(Press-News.org) Mice exposed to low doses of arsenic in drinking water, similar to what some people might consume, developed lung cancer, researchers at the National Institutes of Health have found.
Arsenic levels in public drinking water cannot exceed 10 parts per billion (ppb), which is the standard set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. However, there are no established standards for private wells, from which millions of people get their drinking water.
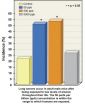
In this study, the concentrations given to the mice in their drinking water were 50 parts per billion (ppb), 500 ppb, and 5,000 ppb. 50 ppb is the lowest concentration that has been tested in an animal study, and researchers say that because of differing rates of metabolism, mice need to be exposed to greater concentrations of arsenic in drinking water than humans to achieve the same biological dose and similar health effects.
The researchers used a model that duplicates how humans are exposed to arsenic throughout their entire lifetime. In the study, the mice were given arsenic three weeks before breeding and throughout pregnancy and lactation. Arsenic was then given to the offspring after weaning, and all through adulthood at concentrations relevant to human exposure. The researchers looked at the tumors in the adult offspring.
"This is the first study to show tumor development in animals exposed to very low levels of arsenic, levels similar to which humans might be exposed," said Michael Waalkes, Ph.D., lead author on the paper and director of the National Toxicology Program (NTP) Laboratory. "The results are unexpected and certainly give cause for concern."
Arsenic is present in the environment as a naturally occurring substance or due to contamination from human activity. Arsenic may be found in many foods, including grains, fruits, and vegetables, where it is present due to absorption from the soil and water. This study focused on inorganic arsenic, which often occurs in excess in the drinking water of millions of people worldwide, and has been previously shown to be a human carcinogen.
In the study, more than half of the male offspring mice developed significant increases in benign and malignant lung tumors at the two lower doses (50 ppb and 500 ppb). Female offspring also developed benign tumors at the lower concentrations. Interestingly, the researchers did not find significant increases in lung tumors in either sex at the highest dose (5,000 ppb).
"Although this is only one study, it adds to a growing body of evidence showing adverse health effects from very low exposures to arsenic, raising the possibility that no level of arsenic appears to be safe," said Linda Birnbaum, Ph.D, director of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) and NTP.
INFORMATION:
The paper from the NTP Laboratory at NIEHS, part of NIH, appears in the Archives of Toxicology.
NIEHS supports research to understand the effects of the environment on human health and is part of NIH. For more information on environmental health topics, visit http://www.niehs.nih.gov. Subscribe to one or more of the NIEHS news lists to stay current on NIEHS news, press releases, grant opportunities, training, events, and publications.
NTP is a federal, interagency program, headquartered at the NIEHS, whose goal is to safeguard the public by identifying substances in the environment that may affect human health. For more information about NTP and its programs, visit http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
Reference: Waalkes MP, Qu W, Tokar EJ, Kissling G, Dixon D. 2014. Lung tumors in mice induced by "whole life" inorganic arsenic exposure at human relevant doses. Arch Toxicol; doi:10.1007/s00204-014-1305-8.
Low doses of arsenic cause cancer in male mice
2014-07-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Recalled yogurt contained highly pathogenic mold
2014-07-08
DURHAM, N.C. -- Samples isolated from Chobani yogurt that was voluntarily recalled in September 2013 have been found to contain the most virulent form of a fungus called Mucor circinelloides, which is associated with infections in immune-compromised people.
The study by Duke University scientists shows that this strain of the fungus can survive in a mouse and be found in its feces as many as 10 days after ingestion.
In August and September 2013, more than 200 consumers of contaminated Chobani Greek Yogurt became ill with vomiting, nausea and diarrhea. The U.S. Food ...
Shining light on the 100-year mystery of birds sensing spring for offspring
2014-07-08
Nagoya, Japan – Professor Takashi Yoshimura and colleagues of the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM) of Nagoya University have finally found the missing piece in how birds sense light by identifying a deep brain photoreceptor in Japanese quails, in which the receptor directly responds to light and controls seasonal breeding activity. Although it has been known for over 100 years that vertebrates apart from mammals detect light deep inside their brains, the true nature of the key photoreceptor has remained to be a mystery up until now. This study led by ...
A healthy lifestyle adds years to life
2014-07-08
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), cancer, diabetes and chronic respiratory disorders - the incidence of these non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is constantly rising in industrialised countries. The Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is, therefore, in the process of developing a national prevention strategy with a view to improving the population's health competence and encouraging healthier behaviour. Attention is focusing, amongst other things, on the main risk factors for these diseases which are linked to personal behaviour – i.e. tobacco smoking, an unhealthy diet, ...
HIV study leads to insights into deadly infection
2014-07-08
Research led by the University of Adelaide has provided new insights into how the HIV virus greatly boosts its chances of spreading infection, and why HIV is so hard to combat.
HIV infects human immune cells by turning the infection-fighting proteins of these cells into a "backdoor key" that lets the virus in. Recent research has found that another protein is involved as well. A peptide in semen that sticks together and forms structures known as "amyloid fibrils" enhances the virus's infection rate by up to an astonishing 10,000 times.
How and why these fibrils enhance ...
AAU launches STEM education initiative website, announces STEM network conference
2014-07-08
The Association of American Universities (AAU), an association of leading public and private research universities, today launched the AAU STEM Initiative Hub, a website that will both support and widen the impact of the association's initiative to improve the quality of
undergraduate teaching and learning in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) fields at its member institutions.
AAU has partnered with HUBzero, a web-based platform for scientific collaboration developed and managed by Purdue University, to create the AAU STEM Initiative Hub. The new ...
Silicon sponge improves lithium-ion battery performance
2014-07-08
RICHLAND, Wash. – The lithium-ion batteries that power our laptops and electric vehicles could store more energy and run longer on a single charge with the help of a sponge-like silicon material.
Researchers developed the porous material to replace the graphite traditionally used in one of the battery's electrodes, as silicon has more than 10 times the energy storage capacity of graphite. A paper describing the material's performance as a lithium-ion battery electrode was published today in Nature Communications.
"Silicon has long been sought as a way to improve the ...
Underage drinkers overexposed to magazine advertising for the brands they consume
2014-07-08
PISCATAWAY, NJ – The brands of alcohol popular with underage drinkers also happen to be the ones heavily advertised in magazines that young people read, a new study finds.
The findings, reported in July's Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, add to evidence that alcohol ads can encourage kids to drink.
They also suggest that the alcohol industry's self-imposed standards on advertising are inadequate, said lead researcher Craig Ross, Ph.D., M.B.A., of the Natick, Mass.,-based Virtual Media Resources.
"All of the ads in our study were in complete compliance with ...
Underage drinkers heavily exposed to magazine ads for alcohol brands they consume
2014-07-08
Underage drinkers between the ages of 18 and 20 see more magazine advertising than any other age group for the alcohol brands they consume most heavily, raising important questions about whether current alcohol self-regulatory codes concerning advertising are sufficiently protecting young people.
This is the conclusion of a new study from the Center on Alcohol Marketing and Youth (CAMY) at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health that examined which age groups saw the most magazine advertising for the 25 alcohol brands most popular among underage boys and ...
Study reveals fungus in yogurt outbreak poses a threat to consumers
2014-07-08
The fungus responsible for an outbreak of contaminated Greek yogurt last year is not harmless after all but a strain with the ability to cause disease, according to research published in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
In September 2013, customers of Chobani brand Greek yogurt complained of gastrointestinal (GI) problems after consuming products manufactured in the company's Idaho plant. The company issued a recall, and it was believed at the time that the fungal contaminant Murcor circinelloides was only a potential danger ...
Sibling composition impacts childhood obesity risk
2014-07-08
Ann Arbor, MI, July 8, 2014 – It is well documented that children with obese parents are at greater risk for obesity. In a new study, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital, Cornell University, and Duke University looked at how different kinds of family associations affect obesity, specifically how sibling relationships affect a child's weight. They not only found a correlation between parents and child, but also discovered a link between having an obese sibling and a child's obesity risk, after adjusting for the parent-child relationship. Their findings are published ...