(Press-News.org) FRANKFURT.In what parts of the world and to what degree have groundwater reservoirs been depleted over the past 50 years? The Frankfurt hydrologist Prof. Petra Döll has been researching this using the global water model WaterGAP. She has arrived at the most reliable estimate to date by taking into consideration processes which are important in dry regions of the world. The values calculated were compared with monitoring data from many different wells and data from the GRACE satellites. These satellites measure changes in the Earth's gravity field. Döll has come to the conclusion that the rate at which groundwater reservoirs are being depleted is increasing, but that the rate is not as high as previously estimated.
90 percent of water consumption is due to irrigation for farming purposes. Only the comparatively small remainder is used for potable water and industrial production. As an example, 40 percent of the cereals produced around the world is irrigated. However, in many cases this results in increased scarcity of water resources and puts a burden on ecosystems. In dry regions, the amount taken from groundwater reservoirs can easily exceed the amount being replenished, so that the groundwater reservoir is overused and depleted.
"By comparing the modelled and measured values of groundwater depletion, we were able for the first time to show on a global scale that farmers irrigate more sparingly in regions where groundwater reservoirs are being depleted. They only use about 70 percent of the optimal irrigation amounts", explains Petra Döll from the Institute of Physical Geography at the Goethe University.
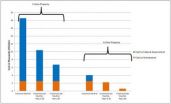
The rate at which the Earth's groundwater reservoirs are being depleted is constantly increasing. Annual groundwater depletion during the first decade of this century was twice as high as it was between 1960 and 2000. India, the USA, Iran, Saudi Arabia and China are the countries with the highest rates of groundwater depletion. About 15 percent of global groundwater consumption is not sustainable, meaning that it comes from non-renewable groundwater resources. On the Arabian Peninsula, in Libya, Egypt, Mali, Mozambique and Mongolia, over 30 percent of groundwater consumption is from non-renewable groundwater.
The new estimate of global groundwater depletion is 113,000 million cubic meters per year for the period from 2000 to 2009, which is lower than previous, widely varying estimates. This can be considered to be the most reliable value to date, since it is based on improved groundwater consumption data which takes the likely deficit irrigation into account, and since the model results correlate well with independent comparative data.
The increased use of groundwater for irrigation also results in a rise in sea levels: According to Döll's calculations, sea level rise due to groundwater depletion was 0.31 millimetres per year during the period from 2000 to 2009. This corresponds to roughly one tenth of the total sea level rise.
INFORMATION:
The work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft through the priority program "Mass transport and Mass distribution in the System Earth".
Publication Döll, P., Müller Schmied, H., Schuh, C., Portmann, F.T., Eicker, A., (2014): Global-scale assessment of groundwater depletion and related groundwater abstractions: Combining hydrological modelling with information from well observations and GRACE satellites. Water Resour. Res. 50, doi: 10.1002/2014WR015595.
Online publication: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/2014WR015595
Information Prof. Petra Döll, Institute of Physical Geography, Riedberg Campus, Phone: (069)798-40219: p.doell@em.uni-frankfurt.de.
The Goethe University is an institution with particularly strong research capabilities based in the European financial metropolis of Frankfurt. It celebrated its 100th year of existence in 2014. The university was founded in 1914 through private means from liberally orientate citizens of Frankfurt and has devoted itself to fulfilling its motto "Science for the Society" in its research and teaching activity right up to the present day. Many of the founding donors were of Jewish origin. During the last 100 years, the pioneering services offered by the Goethe University have impacted the fields of social, societal and economic sciences, chemistry, quantum physics, neurological research and labour law. On January 1st, 2008, it achieved an exceptional degree of independence as it returned to its historical roots as a privately funded university. Today it is one of the ten universities that are most successful in obtaining external research funding and one of the three largest universities in Germany with centres of excellence in medicine, life sciences and humanities.
Publisher: The president of the Goethe University Frankfurt am Main. Editorial department: Dr. Anne Hardy, Public Relations Officer for Scientific Communication. Abteilung Marketing und Kommunikation, Grüneburgplatz 1, 60629 Frankfurt am Main, Phone: (069) 798-12498.
The rate at which groundwater reservoirs are being depleted is increasing
Frankfurt hydrologist publishes more accurate data
2014-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What are the risks of post-traumatic stress disorder after an accident?
2014-07-17
This news release is available in French. Many patients continue to suffer from symptoms (headaches, pain) several months after an accident, which can pose a real handicap to their lives. The team of Emmanuel Lagarde, research director at Inserm's Research Centre for Epidemiology and Biostatistics (Inserm/University of Bordeaux) has studied the subsequent development of 1,300 people who were admitted to A&R between 2007 and 2009 for trauma. The researchers demonstrate that it is possible to identify people who will develop post-traumatic stress disorder, which generally ...
Danish DNA could be key to happiness
2014-07-17
Genetics could be the key to explaining nation's levels of happiness, according to research from the University of Warwick.
Economists at the University's Centre for Competitive Advantage in the Global Economy (CAGE) have looked at why certain countries top the world happiness rankings. In particular they have found the closer a nation is to the genetic makeup of Denmark, the happier that country is. The research could help to solve the puzzle of why a country like Denmark so regularly tops the world happiness rankings.
Dr Eugenio Proto and Professor Andrew Oswald ...
Potential new therapy with brain-on-a-chip axonal strain injury model
2014-07-17
University of Houston researchers have devised a new method for extracting molecules from live cells without disrupting cell development, work that could provide new avenues for the diagnosis of cancer and other diseases.
The researchers used magnetized carbon nanotubes to extract biomolecules from live cells, allowing them to retrieve molecular information without killing the individual cells. A description of the work appears this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Most current methods of identifying intracellular information result ...
Is the US National Flood Insurance Program affordable?
2014-07-17
There is often tension between setting insurance premiums that reflect risk and dealing with equity/affordability issues. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) in the United States recently moved toward elimination of certain premium discounts, but this raised issues with respect to the affordability of coverage for homeowners in flood-prone areas. Ultimately, Congress reversed course and reinstated discounted rates for certain classes of policyholders.
Carolyn Kousky (Resources for the Future, USA) and Howard Kunreuther's (The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania, ...
Plasmon-enhanced Polarization-selective filter
2014-07-17
As we all know, some optical devices can only work with a certain incident polarization direction. In this case, a polarizer is necessary to shift the polarization direction of linearly polarized light. A common polarizer is also called half-wave plate, which constructed out of a birefringent material (such as quartz or mica). The behaviour of a half-wave plate depends on the thickness of the crystal, the wavelength of light. Considering the fabrication of crystal, a half-wave plate is difficulty to integrate on circuits. Then what kind of polarizer can be integrated on ...
Do urban casinos increase local crime? Not in this case study
2014-07-17
Philadelphia's SugarHouse Casino opened its doors in September 2010 after years of protests from community members who feared that the casino would lead to an increase in neighborhood crime. However, a new study by researchers at Drexel University and Temple University reveals that these concerns were unfounded.
The study, which used geolocated crime data to examine changes in crime volume in the immediate neighborhood of the casino since its opening, found that crime rates in the Fishtown neighborhood of Philadelphia were largely unaffected by the introduction of the ...
University of Houston researchers create new method to draw molecules from live cells
2014-07-17
University of Houston researchers have devised a new method for extracting molecules from live cells without disrupting cell development, work that could provide new avenues for the diagnosis of cancer and other diseases.
The researchers used magnetized carbon nanotubes to extract biomolecules from live cells, allowing them to retrieve molecular information without killing the individual cells. A description of the work appears this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Most current methods of identifying intracellular information result ...
Study: Hour-long home coaching decreases re-admission, costs for Medicare patients
2014-07-17
CLEVELAND -- A new study in Journal of General Internal Medicine reports that an hour-long educational coaching session and two or three follow-up phone calls after a hospital stay reduced re-admission odds by 39 percent among Medicare patients. The study also found that the average cost of care was reduced by $3,700 per patient for those patients who received the education session versus those who did not.
This study is the first to report on a more comprehensive picture of healthcare use in the six months following the patient-centered coaching, called Care Transitions ...
Splice-switching oligonucleotide therapeutics is new method for editing gene transcript
2014-07-17
Splice-Switching Oligonucleotide Therapeutics Is Promising New Method for Editing Gene Transcripts
New Rochelle, NY, July 17, 2014—In splice-switching, an innovative therapeutic approach, targeted oligonucleotide drugs alter the editing of a gene transcript to produce the desired form of a protein. Developments in this rapidly advancing field have already led to promising treatments for such diseases as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy, as described in an article in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. ...
Preventing foodborne illness, naturally -- with cinnamon
2014-07-17
PULLMAN, Wash. – Seeking ways to prevent some of the most serious foodborne illnesses caused by pathogenic bacteria, two Washington State University scientists have found promise in an ancient but common cooking spice: cinnamon.
Recent findings published in Food Control journal online suggest Cinnamomum cassia oil can work effectively as a natural antibacterial agent in the food industry. The study results add to a body of knowledge that will help improve food safety and reduce or eliminate cases of food poisoning and related deaths.
In the study, the essential oil ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] The rate at which groundwater reservoirs are being depleted is increasingFrankfurt hydrologist publishes more accurate data