(Press-News.org) ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — You wouldn't think that mechanical force — the simple kind used to eject unruly patrons from bars, shoe a horse or emboss the raised numerals on credit cards — could process nanoparticles more subtly than the most advanced chemistry.
Yet, in a current paper in Nature Communications, Sandia National Laboratories researcher Hongyou Fan and colleagues appear to have achieved a start toward that end.
Their newly patented and original method uses simple pressure — a kind of high-tech embossing — to produce finer and cleaner results in forming silver nanostructures than do chemical methods, which are not only inflexible in their results but leave harmful byproducts to dispose of.
Fan calls his approach "a simple stress-based fabrication method" that, when applied to nanoparticle arrays, forms new nanostructures with tunable properties.
"There is a great potential market for this technology," he said. "It can be readily and directly integrated into current industrial manufacturing lines without creating new expensive and specialized equipment."
Said Sandia co-author Paul Clem, "This is a foundational method that should enable a variety of devices, including flexible electronics such as antennas, chemical sensors and strain detectors." It also would produce transparent electrodes for solar cells and organic light-emitting diodes, Clem said.
The method was inspired by industrial embossing processes in which a patterned mask is applied with high external pressure to create patterns in the substrate, Fan said. "In our technology, two diamond anvils were used to sandwich nanoparticulate thin films. This external stress manually induced transitions in the film that synthesized new materials," he said.
The pressure, delivered by two diamond plates tightened by four screws to any controlled setting, shepherds silver nanospheres into any desired volume. Propinquity creates conditions that produce nanorods, nanowires and nanosheets at chosen thicknesses and lengths rather than the one-size-fits-all output of a chemical process, with no environmentally harmful residues.
While experiments reported in the paper were performed with silver — the most desirable metal because it is the most conductive, stable and optically interesting and becomes transparent at certain pressures — the method also has been shown to work with gold, platinum and other metallic nanoparticles
Clem said the researchers are now starting to work with semiconductors.
Bill Hammetter, manager of Sandia's Advanced Materials Laboratory, said, "Hongyou has discovered a way to build one structure into another structure — a capability we don't have now at the nanolevel. Eight or nine gigapascal —the amount of pressure at which phase change and new materials occur — are not difficult to reach. Any industry that has embossing equipment could lay a film of silver on a piece of paper, build a conductive pattern, then remove the extraneous material and be left with the pattern. A coating of nanoparticles that can build into another structure has a certain functionality we don't have right now. It's a discovery that hasn't been commercialized, but could be done today with the same equipment used by anyone who makes credit cards."
The method can be used to configure new types of materials. For example, under pressure, the dimensions of ordered three-dimensional nanoparticle arrays shrink. By fabricating a structure in which the sandwiching walls permanently provide that pressure, the nanoparticle array will remain at a constant state, able to transmit light and electricity with specific characteristics. This pressure-regulated fine-tuning of particle separation enables controlled investigation of distance-dependent optical and electrical phenomena.
At even higher pressures, nanoparticles are forced to sinter, or bond, forming new classes of chemically and mechanically stable nanostructures that no longer need restraining surfaces. These cannot be manufactured using current chemical methods.
Depending on the size, composition and phase orientation of the initial nanoparticle arrays, a variety of nanostructures or nanocomposites and 3-D interconnected networks are achievable.
The stress-induced synthesis processes are simple and clean. No thermal processing or further purification is needed to remove reaction byproducts.
INFORMATION:
This work was funded by the Department of Energy's Office of Science. Other authors of the paper are from Cornell University and Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-program laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Lockheed Martin Corp., for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration. With main facilities in Albuquerque, N.M., and Livermore, Calif., Sandia has major R&D responsibilities in national security, energy and environmental technologies and economic competitiveness.
Diamond plates create nanostructures through pressure, not chemistry
Method is more ecological than chemical processes
2014-06-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research may yield new ways to treat antibiotic-resistant TB
2014-06-27
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists in the United States and India have successfully modified the precursor to one of the drugs used to treat tuberculosis, an important first step toward new drugs that can transcend antibiotic resistance issues that experts consider a serious threat to global health.
The findings, reported in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, indicate that a new compound, 24-desmethylrifampicin, has much better antibacterial activity than rifampicin against multi-drug-resistant strains of the bacteria that cause tuberculosis.
Rifampicin and related drugs ...
Youth regularly receive pro-marijuana tweets
2014-06-27
AUDIO:
Twitter has become one of the most popular social media sites among young people, and researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have been looking at Twitter....
Click here for more information.
Hundreds of thousands of American youth are following marijuana-related Twitter accounts and getting pro-pot messages several times each day, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found.
The tweets are cause for ...
A new species of moth from the Appalachian Mountains named to honor the Cherokee Nation
2014-06-27
A small, drab and highly inconspicuous moth has been flitting nameless about its special niche among the middle elevations of one of the world's oldest mountain ranges, the southern Appalachian Mountains in North America. A team of American scientists has now identified this new to science species as Cherokeea attakullakulla and described it in a special issue of the open access journal ZooKeys.
In all probability, it has been frequenting these haunts for tens of millions of years before the first humans set foot on this continent, all the while not caring in the least ...
Kids who know unhealthy food logos more likely to be overweight
2014-06-27
The more a child is familiar with logos and other images from fast-food restaurants, sodas and not-so-healthy snack food brands, the more likely the child is to be overweight or obese.
And, unfortunately, studies have shown that people who are overweight at a young age, tend to stay that way.
A research team that included a Michigan State University professor tested kids on their knowledge of various brands – including their ability to identify items such as golden arches, silly rabbits and a king's crown – and found that those who could identify them the most tended ...
'Compressive sensing' provides new approach to measuring a quantum system
2014-06-27
In quantum physics, momentum and position are an example of conjugate variables. This means they are connected by Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle, which says that both quantities cannot be simultaneously measured precisely. Recently, researchers have been developing novel techniques, such as "weak measurement," to measure both at the same time. Now University of Rochester physicists have shown that a technique called compressive sensing also offers a way to measure both variables at the same time, without violating the Uncertainty Principle.
In a paper published in ...
Developmental psychologist explains her life's work studying the mysteries of the mind
2014-06-27
HAMILTON, ON, June 27, 2014—Developmental psychologist Daphne Maurer has spent more than four decades studying the complexities of the human mind.
As the director of the Visual Development Lab at McMaster University and president of the International Society on Infant Studies, Maurer will present her life's work at the Biennial International Conference on Infant Studies in Berlin July 4th.
Over the course of her career she has established a reputation for building new understanding of one of the most challenging and mysterious aspects of human development: how our ...
Monkeys also believe in winning streaks, study shows
2014-06-27
Humans have a well-documented tendency to see winning and losing streaks in situations that, in fact, are random. But scientists disagree about whether the "hot-hand bias" is a cultural artifact picked up in childhood or a predisposition deeply ingrained in the structure of our cognitive architecture.
Now in the first study in non-human primates of this systematic error in decision making, researchers find that monkeys also share our unfounded belief in winning and losing streaks. The results suggests that the penchant to see patterns that actually don't exist may be ...
EARTH Magazine: Rosetta off to decipher a comet's secrets
2014-06-27
Alexandria, Va. — "Hello World." Upon hearing that brief message, scientists at the European Space Agency (ESA) and followers around the world sent up a collective cheer. Rosetta — the ESA spacecraft currently on a 10-year mission to orbit and land on a comet — awoke in January after a three-year hibernation, and was ready to get to work.
The Rosetta spacecraft launched on March 2, 2004, to study Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. In August, Rosetta will enter the comet's orbit. By November, scientists will plant a lander on the comet, in the hope of learning more about ...
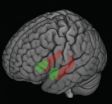
Early life stress can leave lasting impacts on the brain
2014-06-27
MADISON, Wis. — For children, stress can go a long way. A little bit provides a platform for learning, adapting and coping. But a lot of it — chronic, toxic stress like poverty, neglect and physical abuse — can have lasting negative impacts.
A team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers recently showed these kinds of stressors, experienced in early life, might be changing the parts of developing children's brains responsible for learning, memory and the processing of stress and emotion. These changes may be tied to negative impacts on behavior, health, employment ...
Are conservatives more obedient and agreeable than their liberal counterparts?
2014-06-27
Over the last few years, we've seen increasing dissent among liberals and conservatives on important issues such as gun control, health care and same-sex marriage. Both sides often have a difficult time reconciling their own views with their opposition, and many times it appears that liberals are unable to band together under a unifying platform. Why do conservatives appear to have an affinity for obeying leadership? And why do conservatives perceive greater consensus among politically like-minded others? Two studies publishing in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] Diamond plates create nanostructures through pressure, not chemistryMethod is more ecological than chemical processes