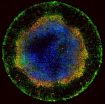
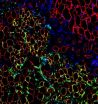
(Press-News.org) A Binghamton University physicist and his colleagues say they have unlocked one key mystery surrounding high-temperature superconductivity. Their research, published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, found a remarkable phenomenon in copper-oxide (cuprate) high-temperature superconductors.
Michael Lawler, assistant professor of physics at Binghamton, is part of an international team of physicists with an ongoing interest in the mysterious pseudogap phase, the phase situated between insulating and superconducting phases in the cuprate phase diagram.
"Evidence has been accumulating that this phase supports an exotic density wave state that may be key to its existence," the physicists write in the new journal article. A density wave forms in a metal if the fluid electrons themselves crystalize.
Using a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) to visualize the electronic structure of the oxygen sites within a superconductor, the team found a density wave with a d-orbital structure. (The electron density near each copper atom looks a bit like a daisy in the crystallized pattern.) That's especially surprising because most density waves have an s-orbital structure; their electron density is isotropic. "It's not the pattern you would expect," Lawler says.
In this research, Lawler and his colleagues focused on a member of the cuprate class of superconductors called bismuth strontium calcium copper oxide (BSCCO). "We now believe these density waves exist in all cuprates," says Lawler, a theorist whose contribution to the research involved subtle uses of the Fourier transform, a mathematical analysis that's useful when examining amplitude patterns in waves.
Superconductors conduct electricity without resistance below a certain temperature. For decades, it was thought that these materials could conduct electricity only at temperatures far below freezing. Since 1987, however, scientists have discovered several compounds that superconduct at much higher temperatures.
Development of this technology could lead to near lossless delivery of electricity to homes and businesses as well as to improvements in cell phone tower receptions and even high-speed trains.
INFORMATION:
Study helps unlock mystery of high-temp superconductors
2014-06-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tropical countries' growing wealth may aid conservation
2014-06-30
DURHAM, N.C. -- While inadequate funding has hampered international efforts to conserve biodiversity in tropical forests, a new Duke University-led study finds that people in a growing number of tropical countries may be willing to shoulder more of the costs on their own.
"In wealthier developing countries, there has been a significant increase in public demand for conservation, which has not yet been matched by an equivalent increase in protective actions by the governments of those countries," said Jeffrey R. Vincent, a Duke environmental economist who led the study, ...
Using geometry, researchers coax human embryonic stem cells to organize themselves
2014-06-30
About seven days after conception, something remarkable occurs in the clump of cells that will eventually become a new human being. They start to specialize. They take on characteristics that begin to hint at their ultimate fate as part of the skin, brain, muscle or any of the roughly 200 cell types that exist in people, and they start to form distinct layers.
Although scientists have studied this process in animals, and have tried to coax human embryonic stem cells into taking shape by flooding them with chemical signals, until now the process has not been successfully ...
Research team pursues techniques to improve elusive stem cell therapy
2014-06-30
Stem cell scientists had what first appeared to be an easy win for regenerative medicine when they discovered mesenchymal stem cells several decades ago. These cells, found in the bone marrow, can give rise to bone, fat, and muscle tissue, and have been used in hundreds of clinical trials for tissue repair. Unfortunately, the results of these trials have been underwhelming. One problem is that these stem cells don't stick around in the body long enough to benefit the patient.
But Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) scientists at Boston Children's Hospital aren't ready ...
Oil palm plantations threaten water quality, Stanford scientists say
2014-06-30
If you've gone grocery shopping lately, you've probably bought palm oil.
Found in thousands of products, from peanut butter and packaged bread to shampoo and shaving cream, palm oil is a booming multibillion-dollar industry. While it isn't always clearly labeled in supermarket staples, the unintended consequences of producing this ubiquitous ingredient have been widely publicized.
The clearing of tropical forests to plant oil palm trees releases massive amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas fueling climate change. Converting diverse forest ecosystems to these ...
New study: Ancient Arctic sharks tolerated brackish water 50 million years ago
2014-06-30
Sharks were a tolerant bunch some 50 million years ago, cruising an Arctic Ocean that contained about the same percentage of freshwater as Louisiana's Lake Ponchatrain does today, says a new study involving the University of Colorado Boulder and the University of Chicago.
The study indicates the Eocene Arctic sand tiger shark, a member of the lamniform group of sharks that includes today's great white, thresher and mako sharks, was thriving in the brackish water of the western Arctic Ocean back then. In contrast, modern sand tiger sharks living today in the Atlantic Ocean ...
First pediatric autism study conducted entirely online
2014-06-30
UC San Francisco researchers have completed the first Internet-based clinical trial for children with autism, establishing it as a viable and cost effective method of conducting high-quality and rapid clinical trials in this population.
In their study, published in the June 2014 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, the researchers looked at whether an Internet-based trial was a feasible way to evaluate whether omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce hyperactivity in children with autism. The authors found that not only was it a valuable ...
Research proves shock wave from explosives causes significant eye damage
2014-06-30
Researchers at The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) are discovering that the current protective eyewear used by our U.S. armed forces might not be adequate to protect soldiers exposed to explosive blasts.
According to a recent study, ocular injuries now account for 13 percent of all battlefield injuries and are the fourth most common military deployment-related injury.
With the support of the U.S. Department of Defense, UTSA biomedical engineering assistant professor Matthew Reilly and distinguished senior lecture in geological sciences Walter Gray have been ...
Earth-Kind roses analyzed for salt tolerance
2014-06-30
COLLEGE STATION, TX – Earth-Kind® roses are favorites with gardeners and landscapers. Chosen for their superior tolerance to heat, drought, and pests, as well as their outstanding performance in landscapes, Earth-Kind® roses can thrive in most environments, even with limited care. A new study focused on determining the best Earth-Kind® varieties for withstanding the challenges of salt stress.
As alternative water sources such as reclaimed water are becoming more commonly used as irrigation for urban landscapes and agricultural crops, plants are being subjected to higher ...
New method to grow zebrafish embryonic stem cells can regenerate whole fish
2014-06-30
New Rochelle, NY, June 30, 2014—Zebrafish, a model organism that plays an important role in biological research and the discovery and development of new drugs and cell-based therapies, can form embryonic stem cells (ESCs). For the first time, researchers report the ability to maintain zebrafish-derived ESCs for more than 2 years without the need to grow them on a feeder cell layer, in a study published in Zebrafish, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Zebrafish website.
Ho Sing Yee and coauthors from the ...
With climate change, heat more than natural disasters will drive people away
2014-06-30
Although scenes of people fleeing from dramatic displays of Mother Nature's power dominate the news, gradual increases in an area's overall temperature — and to a lesser extent precipitation — actually lead more often to permanent population shifts, according to Princeton University research.
The researchers examined 15 years of migration data for more than 7,000 families in Indonesia and found that increases in temperature and, to a lesser extent, rainfall influenced a family's decision to permanently migrate to another of the country's provinces. They report in the ...