(Press-News.org) NOAA scientists have developed a new high-resolution climate model that shows southwestern Australia's long-term decline in fall and winter rainfall is caused by increases in manmade greenhouse gas emissions and ozone depletion, according to research published today in Nature Geoscience.
"This new high-resolution climate model is able to simulate regional-scale precipitation with considerably improved accuracy compared to previous generation models," said Tom Delworth, a research scientist at NOAA's Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory in Princeton, N.J., who helped develop the new model and is co-author of the paper. "This model is a major step forward in our effort to improve the prediction of regional climate change, particularly involving water resources."
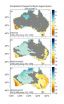
NOAA researchers conducted several climate simulations using this global climate model to study long-term changes in rainfall in various regions across the globe. One of the most striking signals of change emerged over Australia, where a long-term decline in fall and winter rainfall has been observed over parts of southern Australia. Simulating natural and manmade climate drivers, scientists showed that the decline in rainfall is primarily a response to manmade increases in greenhouse gases as well as a thinning of the ozone caused by manmade aerosol emissions. Several natural causes were tested with the model, including volcano eruptions and changes in the sun's radiation. But none of these natural climate drivers reproduced the long-term observed drying, indicating this trend is due to human activity.
Southern Australia's decline in rainfall began around 1970 and has increased over the last four decades. The model projects a continued decline in winter rainfall throughout the rest of the 21st century, with significant implications for regional water resources. The drying is most severe over southwest Australia where the model forecasts a 40 percent decline in average rainfall by the late 21st century.
"Predicting potential future changes in water resources, including drought, are an immense societal challenge," said Delworth. "This new climate model will help us more accurately and quickly provide resource planners with environmental intelligence at the regional level. The study of Australian drought helps to validate this new model, and thus builds confidence in this model for ongoing studies of North American drought."
INFORMATION: END
Australia drying caused by greenhouse gases
New NOAA climate model zeroes in on regional climate trends
2014-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deep within spinach leaves, vibrations enhance efficiency of photosynthesis
2014-07-13
ANN ARBOR – Biophysics researchers at the University of Michigan have used short pulses of light to peer into the mechanics of photosynthesis and illuminate the role that molecule vibrations play in the energy conversion process that powers life on our planet.
The findings could potentially help engineers make more efficient solar cells and energy storage systems. They also inject new evidence into an ongoing "quantum biology" debate over exactly how photosynthesis manages to be so efficient.
Through photosynthesis, plants and some bacteria turn sunlight, water and ...
Researchers discover boron 'buckyball'
2014-07-13
PROVIDENCE, R.I. (Brown University) -- The discovery 30 years ago of soccer-ball-shaped carbon molecules called buckyballs helped to spur an explosion of nanotechnology research. Now, there appears to be a new ball on the pitch.
Researchers from Brown University, Shanxi University and Tsinghua University in China have shown that a cluster of 40 boron atoms forms a hollow molecular cage similar to a carbon buckyball. It's the first experimental evidence that a boron cage structure—previously only a matter of speculation—does indeed exist.
"This is the first time that ...
Study finds cause of mysterious food allergy, suggests new treatment strategy
2014-07-13
New research in Nature Genetics identifies a novel genetic and molecular pathway in the esophagus that causes eosinophillic esophagitis (EoE), opening up potential new therapeutic strategies for an enigmatic and hard-to-treat food allergy.
EoE is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the esophagus. The condition is triggered by allergic hypersensitivity to certain foods and an over-accumulation in the esophagus of white blood cells called eosinophils (part of the body's immune system). EoE can cause a variety of gastrointestinal complaints including reflux-like symptoms, ...
Antibody halts cancer-related wasting condition
2014-07-13
BOSTON – New research raises the prospect of more effective treatments for cachexia, a profound wasting of fat and muscle occurring in about half of all cancer patients, raising their risk of death, according to scientists from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
Many strategies have been tried to reverse the condition, which may cause such frailty that patients can't endure potentially life-saving treatments, but none have had great success.
Scientists reporting in the July 13 advanced online edition of Nature, led by Bruce Spiegelman, PhD, demonstrated that in mice bearing ...
Stanford researchers invent nanotech microchip to diagnose type-1 diabetes
2014-07-13
An inexpensive, portable, microchip-based test for diagnosing type-1 diabetes could improve patient care worldwide and help researchers better understand the disease, according to the device's inventors at the Stanford University School of Medicine.
Described in a paper to be published online July 13 in Nature Medicine, the test employs nanotechnology to detect type-1 diabetes outside hospital settings. The handheld microchips distinguish between the two main forms of diabetes mellitus, which are both characterized by high blood-sugar levels but have different causes ...
Study of noninvasive retinal imaging device presented at Alzheimer's conference
2014-07-13
LOS ANGELES – A noninvasive optical imaging device developed at Cedars-Sinai can provide early detection of changes that later occur in the brain and are a classic sign of Alzheimer's disease, according to preliminary results from investigators conducting a clinical trial in Australia.
The researchers will present their findings July 15 in an oral presentation at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference 2014 in Copenhagen, Denmark. They also were invited by conference organizers to participate in a "breaking news" news conference beginning at 7:30 a.m. Sunday, ...
Smell and eye tests show potential to detect Alzheimer's early
2014-07-13
COPENHAGEN, July 13, 2014 – A decreased ability to identify odors might indicate the development of cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease, while examinations of the eye could indicate the build-up of beta-amyloid, a protein associated with Alzheimer's, in the brain, according to the results of four research trials reported today at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference® 2014 (AAIC® 2014) in Copenhagen.
In two of the studies, the decreased ability to identify odors was significantly associated with loss of brain cell function and progression to Alzheimer's ...
Brain activity in sex addiction mirrors that of drug addiction
2014-07-11
Pornography triggers brain activity in people with compulsive sexual behaviour – known commonly as sex addiction – similar to that triggered by drugs in the brains of drug addicts, according to a University of Cambridge study published in the journal PLOS ONE. However, the researchers caution that this does not necessarily mean that pornography itself is addictive.
Although precise estimates are unknown, previous studies have suggested that as many as one in 25 adults is affected by compulsive sexual behaviour, an obsession with sexual thoughts, feelings or behaviour ...
When good gut bacteria get sick
2014-07-11
Boston, MA – Being sick due to an infection can make us feel lousy. But what must the ecosystem of bacteria, or microbiota, colonizing our guts be going through when hit with infection? A study from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) has utilized unique computational models to show how infection can affect bacteria that naturally live in our intestines. The findings may ultimately help clinicians to better treat and prevent gastrointestinal infection and inflammation through a better understanding of the major alterations that occur when foreign bacteria disrupt the gut ...
'Expressive therapy' intervention assists women living with HIV
2014-07-11
New research from UC San Francisco shows that an "expressive therapy" group intervention conducted by The Medea Project helps women living with HIV disclose their health status and improves their social support, self-efficacy and the safety and quality of their relationships.
"Medication alone is totally insufficient," said the study's first author, Edward L. Machtinger, MD, director of the Women's HIV Program at UCSF. "Over 90 percent of our patients are on effective antiretroviral therapy but far too many are dying from suicide, addiction, and violence. Depression, addiction, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
[Press-News.org] Australia drying caused by greenhouse gasesNew NOAA climate model zeroes in on regional climate trends