(Press-News.org) The annually recurring devastating tornado attacks in US Tornado Alley raise an important question: Can we eliminate the major tornado threat in Tornado Alley? Some people may claim that such a question is beyond imagination as people are powerless in facing violent tornadoes. However, according to Professor Rongjia Tao's recent publication in IJMPB, human beings are not powerless on this issue: if we build three east-west great walls in Tornado Alley, we will eliminate major tornado threat there forever. These walls can be built locally at high tornado risk areas to eliminate tornado threat there first, then gradually extended.
In the US, most devastating tornadoes occur in Tornado Alley, which is a strip of land between the Appalachian Mountains and the Rocky Mountains, including most American Midwest states. In 2013, there were 811 confirmed tornadoes in USA, 57 in Europe and 3 in China. Among 811 tornadoes in USA, most of them, especially the most devastating ones, occurred in Tornado Alley. What causes such huge differences?
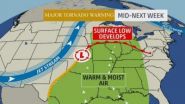
From the atmospheric circulation point of view, Tornado Alley is inside the "zone of mixing", where the warm and moist air flows northbound and cold air flows southbound. At a certain season, the warm air flow front clashes with the cold air flow front at some place in Tornado Alley. Major tornadoes in Tornado Alley all start with such clashes (Fig.1). Especially as there is no east-west mountain in Tornado Alley to weaken or block the air flows, some clashes are violent, creating vortex turbulence. Such violent vortexes, supercells, are initially in horizontal spinning motion at the lower atmosphere, then tilt as the air turns to rise in the storm's updraft, creating a component of spin around a vertical axis. If the vortex stretching during the vortex tilting intensifies the vertical vorticity enough to create a tornado, the vortex size is getting much smaller as the rotation speed gets much faster. About 30% of supercells lead to tornadoes (Fig.2).
Calculations show that the chance to produce tornadoes depends on the wind speeds during the clashes. For example, if both cold wind and warm wind have speed 30 miles/h (13.3m/s), the chance to develop tornados from the clash is very high. On the other hand, if the both winds have speed below 15 miles/h, there is almost no chance for the clash to develop into tornadoes. Hence reducing the wind speed and eliminating the violent air mass clashes are the key to prevent tornado formation in Tornado Alley. We can learn from the Nature how to do so.
United States and China have similar geographic locations. In particular, the Northern China Plain and the Eastern China Plain is also in the zone of mixing, similar to Tornado Alley. However, very few violent tornadoes occur in this region of China because there are three east-west mountain ranges to protect these plains from tornado threat. The first one is 300km long Yan Mountain which lies at the northern boundary of these plains. The second one is 600km long Nanling (Nan Mountains) at the south boundary of these plains. The third one is 800kom long Jiang-Huai Hills through the middle of the plains. Especially, Jiang-Huai Hills are only about 300 meters above sea level, but effectively eliminate the major tornado threat for the areas. This is evidenced by the following fact.
Jiang-Huai Hills do not extend to Pacific ocean, leaving a small plain area, north part of Jiangsu province, unprotected. This small area, similar to US Tornado Alley, has annually recurring tornado outbreaks. For example, the city Gaoyou in this area has a nickname "Tornado hometown", which has tornado outbreaks once in two years on average. It is thus clear that Jiang-Huai Hills are extremely effectively in eliminating tornadoes formation. Without Jiang-Huai Hills, a quite big area in China would become "Tornado Hometown"
While there are no mountains in Tornado Alley to play the same role as Jiang-Huai Hills etc in China, there are two small mountains, Ozarks Mountains and Shawnee Hills, which significantly reduce tornado risk for some local areas.
Ozark Mountain consists of high and deeply dissected plateaus; the mountain hills are south-north ranged. Most parts of these north-south hills cannot block or weaken air mass flow between north and south. Therefore, for example, Joplin has very high tornado risk as it faces the north-south deeps and valleys formed by these hills, the winds get more strength as they pass these valleys and deeps. On the other hand, some small sections of St. Francois Mountains and Boston Mountains have the hills east-west connected. Therefore, for example, Rolla, Missouri has very low tornado risk, as analyzed by http://www.homefact.com/tornadoes/.
The devastating tornado outbreak in Washington County, IL on November 17, 2013 also reminds us about Shawnee Hills, which is a small mountain, 60 miles east from Washington County. Most Shawnee Hills are along the south - north direction, but some sections are east-west connected, located at the south border of Gallatin County. Therefore, Gallatin County has very low tornado risk, although the most land in Gallatin County is flat farm land, same as Washington county.
According to Dr. Tao, the above information learned from Nature is very encouraging. Although there are no east-west mountains in Tornado Alley, we can build some east-west great walls to play the same role. Also learned from Jiang-Huai Hills and Shawnee Hills, the wall needs about 300 meter high and 50 meter wide.
To eliminate the tornado threat for the entire Tornado Alley, we may need to build three great walls. The first one should be close to the northern boundary of the Tornado Alley, maybe in North Dakota. The second one should be in the middle, maybe in the middle of Oklahoma and going to east. The third one can be in the south of Texas and Louisiana.
Such great walls may affect the weather, but their effect on the weather will be minor, as evidenced by Shawnee Hills in Illinois. In fact, with scientific design, we may also use these walls to improve the local climate.
In Philadelphia, there is one skyscraper building, Comcast Center, about 300 meter high. From the cost of Comcast Center, we estimate that to build one mile such wall, we need about $160 million. On the other hand, the damages caused by single tornado attack in Moore, Oklahoma on May 20, 2013 alone were multi billion dollars. Therefore, it seems that the cost for building such a wall is affordable.
While building the three great walls will eventually eliminate major tornadoes in the entire Tornado Alley, we do not expect to start such a huge project in the near future. On the other hand, it is more realistic to build such great walls locally at high tornado risk areas first, then connect them piece by piece. To do so locally, we must remember that from air fluid dynamics, the area protected by the wall is roughly a circle with the wall as its diameter.
Also in developing any new city in Tornado Alley in future, we may consider to build east-west skyscraper buildings first, then allocate the other parts of the city surrounding the skyscraper buildings. In such a way, the skyscraper buildings will serve as a wall, eliminating major tornado formation in their surroundings to protect the whole city.
INFORMATION:
Acknowledgments: This work is supported in part by a grant from US Naval Research Lab.
Corresponding author for this study is Rongjia Tao, rtao@temple.edu
The paper will appear in IJMPB.
We can eliminate the major tornado threat in Tornado Alley
2014-06-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Not even cell death can stop the alarm
2014-06-23
Even after a cell dies, components of the immune system remain active and continue to fuel inflammatory reactions. An international team of researchers under the direction of scientists from the Institute of Innate Immunity at the University Hospital of Bonn has discovered how this incredible form of communication works. The findings offer potentially novel approaches for therapies against many serious diseases that affect a large part of the population, such as gout, atherosclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. The exciting new results are now published in the renowned journal ...
LED phosphors: Better red makes brighter white
2014-06-23
Chemists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have developed a novel type of red phosphor material, which significantly enhances the performance of white-emitting LEDs.
In cooperation with Dr. Peter Schmidt of Philips Technologie GmbH in Aachen, a team of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Schnick, who holds the Chair of Inorganic Solid-State Chemistry at LMU Munich, has developed a new material for application in light-emitting diodes (LEDs). "With its highly unusual properties, the new material has the potential to revolutionize the LED market," says ...
Magnetic fields to measure positions of ferromagnetic objects accurately
2014-06-23
Many creatures in nature, including butterflies, newts and mole rats, use the Earth's inherent magnetic field lines and field intensity variations to determine their geographical position. A research team at the University of Minnesota has shown that the inherent magnetic fields of ferromagnetic objects can be similarly exploited for accurate position measurements of these objects. Such position measurement is enabled in this research by showing that the spatial variation of magnetic field around an object can be modeled using just the geometry of the object under consideration. ...
The colon has a safety mechanism that restricts tumor formation
2014-06-23
Colon cancer development starts with the formation of benign tumours called adenomas. It is estimated that between 30% and 50% of people over 50 will develop one of these tumours. These adenomas or polyps are the pre-cancerous lesions that, once they accumulate further genetic mutations over many years, can progress to colon cancer. A team headed by scientists at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and headed by the ICREA researcher Eduard Batlle has discovered that the colon has a safety mechanism to restrict the formation and growth of adenomas. ...
Researchers discover new genes that promote brain cancer
2014-06-23
La Jolla, Calif., June 22, 2014, A new collaborative study carried out by researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham), UC San Diego, the German Cancer Research Center, the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and 33 other research institutions has identified two oncogenes, called GFI1 and GFI1B, that drive the development of medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in children.
The findings, published June 22 in Nature, suggest that GFI1 and GFI1B are worthy gene candidates for molecular-targeted therapy.
"Using state-of-the-art ...
Vitamin D can lower weight, blood sugar via the brain
2014-06-23
CHICAGO, IL—Women with type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol are less likely than their male peers to reach treatment goals to lower their "bad" cholesterol, or low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, despite access to cholesterol-lowering medication, a Canadian study finds. The results were presented on Saturday at the joint meeting of the International Society of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society: ICE/ENDO 2014 in Chicago.
Although other research has shown a similar gender gap in reduction of LDL cholesterol among adults with diabetes, the new study found that ...
Low number of taste buds linked to older age, higher fasting blood sugar
2014-06-23
CHICAGO, IL—A study finds that the number of taste buds we have on our tongue decreases as we get older, and that the lower the number of taste buds, the more likely for fasting blood glucose (sugar) levels to be higher than normal. The results were presented Sunday at the joint meeting of the International Society of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society: ICE/ENDO 2014 in Chicago.
Because high fasting blood sugar level is a main characteristic of diabetes, the study findings suggest that the number of taste buds plays a role in glucose metabolism—how the body uses ...
Growth hormone defect may protect against diabetes, cancer in unique ecuador population
2014-06-23
CHICAGO, IL — People who lack growth hormone (GH) receptors also appear to have marked insulin sensitivity that prevents them from developing diabetes and lowers their risk for cancer, despite their increased percentage of body fat, new research finds. The results were presented Sunday, June 22, at ICE/ENDO 2014, the joint meeting of the International Society of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society in Chicago.
"We have shown that people who, due to a genetic defect, are unable to respond to growth hormone have an increased sensitivity to insulin that safeguards them ...
Hypothyroidism may lead to impaired driving
2014-06-23
CHICAGO, IL — People with significant hypothyroidism can experience impaired driving similar to those who are driving when intoxicated by alcohol, a new study finds. The results were presented Sunday at the joint meeting of the International Society of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society: ICE/ENDO 2014 in Chicago.
Hypothyroidism, insufficient thyroid hormone, is very common and has been known to cause impairment of many bodily functions, including brain function. Until now, studies have not sufficiently explored the extent of brain impairment and whether hypothyroid ...
High blood sugar causes brain changes that raise depression risk
2014-06-23
CHICAGO, IL — Researchers have found a possible biological reason why people with diabetes are prone to depression. A new study shows that high blood glucose (sugar) levels in patients with Type 1 diabetes increase the levels of a brain neurotransmitter associated with depression, and alter the connections between regions of the brain that control emotions. The results will be presented Sunday at the joint meeting of the International Society of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society: ICE/ENDO 2014 in Chicago.
"It was traditionally thought that patients with Type 1 or ...