(Press-News.org) A telephone-delivered intervention, which included automated symptom monitoring, produced clinically meaningful improvements in chronic musculoskeletal pain compared to usual care, according to a study in the July 16 issue of JAMA.
Pain is the most common symptom reported both in the general population and patients seen in primary care, the leading cause of work disability, and a condition that costs the United States more than $600 billion each year in health care and lost productivity. Musculoskeletal pain accounts for nearly 70 million outpatient visits annually in the United States each year. Telemedicine strategies for pain care have been proposed but not rigorously tested to date, according to background information in the article.
Kurt Kroenke, M.D., of Roudebush VA Medical Center, Indiana University School of Medicine, and the Regenstrief Institute, Indianapolis, and colleagues randomly assigned 250 patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain to an intervention group (n = 124) or to a usual care group whose members received all pain care as usual from their primary care physicians (n = 126). The intervention group received 12 months of telecare management that included automated symptom monitoring with an algorithm-guided approach to optimizing pain medications.
Among the key results of the trial:
Patients in the intervention group were nearly twice as likely to report at least a 30 percent improvement in their pain score by 12 months (51.7 percent vs 27.1 percent);
The intervention was associated with clinically meaningful improvements in pain and a greater rate of improvement (56 percent vs 31 percent);
Patients in the usual care group were almost twice as likely to experience worsening of pain by 6 months compared with those in the intervention group (36 percent vs 19 percent);
Few patients in either group were started on opioids or had escalations in their opioid dose during the study period;
Patients in the intervention group were also more likely to rate as good to excellent the medication prescribed for their pain (73.9 percent vs 50.9 percent) as well as the overall treatment of their pain (76.7 percent vs 51.6 percent).
"The intervention was effective, even though most trial participants reported pain that had been present for many years, that involved multiple sites, and that had been unsuccessfully treated with numerous analgesics," the authors write. "The improvement in pain with minimal opioid initiation or dose escalation is noteworthy, given increasing concerns about the consequences of long-term opioid use."
The researchers add that the results of this trial, along with findings from a previous trial conducted among patients with cancer, show that algorithm-guided optimization of pain medication can be efficiently delivered through a predominantly telephone and Internet-based approach.
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.7689; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
There will also be a digital news release available for this study, including the JAMA Report video, embedded and downloadable video, audio files, text, documents, and related links. This content will be available at 3 p.m. CT Tuesday, July 15 at this link.
Editorial - Advancing Telecare for Pain Treatment in Primary Care
Michael E. Ohl, M.D., M.S.P.H., and Gary E. Rosenthal, M.D., of the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine, Iowa City, comment on this study in an accompanying editorial.
"Historically, implementation of collaborative care innovations—such as collaborative care for depression—has been slow. However, there is reason to believe that telecare for chronic pain can be more rapidly implemented into routine practice. Adoption of collaborative care for depression was hindered by the fee-for-service payment system, which favors procedures and in-person physician visits over team-based and between-visit care. Recent movement toward reimbursement for telehealth and between-visit care may make telecare for pain management more attractive to primary care practices."
"In summary, Kroenke et al describe a promising telecare strategy that may enhance the ability of primary care practices to effectively treat patients with chronic pain. Additional studies are required to determine the generalizability, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness of this strategy and to assess how it may best be incorporated within primary care practices."
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.7690; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
INFORMATION: END
Telecare intervention improves chronic pain
2014-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
History of stroke linked with increased risk of adverse outcomes after non-cardiac surgery
2014-07-15
In an analysis that included more than 480,000 patients who underwent elective noncardiac surgery, a history of stroke was associated with an increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and death, particularly if time elapsed between stroke and surgery was less than 9 months, according to a study in the July 16 issue of JAMA.
Noncardiac surgeries performed in patients with a recent heart attack or stent implantation have been associated with increased risk of perioperative cardiac events, as well as stent thrombosis (blood clot), and bleeding compared with ...
Physicians have higher rate of organ donation registration than general public
2014-07-15
A study that included about 15,000 physicians found that they were more likely to be registered as an organ donor compared to the general public, according to a study in the July 16 issue of JAMA.
A shortage of organs for transplant has prompted many countries to encourage citizens to register ("opt in") to donate their organs and tissues when they die. However, less than 40 percent of the public is registered for organ donation in most countries with a registry. "One common fear is that physicians will not take all measures to save the life of a registered citizen at ...
Common treatment of certain autoimmune disease does not appear effective
2014-07-15
Among patients with the systemic autoimmune disease primary Sjögren syndrome, use of hydroxychloroquine, the most frequently prescribed treatment for the disorder, did not improve symptoms during 24 weeks of treatment compared with placebo, according to a study in the July 16 issue of JAMA.
Primary Sjögren syndrome is characterized by mouth and eye dryness, pain, and fatigue, with systemic manifestations occurring in approximately one-third of patients. Despite the wide use of hydroxychloroquine in clinical practice, evidence regarding its efficacy is limited, according ...
JAMA study: Telecare program optimizing non-opioid chronic pain medication very effective
2014-07-15
INDIANAPOLIS -- Chronic pain in the back, neck and other joints due to arthritis or other musculoskeletal disorders is extremely common but difficult to treat. In a new study published in the July 16 issue of Journal of the American Medical Association, primary-care patients enrolled in a 12-month telecare program optimizing non-opioid medications for chronic pain were twice as likely to see improvement as patients who received usual care for chronic pain.
In addition to experiencing pain improvement, patients in the telecare arm of the pain management study reported ...
Do daughters really cause divorce? Maybe not
2014-07-15
DURHAM, N.C. -- In the U.S., couples with daughters are somewhat more likely to divorce than couples with sons. Many scholars have read those numbers as evidence that daughters cause divorce.
But new research from Duke University suggests something quite different may be at play: Girls may be hardier than boys, even in the womb, and may be better able to survive pregnancies stressed by a troubled marriage.
Previous studies have argued that fathers prefer boys and are more likely to stay in marriages that produce sons. Conversely, the argument runs, men are more likely ...
Gene discovery could lead to better soybean varieties for Northern United States
2014-07-15
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers from Purdue University and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln have discovered a soybean gene whose mutation affects plant stem growth, a finding that could lead to the development of improved soybean cultivars for the northern United States.
Purdue agronomy professor Jianxin Ma (pronounced Jen-SHIN' Ma) and collaborators identified a gene known as Dt2, which causes semideterminacy in soybean plants. Semideterminate soybean plants - mid-size plants that continue vegetative growth even after flowering - can produce as many or more pods ...
Transparency lacking in clinical trials, BU study finds
2014-07-15
A significant percentage of completed drug clinical trials, especially those funded by industry, are not disclosed to the public, years after being completed—a trend that "threatens the validity of the clinical research literature in the U.S.," according to a study led by a Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researcher.
The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, found that close to 30 percent of 400 randomly selected clinical trials completed in 2008 had not resulted, four years later, in either publication in a journal or the posting of results to the ...
Do women talk more than men? It's all about context
2014-07-15
We've all heard the stereotype: Women like to talk. We bounce ideas off each other about everything from career moves to dinner plans. We hash out big decisions through our conversations with one another and work through our emotions with discussion.
At least, that's what "they" say. But is any of it actually true? A new study from Northeastern University professor David Lazer's lab says it isn't that simple.
Lazer, who researches social networks and holds joint appointments in the Department of Political Science and the College of Computer and Information Sciences, ...
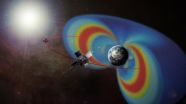
NASA's Van Allen Probes show how to accelerate electrons
2014-07-15
One of the great, unanswered questions for space weather scientists is just what creates two gigantic donuts of radiation surrounding Earth, called the Van Allen radiation belts. Recent data from the Van Allen Probes -- two nearly identical spacecraft that launched in 2012 -- address this question.
The inner Van Allen radiation belt is fairly stable, but the outer one changes shape, size and composition in ways that scientists don't yet perfectly understand. Some of the particles within this belt zoom along at close to light speed, but just what accelerates these particles ...
NOAA's GOES-R satellite Magnetometer ready for spacecraft integration
2014-07-15
The Magnetometer instrument that will fly on NOAA's GOES-R satellite when it is launched in early 2016 has completed the development and testing phase and is ready to be integrated with the spacecraft.
The Magnetometer will monitor magnetic field variations around the Earth and enable forecasters at NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center to better predict the consequences of geomagnetic storms. These storms pose a threat to orbiting spacecraft and human spaceflight. In addition, the measurements taken by the Magnetometer will aid in providing alerts and warnings to power ...