(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. — For the first time, the genome of the electric eel has been sequenced. This discovery has revealed the secret of how fishes with electric organs have evolved six times in the history of life to produce electricity outside of their bodies.
The research, published in the current issue of Science, sheds light on the genetic blueprint used to evolve these complex, novel organs. It was co-led by Michigan State University, University of Wisconsin-Madison, University of Texas-Austin and the Systemix Institute.
"It's truly exciting to find that complex structures like the electric organ, which evolved completely independently in six groups of fish, seem to share the same genetic toolkit," said Jason Gallant, MSU zoologist and co-lead author of the paper. "Biologists are starting to learn, using genomics, that evolution makes similar structures from the same starting materials, even if the organisms aren't even that closely related."
Worldwide, there are hundreds of species of electric fish in six broad lineages. Their diversity is so great that Darwin himself cited electric fishes as critical examples of convergent evolution, where unrelated animals independently evolve similar traits to adapt to a particular environment or ecological niche.
All muscle and nerve cells have electrical potential. Simple contraction of a muscle will release a small amount of voltage. But between 100 and 200 million years ago, some fish began to amplify that potential by evolving electrocytes from muscle cells, organized in sequence and capable of generating much higher voltages than those used to make muscles work.
"Evolution has removed the ability of muscle cells to contract and changed the distribution of proteins in the cell membrane; now all electrocytes do is push ions across a membrane to create a massive flow of positive charge," said Lindsay Traeger, U-W graduate student and co-author of the study.
The "in-series alignment" of the electrocytes and unique polarity of each cell allows for the "summation of voltages, much like batteries stacked in series in a flashlight," said Michael Sussman, U-W biochemist.
The additional current required for the power comes from the fact that an eel body contains many millions of such "batteries" working together and firing their electrical discharge simultaneously.
The new work provides the world's first electric fish genome sequence assembly. It also identifies the genetic factors and developmental pathways the animals use to grow an organ that, in the case of the electric eel, can deliver a jolt several times more powerful than the current from a standard household electrical outlet. Other electric fishes use electricity for defense, predation, navigation and communication.
Future MSU research will focus on testing the role of these genes in the development of electric organs, using state-of-the-art transgenic techniques in Gallant's newly constructed laboratory.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation, the W.M. Keck Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
Michigan State University has been working to advance the common good in uncommon ways for more than 150 years. One of the top research universities in the world, MSU focuses its vast resources on creating solutions to some of the world's most pressing challenges, while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 200 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
For MSU news on the Web, go to MSUToday. Follow MSU News on Twitter at twitter.com/MSUnews.
Sequencing electric eel genome unlocks shocking secrets
2014-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Water-cleanup catalysts tackle biomass upgrading
2014-06-26
Rice University chemical engineer Michael Wong has spent a decade amassing evidence that palladium-gold nanoparticles are excellent catalysts for cleaning polluted water, but even he was surprised at how well the particles converted biodiesel waste into valuable chemicals.
Through dozens of studies, Wong's team focused on using the tiny metallic specks to break down carcinogenic and toxic compounds. But his latest study, which is available online and due for publication in an upcoming issue of the Royal Society of Chemistry's journal Chemical Science, examined whether ...
Not much force: Berkeley researchers detect smallest force ever measured
2014-06-26
What is believed to be the smallest force ever measured has been detected by researchers with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley. Using a combination of lasers and a unique optical trapping system that provides a cloud of ultracold atoms, the researchers detected a force of approximately 42 yoctonewtons. A yoctonewton is one septillionth of a newton and there are approximately 3 x 1023 yoctonewtons in one ounce of force.
"We applied an external force to the center-of-mass motion of an ultracold atom ...
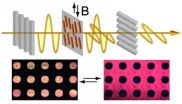
Let there be light: Chemists develop magnetically responsive liquid crystals
2014-06-26
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Chemists at the University of California, Riverside have constructed liquid crystals with optical properties that can be instantly and reversibly controlled by an external magnetic field. The research opens the door to display applications relying on the instantaneous and contactless nature of magnetic manipulation—such as signage, posters, writing tablets, and billboards.
Commercially available liquid crystals, used in modern electronic displays, are composed of rod-like or plate-like molecules. When an electric field is applied, the molecules rotate ...
Researchers conduct comprehensive review of treatments for depression in cancer patients
2014-06-26
Depression is common in cancer, up to half of all patients facing the disease experience depressive symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. When depression co-exists with cancer, patients may be at an increased risk of death from cancer and from suicide.
Antidepressants are commonly prescribed, but the evidence on their efficacy is mixed. The role of antidepressants in treating cancer-related depression has not been rigorously studied. To identify best practice for the treatment of depression in cancer, Dartmouth researchers completed a systematic review and meta-analysis ...
Ask the crowd: Robots learn faster, better with online helpers
2014-06-26
University of Washington computer scientists have shown that crowdsourcing can be a quick and effective way to teach a robot how to complete tasks. Instead of learning from just one human, robots could one day query the larger online community, asking for instructions or input on the best way to set the table or water the garden.
The research team presented its results at the 2014 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Hong Kong in early June.
"We're trying to create a method for a robot to seek help ...
New species of small mammal discovered by scientists from California Academy of Sciences
2014-06-26
SAN FRANCISCO (June 26, 2014) – Scientists from the California Academy of Sciences have discovered a new species of round-eared sengi, or elephant-shrew, in the remote deserts of southwestern Africa. This is the third new species of sengi to be discovered in the wild in the past decade. It is also the smallest known member of the 19 sengis in the order Macroscelidea. The team's discovery and description of the Etendeka round-eared sengi (Macroscelides micus) is published this week in the Journal of Mammalogy.
While collecting and examining sengi specimens from southwestern ...
Miriam Hospital researchers develop app focused on making obese adults less sedentary
2014-06-26
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – Even individuals who exercise a lot can be at risk for health problems if they also spend a lot of time in sedentary behaviors, such as sitting. More sedentary time, regardless of physical activity levels, is associated with greater risk for obesity, cardiovascular disease and mortality. However, a smartphone-based intervention developed by researchers at The Miriam Hospital can produce short-term reductions in sedentary behavior that may be effective in improving health. The findings of a study that utilized this app are published in PLOS ONE, a peer-reviewed ...
You can't teach speed: Sprinters break 10-year rule
2014-06-26
ALLENDALE, Mich. — New research shows world-class sprinters are born, not created. Grand Valley State University researchers found that exceptional speed prior to formal training is a prerequisite for becoming a world-class sprinter. The findings are published in the online journal PeerJ, https://peerj.com/articles/445/.
The research, conducted by Michael Lombardo, professor of biology, and Robert Deaner, associate professor of psychology, shows that the developmental histories of elite sprinters contradict the popular deliberate practice model of expertise. According ...
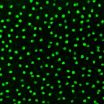
The social psychology of nerve cells
2014-06-26
The functional organization of the central nervous system depends upon a precise architecture and connectivity of distinct types of neurons. Multiple cell types are present within any brain structure, but the rules governing their positioning, and the molecular mechanisms mediating those rules, have been relatively unexplored.
A new study by UC Santa Barbara researchers demonstrates that a particular neuron, the cholinergic amacrine cell, creates a "personal space" in much the same way that people distance themselves from one another in an elevator. In addition, the study, ...
US should re-evaluate definition of skilled workers in immigration policy
2014-06-26
New immigration research from Rice University, the University of North Carolina and the Centre for Population, Poverty and Public Policy Studies suggests the U.S. should re-evaluate its definition of skilled workers to include informal skills of migrant workers.
The study, "Identifying and Measuring the Lifelong Human Capital of 'Unskilled' Migrants in the Mexico-U.S. Migrator Circuit," draws on a binational multistage research project that involved interviews with 320 Mexican migrants and return migrants in North Carolina and Guanajuato, Mexico. The study identifies ...