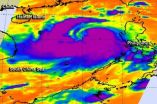
(Press-News.org) Typhoon Rammasun dropped large amounts of rainfall over the Philippines, and the TRMM satellite was used to measure it from space. Rammasun is now making its way toward Hainan Island, China.
NASA and the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency partner on the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite. As TRMM orbits the Earth it has the ability to calculate rainfall occurring in storms and a rainfall analysis using TRMM and other data helps scientists calculate total rainfall.
A preliminary analysis of rainfall during the period when typhoon Rammasun was moving over the Philippines. The analysis is the result of a TRMM-calibrated merged global Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) performed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland These TMPA rainfall total estimates were for the period from July 9-16, 2014. The analysis indicated that rainfall totals of over 325 mm (about 12.8 inches) were located over many parts of the Philippines. The analysis also showed that northern Luzon had received lower amounts of rainfall than the central Philippines.
Typhoon Rammasun known locally as "Glenda" is the most powerful typhoon to hit the Philippines this year. As of today, At least ten deaths have been attributed to Rammasun. Typhoon Rammasun's track was north of Super Typhoon Haiyan's path of destruction through the Philippines in November 2013.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Rammasun on July 16 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard captured infrared data that showed powerful thunderstorms continued to circle the storm's center. Cloud top temperatures around the center of circulation were colder than -63 F/-52C indicating cloud tops were near the top of the troposphere and there was strong uplift in the storm. Cloud top temperatures that high indicate strong storms with the potential for heavy rainfall, according to previous NASA studies.
On July 17 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) Rammasun's maximum sustained winds were near 75 knots (86.3 mph/138.9 kph). It was located near 17.2 north latitude and 114.5 east longitude, about 333 nautical miles (383.2 miles/ 616.7 km) south of Hong Kong, China. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) expects the storm to strengthen slightly over the next day. The China Meteorological Agency (CMA) issued an orange warning for Hainan Island and the mainland. CMA forecasters expect that Rammasun will approach the coastal area of eastern Hainan to western Guangxi and will make landfall on Lingshui of Hainan Island at 0600 UTC (2 a.m. EDT) on the morning of July 18 before heading toward Vietnam. The JTWC expects a second and final landfall near the northeastern border of Vietnam and China on July 19.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Rob Gutro / Hal Pierce
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA's TRMM satellite adds up Typhoon Rammasun's Philippines deluge
2014-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists track gene activity when honey bees do and don't eat honey
2014-07-17
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Many beekeepers feed their honey bees sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup when times are lean inside the hive. This practice has come under scrutiny, however, in response to colony collapse disorder, the massive -- and as yet not fully explained -- annual die-off of honey bees in the U.S. and Europe. Some suspect that inadequate nutrition plays a role in honey bee declines.
In a new study, described in Scientific Reports, researchers took a broad look at changes in gene activity in response to diet in the Western honey bee (Apis mellifera), and found ...
Measuring nurture: Study shows how 'good mothering' hardwires infant brain
2014-07-17
By carefully watching nearly a hundred hours of video showing mother rats protecting, warming, and feeding their young pups, and then matching up what they saw to real-time electrical readings from the pups' brains, researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center have found that the mother's presence and social interactions — her nurturing role — directly molds the early neural activity and growth of her offsprings' brain.
Reporting in the July 21 edition of the journal Current Biology, the NYU Langone team showed that the mother's presence in the nest regulated and controlled ...
Scripps Florida scientists identify gene that plays a surprising role in combating aging
2014-07-17
JUPITER, FL, July 17, 2014 – It is something of an eternal question: Can we slow or even reverse the aging process? Even though genetic manipulations can, in fact, alter some cellular dynamics, little is known about the mechanisms of the aging process in living organisms.
Now scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have found in animal models that a single gene plays a surprising role in aging that can be detected early on in development, a discovery that could point toward the possibility of one day using therapeutics, even some commonly ...
Crohn's disease research
2014-07-17
University of Delaware researchers have identified a protein, hiding in plain sight, that acts like a bodyguard to help protect and stabilize another key protein, that when unstable, is involved in Crohn's disease. The fundamental research points to a possible pathway for developing an effective therapy for the inflammatory bowel disease.
The research, by Catherine Leimkuhler Grimes, assistant professor of chemistry and biochemistry at UD, and Vishnu Mohanan, doctoral student in biological sciences, is published in the July 4 issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry. ...
Carnegie Mellon combines hundreds of videos to reconstruct 3D motion without markers
2014-07-17
PITTSBURGH—Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed techniques for combining the views of 480 video cameras mounted in a two-story geodesic dome to perform large-scale 3D motion reconstruction, including volleyball games, the swirl of air currents and even a cascade of confetti.
Though the research was performed in a specialized, heavily instrumented video laboratory, Yaser Sheikh, an assistant research professor of robotics who led the research team, said the techniques might eventually be applied to large-scale reconstructions of sporting events or performances ...
Incidence of stroke in the elderly has dropped by 40 percent over the last 20 years
2014-07-17
Philadelphia, PA, July 17, 2014 – A new analysis of data from 1988-2008 has revealed a 40% decrease in the incidence of stroke in Medicare patients 65 years of age and older. This decline is greater than anticipated considering this population's risk factors for stroke, and applies to both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. Investigators also found death resulting from stroke declined during the same period. Their findings are published in the July issue of The American Journal of Medicine.
Preventable but deadly, stroke is the fourth leading cause of mortality in the ...
NYU Langone investigators to present new research at 2014 Alzheimer's Association International Conference
2014-07-17
(New York, NY, July 12, 2014) - Researchers from the Center for Cognitive Neurology (CCN) at NYU Langone Medical Center, NYU School of Medicine, and the Nathan S. Kline Research Institute will present new findings at the 2014 Alzheimer's Association International Conference in Copenhagen, Denmark, July 12 – 17, 2014.
The Center for Cognitive Neurology is a multidisciplinary, integrated center devoted to research, clinical care and clinical advances toward the treatment and cure of neurological diseases affecting cognition -- focused on memory, language, attention, auditory, ...
The rate at which groundwater reservoirs are being depleted is increasing
2014-07-17
FRANKFURT.In what parts of the world and to what degree have groundwater reservoirs been depleted over the past 50 years? The Frankfurt hydrologist Prof. Petra Döll has been researching this using the global water model WaterGAP. She has arrived at the most reliable estimate to date by taking into consideration processes which are important in dry regions of the world. The values calculated were compared with monitoring data from many different wells and data from the GRACE satellites. These satellites measure changes in the Earth's gravity field. Döll has come to the conclusion ...
What are the risks of post-traumatic stress disorder after an accident?
2014-07-17
This news release is available in French. Many patients continue to suffer from symptoms (headaches, pain) several months after an accident, which can pose a real handicap to their lives. The team of Emmanuel Lagarde, research director at Inserm's Research Centre for Epidemiology and Biostatistics (Inserm/University of Bordeaux) has studied the subsequent development of 1,300 people who were admitted to A&R between 2007 and 2009 for trauma. The researchers demonstrate that it is possible to identify people who will develop post-traumatic stress disorder, which generally ...
Danish DNA could be key to happiness
2014-07-17
Genetics could be the key to explaining nation's levels of happiness, according to research from the University of Warwick.
Economists at the University's Centre for Competitive Advantage in the Global Economy (CAGE) have looked at why certain countries top the world happiness rankings. In particular they have found the closer a nation is to the genetic makeup of Denmark, the happier that country is. The research could help to solve the puzzle of why a country like Denmark so regularly tops the world happiness rankings.
Dr Eugenio Proto and Professor Andrew Oswald ...