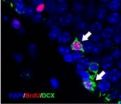
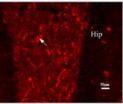
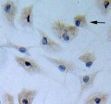
(Press-News.org) There is evidence that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants can promote neuronal cell proliferation and enhance neuroplasticity both in vitro and in vivo. Dr. Javad Verdi and his team, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran proposed that citalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, can increase the efficacy of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) differentiating into neuronal-like cells. Experimental results confirmed that citalopram can improve the neuronal-like cell differentiation of BMSCs by increasing cell proliferation and survival while maintaining their neuronal characteristics. These results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 8, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: "Citalopram increases the differentiation efficacy of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neuronal-like cells" by Javad Verdi1, 2, Seyed Abdolreza Mortazavi-Tabatabaei1, 2, Shiva Sharif 2, 3, Hadi Verdi2, Alireza Shoae-Hassani1, 2 (1 Department of Applied Cell Sciences, School of Advanced Technologies in Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; 2 Department of Stem Cells and Tissue Engineering, Research Center for Science and Technology in Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; 3 Department of Tissue Engineering, School of Advanced Technologies in Medicine, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran)
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Citalopram increases the differentiation efficacy of BMSCs into neuronal-like cells
2014-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ADSCs transplantation promotes neurogenesis in Alzheimer's disease
2014-07-11
Recent evidence has demonstrated that transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells can stimulate neurogenesis in the brain of adult rat or mouse models of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and improve tissue and function injury under the condition of cerebral ischemia. Few studies are reported on the therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) transplantation in mice with AD and on the effect on oxidative injury and neurogenesis in the brain of AD mice. Dr. Yufang Yan and her team, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, China transplanted ADSCs into the hippocampus ...
Substance P in hippocampus versus striatal marginal division for learning/memory function
2014-07-11
In addition to the hippocampus, the marginal division of the striatum is also involved in learning and memory. What is the impact degree of substance P in the striatal marginal division on learning and memory function? Yan Yu and his team, College of Biophotonics, South China Normal University, China found, using immunofluorescence staining, that substance P receptor, neurokinin 1 was highly expressed in the hippocampus and striatal marginal division of normal rats. Unilateral or bilateral injection of an antisense oligonucleotide against neurokinin 1 receptor mRNA in the ...
An obstacle to the differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells into astrocytes
2014-07-11
There is evidence that under the normal circumstances, astrocytes participate in normal physiological activities and development, maintain neuronal environment, and exhibit therapeutic and repairing effects on brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. Previous studies have found that nerve cells differentiated from adipose-derived stromal cells after chemical induction have reduced viability, which produces influences on subsequent studies and application. Prof. Xiaodong Yuan, Kailuan General Hospital, Hebei United University, China demonstrated that after chemical induction, ...
Why anandamide can increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration?
2014-07-11
Evidence exists that cannabinoid receptor type 1 can inhibit voltage-gated calcium channel, decrease intracellular Ca2+ influx, and reduce neurotransmitter release. However, some scholars demonstrated that cannabinoid receptor type 1 can increase extracellular Ca2+ influx and increase neurotransmitter release. Dr. Yi Zhang and his team, Tongji Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China used whole cell voltage-clamp and calcium imaging in cultured trigeminal ganglion neurons and found that anandamide directly caused ...
Exercise is the best medicine: QUT study
2014-07-11
Women would benefit from being prescribed exercise as medicine, according to a QUT study that revealed moderate to high intensity activity is essential to reducing the risk of death in older women.
Professor Debra Anderson, from QUT's Institute of Health and Biomedical Innovation, said that in addition to conventional treatments for physical and mental health, health professionals should be prescribing tailored exercise programs for older women.
Professor Anderson and QUT's Dr Charlotte Seib co-authored a paper published in the international journal of midlife health ...
'Expressive therapy" intervention assists women living with HIV
2014-07-11
New research from UC San Francisco shows that an "expressive therapy" group intervention conducted by The Medea Project helps women living with HIV disclose their health status and improves their social support, self-efficacy and the safety and quality of their relationships.
"Medication alone is totally insufficient," said the study's first author, Edward L. Machtinger, MD, director of the Women's HIV Program at UCSF. "Over 90 percent of our patients are on effective antiretroviral therapy but far too many are dying from suicide, addiction, and violence. Depression, addiction, ...
Growing up on a livestock farm halves the risk of inflammatory bowel diseases
2014-07-11
New research conducted at Aarhus University has revealed that people who have grown up on a farm with livestock are only half as likely as their urban counterparts to develop the most common inflammatory bowel diseases: ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. The study findings have recently been published in the European Journal of Epidemiology.
"It is extremely exciting that we can now see that not only allergic diseases, but also more classic inflammatory diseases appear to depend on the environment we are exposed to early in our lives," relates Vivi Schlünssen, Associate ...
BGI reports a novel gene for salt tolerance found in wild soybean
2014-07-11
Shenzhen, July 10, 2014---A team of researchers from The Chinese University of Hong Kong, BGI and other institutes have identified a gene of wild soybean linked to salt tolerance, with implication for improving this important crop to grow in saline soil. This study published online in Nature Communications provides an effective strategy to unveil novel genomic information for crop improvement.
Soybean is an important crop for the world. Due to domestication and human selection, cultivated soybeans have less genetic diversities than their wild counterparts. Among the lost ...
A new genome editing method brings the possibility of gene therapies closer to reality
2014-07-11
July 3, 2014, Shenzhen, China— Researchers from Salk Institute for Biological Studies, BGI, and other institutes for the first time evaluated the safety and reliability of the existing targeted gene correction technologies, and successfully developed a new method, TALEN-HDAdV, which could significantly increased gene-correction efficiency in human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC). This study published online in Cell Stell Cell provides an important theoretical foundation for stem cell-based gene therapy.
The combination of stem cells and targeted genome editing technology ...
Opening-up the stem cell niche
2014-07-11
For many years scientists have been trying to unravel mechanisms that guide function and differentiation of blood stem cells, those cells that generate all blood cells including our immune system. The study of human blood stem cells is difficult because they can only be found in the bone marrow in specialized "niches" that cannot be recapitulated in a culture dish. Now a group of scientists from Dresden led by stem cell researcher Prof. Claudia Waskow (Technische Universität Dresden) was able to generate a mouse model that supports the transplantation of human blood stem ...