The Lancet: Chronic disease prevention one of 21st century's key challenges
2014-07-02
(Press-News.org) According to a report on chronic diseases by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention researchers, published in The Lancet as part of a new Series, The health of Americans [1], half of all adults in the USA suffer from at least one chronic condition, such as diabetes, heart disease, or obesity, and over a quarter of adults have two or more. The majority of these chronic conditions stem from a small number of risk factors that are largely preventable, including tobacco use, poor diet, and physical inactivity (both strongly associated with obesity), alcohol consumption, and uncontrolled high blood pressure. The report indicates Medicare enrollees (the majority of whom are over 65) accounted for US$300 billion in health care spending, over 90% of which was accounted for by people with two or more chronic conditions. Compared with comparable high-income countries, the USA is less healthy in areas such as obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and chronic lung diseases. Reduction of the chronic disease burden in the USA will require coordinated action, including epidemiology and surveillance to monitor trends and track progress, policies and environments that promote health and support healthy behaviours, healthcare that effectively delivers prevention services, and stronger links between health care and community services.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Predicting the outcome of hepatitis C virus treatment
2014-07-02
Millions of people throughout the world are infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV), which can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and cancer. Directly acting antiviral agents inhibit viral proteins and have been used to successfully treat HCV. Unfortunately, antiviral therapy fails in some patients, resulting in a relapse of HCV. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation identifies a marker that can identify patients likely to have an HCV relapse after antiviral therapy. Shyamasundaran Kottilil and colleagues at the NIH evaluated the immune response of HCV-infected ...
Bone marrow transplantation shows potential for treating adults with sickle cell disease
2014-07-01
Use of a lower intensity bone marrow transplantation method showed promising results among 30 patients (16-65 years of age) with severe sickle cell disease, according to a study in the July 2 issue of JAMA.
Myeloablative (use of high-dose chemotherapy or radiation) allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT; receipt of hematopoietic stem cells "bone marrow" from another individual) is curative for children with severe sickle cell disease, but associated toxicity has made the procedure prohibitive for adults. The development of nonmyeloablative conditioning ...
Drug everolimus does not improve overall survival in patients with advanced liver cancer
2014-07-01
Despite strong preclinical data, the drug everolimus failed to improve overall survival in patients with advanced liver cancer, compared to placebo, according to a study in the July 2 issue of JAMA.
Patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC; a type of liver cancer) have a median overall survival of less than l year, largely because of the absence of effective therapies. The drug sorafenib is the only systemic therapy shown to significantly improve overall survival in advanced HCC; however its benefits are mostly transient and modest, and disease eventually ...
Study examines neurological outcomes for TBI treatments
2014-07-01
In patients with a traumatic brain injury (TBI), neither the administration of the hormone erythropoietin (EPO) or maintaining a higher hemoglobin concentration through blood transfusion resulted in improved neurological outcome at 6 months, according to a study in the July 2 issue of JAMA. Transfusing at higher hemoglobin concentrations was associated with a higher risk of adverse events.
Patients with severe traumatic brain injury commonly develop anemia. For patients with neurological injury, anemia is a potential cause of secondary injury, which may worsen neurological ...
Whole-exome sequencing helpful to id gene mutations linked to nervous system diseases
2014-07-01
Use of exome sequencing improved the ability to identify the underlying gene mutations in patients with biochemically defined defects affecting multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes (enzymes that are involved in basic energy production), according to a study in the July 2 issue of JAMA.
Defects of the mitochondrial respiratory chain have emerged as the most common cause of childhood and adult neurometabolic disease, with an estimated prevalence of l in 5,000 live births. Clinically these disorders can present at any time of life, are often seen in association ...
Medicare-backed breast cancer screenings skyrocket, but do patients benefit?
2014-07-01
Breast cancer screening costs for Medicare patients skyrocketed between 2001 and 2009, but the increase did not lead to earlier detection of new breast cancer cases, according to a study published by Yale School of Medicine researchers in the July 1 Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
While the number of screening mammograms performed among Medicare patients remained stable during the same time period, the study focused on the adoption of newer imaging technologies in the Medicare population, such as digital mammography. Brigid Killelea, M.D., assistant professor ...
Adults stop anti-rejection drugs after stem-cell transplant reverses sickle cell disease
2014-07-01
Adults stop anti-rejection drugs after stem-cell transplant reverses sickle cell disease
NIH trial success suggests a new treatment option for older, sicker patients
Half of patients in a trial have safely stopped immunosuppressant medication following a modified blood stem-cell transplant for severe sickle cell disease, according to a study in the July 1 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association. The trial was conducted at the National Institutes of Health's Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, by researchers from NIH's National Institute of Diabetes ...
Seeing your true colors: Standards for hyperspectral imaging
2014-07-01
Today, doctors who really want to see if a wound is healing have to do a biopsy or some other invasive technique that, besides injuring an already injured patient, can really only offer information about a small area. But a technology called hyperspectral imaging offers doctors a noninvasive, painless way to discriminate between healthy and diseased tissue and reveal how well damaged tissue is healing over a wide area. The catch? A lack of calibration standards is impeding its use.
After a successful non-human trial, researchers at the National Institute of Standards ...
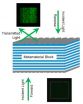
New NIST metamaterial gives light a one-way ticket
2014-07-01
The light-warping structures known as metamaterials have a new trick in their ever-expanding repertoire. Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have built a silver, glass and chromium nanostructure that can all but stop visible light cold in one direction while giving it a pass in the other.* The device could someday play a role in optical information processing and in novel biosensing devices.
In recent years, scientists have designed nanostructured materials that allow microwave or infrared light to propagate in only one direction. ...
Fear, not data, motivates sunscreen users, research shows
2014-07-01
BUFFALO, N.Y. – We're often told that worrying can be harmful to one's health. But University at Buffalo researchers say that when it comes to preventing skin cancer, a little fear is good for you.
In a study published in the Journal of Behavioral Medicine, the UB researchers found that fear and worry about skin cancer had a bigger influence on people's use of sunscreen than information about the statistical likelihood of developing the disease.
"Most health behavior studies don't account for the more visceral, emotional reactions that lead people to do risky behaviors, ...