peer relationship ...
Mechanism discovered for attaching an 'on' switch that helps cells accessorize proteins
2014-06-19
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – June 19, 2014) St. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have discovered how an important "on" switch is attached to the machinery that cells rely on to adapt thousands of proteins to meet changing conditions. The research appears in the current issue of the journal Cell.
The switch is a small protein called NEDD8. Problems with NEDD8 have been associated with several cancers, developmental disorders and infectivity of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS. Drugs that target NEDD8 are in anti-cancer clinical trials. The ability ...
Drug shows promise for the first time against metastatic melanoma of the eye
2014-06-19
NEW YORK, NY (June 19, 2014) — For the first time, a therapy has been found that can delay progression of metastatic uveal melanoma, a rare and deadly form of melanoma of the eye.
Results from a multicenter clinical trial show that a new drug called selumetinib increases progression-free survival, the length of time during and after treatment that a patient with metastases lives with the disease without it progressing. The findings were published today in the online edition of JAMA, the Journal of the American Medical Association.
"Although the effects of the drug were ...
RNA aptamers targeted to plasminogen activator inhibitor
2014-06-19
New Rochelle, NY, June 19, 2014—Plasminogen activators are proteins involved in the breakdown of blood clots, and an elevated level of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is associated with an increased risk for clotting and cardiovascular disease. No PAI-1 inhibitors are currently available for clinical use, but a novel therapeutic approach using a targeted RNA aptamer drug that has been shown to block PAI-1 activity and prevent PAI-1-associated vascular events is described in Nucleic Acid Therapeutics, a peer-reviewed journal from Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. The ...
Humans & monkeys of one mind when it comes to changing it
2014-06-19
Covert changes of mind can be discovered by tracking neural activity when subjects make decisions, researchers from New York University and Stanford University have found. Their results, which appear in the journal Current Biology, offer new insights into how we make decisions and point to innovative ways to study this process in the future.
"The methods used in this study allowed us to see the idiosyncratic nature of decision making that was inaccessible before," explains Roozbeh Kiani, an assistant professor in NYU's Center for Neural Science and the study's lead author. ...
Scientists identify link between stem cell regulation and the development of lung cancer
2014-06-19
UCLA researchers led by Dr. Brigitte Gomperts have discovered the inner workings of the process thought to be the first stage in the development of lung cancer. Their study explains how factors that regulate the growth of adult stem cells that repair tissue in the lungs can lead to the formation of precancerous lesions.
Findings from the three-year study could eventually lead to new personalized treatments for lung cancer, which is responsible for an estimated 29 percent of U.S. cancer deaths, making it the deadliest form of the disease.
The study was published online ...
Evolution of equine influenza led to canine offshoot which could mix with human influenza
2014-06-19
Equine influenza viruses from the early 2000s can easily infect the respiratory tracts of dogs, while those from the 1960s are only barely able to, according to research published ahead of print in the Journal of Virology. The research also suggests that canine and human influenza viruses can mix, and generate new influenza viruses.
Canine influenza is a relatively new disease. The first appearance is believed to be in 2003, as a result of direct transfer of a single equine influenza virus to dogs in a large greyhound training facility and was subsequently carried to ...
Who's your daddy? UCF team programs computer to find out
2014-06-19
A University of Central Florida research team has developed a facial recognition tool that promises to be useful in rapidly matching pictures of children with their biological parents and in potentially identifying photos of missing children as they age.
The work verifies that a computer is capable of matching pictures of parents and their children. The study will be presented at the nation's premier event for the science of computer vision - the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition conference in Columbus, Ohio, which begins Monday, June 23.
Graduate Student ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
[Press-News.org] A better imager for identifying tumorsSmaller, cheaper 2-mode imaging system could help surgeons see and remove cancer