(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. – For those students looking to bump up their grade point averages during college, the answer may not be spending more time in a library or study hall, but in a gym.
New Michigan State University research shows that students who were members of the recreational sports and fitness centers on MSU's campus during their freshman and sophomore years had higher GPAs than those who weren't.
The research also indicated that students with memberships stayed in school longer. An increase of 3.5 percent in two-year retention rates was seen among this group.
"That could equate to about 1,575 people within a student population of 49,000 deciding to move on to a third year of school," said James Pivarnik, a professor of kinesiology and epidemiology at MSU. "These results provide a compelling argument to universities that a higher student retention rate could be enhanced just by having adequate recreational and fitness facilities for students."
The study, led by Pivarnik and MSU doctoral student Samantha Danbert in the Department of Kinesiology, can be found in the most recent issue of the Recreational Sports Journal.
The research supports previous theories suggesting that by creating an environment that connects students to an institution, in this case a university recreational facility, an increase in academic success and retention can occur.
During the project, Pivarnik's team analyzed data from a sample of freshmen and sophomores, totaling 4,843 students, and compared the GPAs of those who purchased a fitness facility membership and those who did not. Results showed that after four consecutive semesters, the students with memberships obtained higher cumulative GPAs. They also had more credits completed by the end of their first year in college.
"We found that these students' cumulative GPAs were 0.13 points higher," Pivarnik said. "Although this number may not appear to be significant, in the end, that amount could mean the difference to those students on the cusp of getting into graduate school or even advancing to the next academic year."
Pivarnik noted that 74 percent of those with memberships successfully gained their sophomore status while only 60 percent reached that goal in the nonmember group.
"The results of this study are important because not only are we retaining more students, but we're retaining those that have higher GPAs which is good for everyone," Pivarnik said.
INFORMATION:
Other researchers involved in the study included Richard McNeil, MSU's director of recreational sports and fitness services, and Ira Washington, a statistics specialist also at the university.
Michigan State University has been working to advance the common good in uncommon ways for more than 150 years. One of the top research universities in the world, MSU focuses its vast resources on creating solutions to some of the world's most pressing challenges, while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 200 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
Want a higher GPA in college? Join a gym
2014-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Feedback control could be key to robust conservation management
2014-07-10
Mathematical algorithms used to control everyday household items such as washing machines could hold the key to winning the fight for conservation, a new study has claimed.
As part of an EPSRC research project, a team of UK scientists and mathematicians, including those from the University of Exeter, have shown how techniques commonly used in control engineering, could be replicated in the natural world to help restock declining populations.
The innovative new study suggests 'integral control' - in essence a built-in feedback control mechanism to maintain a constant – ...
Wildfires dot central Russia's landscape
2014-07-10
This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on July 10, 2014. Each hot spot, which appears as a red mark, is an area where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire.
This area of Russia is extremely remote with little danger coming directly from the fires, although the smoke released by any type of fire (forest, brush, crop, structure, ...
Ferromagnetism at 230 K found in a new diluted magnetic semiconductor by Chinese physicists
2014-07-10
Diluted magnetic semiconductors (DMS) have received much attention due to their potential application in spintronics, or the storage and transfer of information by using an electron's spin state, its magnetic moment and its charge.
In typical systems based on III-V semiconductors, such as (Ga,Mn)As, (In,Mn)As or (Ga,Mn)N, substitution of divalent Mn atoms into trivalent Ga (or In) sites leads to severely limited chemical solubility, resulting in metastable specimens only available as epitaxial thin films. The hetero-valence substitution, which simultaneously dopes both ...
Scientists discover clues why weight-loss surgery cures diabetes
2014-07-10
Scientists at The University of Manchester are a step closer to understanding why diabetes is cured in the majority of patients that undergo gastric bypass surgery.
The research, published in the journal Endocrinology, shows the cure is likely to be explained by the actions of specialised cells in the intestine that secrete a cocktail of powerful hormones when we eat.
During the research, the team showed that gut hormone cells previously thought to contain just one hormone, had up to six hormones including the hunger hormone ghrelin.
Study team leader, Dr Craig ...
Straits of Mackinac 'worst possible place' for a Great Lakes oil spill
2014-07-10
ANN ARBOR – Because the strong currents in the Straits of Mackinac reverse direction every few days, a rupture of the oil pipeline beneath the channel would quickly contaminate shorelines miles away in both lakes Michigan and Huron, according to a new University of Michigan study commissioned by the National Wildlife Federation.
In one scenario examined in the study and accompanying animations, oil from a hypothetical pipeline break reached Mackinac Island and Round Island after 12 hours and Bois Blanc Island after two days. All three islands are in westernmost Lake Huron, ...
New drug active against most aggressive type of lung cancer cells
2014-07-10
Manchester scientists have shown that a new drug could prove useful in treating small cell lung cancer - the most aggressive form of lung cancer.
Scientists from the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute, based at The University of Manchester and part of the Manchester Cancer Research Centre, teamed up with experts at AstraZeneca, as part of a collaboration agreed in 2010, to test a drug – known as AZD3965 - on small cell lung cancer cells.
The research, published in the journal Clinical Cancer Research, also helps identify which patients are most likely to respond ...
New therapeutic combination to slow resistant sarcomas
2014-07-10
Researchers at sarcomas research group at the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL) and the Catalan Institute of Oncology (ICO) have been tested in 19 patients a new therapeutic combination to combat resistant sarcomas. The clinical trial results, which indicate that the new treatment could stabilize the growth of these tumors have been published this week in the British Journal of Cancer.
Sarcomas
Sarcomas are a rare type of tumor and complex since there are several subtypes. It can affect from children to older ages. It is usually diagnosed in advanced and ...
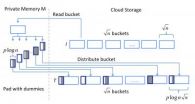
'Melbourne Shuffle' secures data in the cloud
2014-07-10
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To keep data safe in the cloud, a group of computer scientists suggests doing the Melbourne Shuffle.
That may sound like a dance move (and it is), but it's also a computer algorithm developed by researchers at Brown University.
The computing version of the Melbourne Shuffle aims to hide patterns that may emerge as users access data on cloud servers. Patterns of access could provide important information about a dataset — information that users don't necessarily want others to know — even if the data files themselves are encrypted.
"Encrypting ...
The bigger the better: Cigarette warning labels prompt quit attempts
2014-07-10
WASHINGTON - Cigarette warning labels can influence a smoker to try to quit even when the smoker is trying to avoid seeing the labels, according to a survey of thousands of adult smokers in four countries published by the American Psychological Association.
Small, text-only warning labels like those on cigarette packs in the United States prompt people to think about health risks of smoking, and people who notice the warnings regularly are more likely to try to quit, the research found. Larger, more graphic warning labels like those in other countries, such as Australia, ...
Radio-burst discovery deepens astrophysics mystery
2014-07-10
The discovery of a split-second burst of radio waves by scientists using the Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico provides important new evidence of mysterious pulses that appear to come from deep in outer space.
The finding by an international team of astronomers, published July 10 in The Astrophysical Journal, marks the first time that a so-called "fast radio burst" has been detected using an instrument other than the Parkes radio telescope in Australia. Scientists using the Parkes Observatory have recorded a handful of such events, but the lack of any similar findings ...