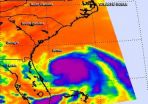
(Press-News.org) When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Arthur on July 2 at 2:50 p.m. EDT on July 2, it saw a cloud-covered eye as the storm was on the way to becoming a hurricane.
This visible image of Tropical Storm Arthur was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. Arthur's center was over the Atlantic Ocean and east of Florida's northeast coast. By 5 a.m. EDT on July 3, Arthur's eye had formed but remained cloud covered even as the storm hit hurricane-strength with maximum sustained winds near 75 mph.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Storm Arthur's cloud tops on July 3 at 2:47 p.m. EDT. The data was made into a false-colored infrared image at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The image showed powerful thunderstorms around Arthur's center with temperatures near -63F/-53C. Cloud tops that cold tower to the near the top of the troposphere and have the ability to produce heavy rainfall.
By 8 a.m. EDT on July 3, watches and warnings peppered the U.S. Southeast. The National Hurricane Center or NHC issued the following: a hurricane warning is in effect for Surf City, North Carolina to the North Carolina/Virginia Border, Pamlico Sound and the Eastern Albemarle Sound. A hurricane watch is in effect for the Little River Inlet to south of Surf City. In addition, a tropical storm warning is in effect for South Santee River, South Carolina to south of Surf City; the North Carolina/Virginia border to Cape Charles Light; and Virginia, including the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay; and the Western Albemarle Sound.
On July 3 at 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) the center of Hurricane Arthur was near latitude 31.8 north and longitude 78.7 west. That puts Arthur's center about 300 miles (480 km) southwest of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, and just 150 miles (240 km) south-southwest of Cape Fear, North Carolina. Maximum sustained winds have increased to near 80 mph (130 kph) and some additional strengthening is forecast during the next 24 hours.
The National Hurricane Center noted that Arthur is moving toward the north-northeast near 9 mph (15 kph and a turn to the northeast is expected. Arthur's center is expected to approach the coast in the hurricane warning area tonight, July 3.
Forecaster Brennan noted in the July 3 discussion on Arthur that after moving very close to the North Carolina Outer Banks late on July 3 and early July 4, the storm should then accelerate northeastward offshore of the mid-Atlantic states and the northeastern U.S. on July 4. By July 5, the NHC expects Arthur to move into the Canadian Maritimes.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees Hurricane Arthur's cloud-covered eye
2014-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cellular defence against fatal associations between proteins and DNA
2014-07-03
This news release is available in German.
DNA - the carrier of genetic information - is constantly threatened by damage originating from exogenous and endogenous sources. Very special DNA lesions are DNA-protein crosslinks - proteins covalently linked to DNA. So far hardly anything was known about repair mechanisms specifically targeting DNA-protein crosslinks. Stefan Jentsch's team at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried, Germany, now discovered a protease that is able to chop down the protein component of DNA-protein crosslinks, thereby enabling ...
'Grass-in-the-ear' technique sets new trend in chimp etiquette
2014-07-03
Chimpanzees are copycats and, in the process, they form new traditions that are often particular to only one specific group of these primates. Such are the findings of an international group of scientists, who waded through over 700 hours of video footage to understand how it came about that one chimpanzee stuck a piece of grass in her ear and started a new trend, and others soon followed suit. The findings of the study, led by Edwin van Leeuwen of the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in The Netherlands, are published in Springer's journal Animal Cognition.
In ...
GW researchers: Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes
2014-07-03
WASHINGTON (July 3, 2014) — For more than 40 years, physicians have treated diminished kidney function as two distinct syndromes: acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, recent epidemiologic and mechanistic studies suggest the two syndromes are not distinct entities, but interconnected. Published today in The New England Journal of Medicine, George Washington University (GW) researchers call for greater follow-up care of patients with AKI, who often present with CKD later in life, and vice versa.
"Our teaching has been wrong and the approach ...
Weighing up the secrets of African elephant body fat
2014-07-03
A research team from The University of Nottingham has carried out the first molecular characterisation of the African elephant's adipose tissue — body fat. This new information will form the basis of future studies aimed at securing the health and future survival of captive elephants.
The population of captive elephants, both Asian and African, in Europe and North America is not self-sustaining, largely due to poor fertility, resulting in a fewer baby elephants being born. It is acknowledged that if a solution for these reproductive difficulties cannot be found quickly, ...
Identifying microbial species
2014-07-03
Millions of microbial species populate the world, but so far only a few have been identified due to the inability of most microbes to grow in the laboratory. Edgar Goluch, an engineer, and Slava Epstein, a biologist, aim to change this. The pair, both researchers at Northeastern University, has developed a device that allows scientists to cultivate a single species of bacteria that can then be studied and identified.
Goluch's previous research devices incorporated permeable membranes that allow sequestered bacteria to be exposed to the nutrients and molecules of their ...
Women veterans want options, follow up support when dealing with intimate partner violence
2014-07-03
(Boston)--Intimate partner violence (IPV) is a significant health issue faced by women veterans, but little has been known up until now about their preferences for IPV-related care. A new study has found that most of these women support routine screening for IPV and want options, follow-up support, transparent documentation and Veterans Health Administration (VHA) and community resources. These findings appear in the journal Research in Nursing and Health.
Although women of all socio-demographic groups are at risk for IPV, population-based research suggests that women ...
Hot Pot with chicken causes campylobacter infections in Switzerland
2014-07-03
This news release is available in German and French. In Switzerland, between 7000 and 8000 persons fall ill with a campylobacter infection annually. This makes it the most frequent bacterial disease transmitted through food. Contamination of chicken meat with campylobacter bacteria during the slaughtering process is one of the known causes of the infection. An increase of campylobacteriosis case numbers is being observed throughout Europe. Human cases of campylobacteriosis must be reported to the relevant authorities in Switzerland.
In Switzerland, an unusual increase ...
Low brain protein levels associated with neurodegeneration
2014-07-03
Persons with reduced levels of the TREM2 protein could be at greater risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease or frontotemporal dementia, according to an international study which included the participation of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona and the Sant Pau Biomedical Research Institute (IIB Sant Pau).
The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, reveals the molecular mechanism by which the mutated forms of this protein prevent the amyloid waste cleaning process from functioning correctly and detects a lower level of ...
Whales as ecosystem engineers
2014-07-03
"Consider the subtleness of the sea; how its most dreaded creatures glide under water, unapparent for the most part," wrote Herman Melville in Moby Dick. Today, we no longer dread whales, but their subtlety remains. "For a long time, whales have been considered too rare to make much of a difference in the oceans," notes University of Vermont conservation biologist Joe Roman. That was a mistake.
In a new paper, Roman and a team of biologists have tallied several decades of research on whales from around the world; it shows that whales, in fact, make a huge difference—they ...
No two lark sparrows are alike (at least when it comes to migration habits)
2014-07-03
A new paper by Dr. Jeremy Ross from the University of Oklahoma describes the use of tiny devices strapped to birds' backs called geolocators, which capture the individual migration routes of lark sparrows in North America. By sensing the light levels, these backpacks can pinpoint the location of a bird anywhere in the world, even if retrieving the data-logger can sometimes pose a major problem.
This study, published in the online journal Animal Migration, mapped for the first time the routes traveled by three lark sparrows after they left their breeding grounds in Ohio. ...