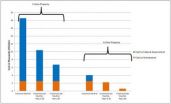
(Press-News.org) There is often tension between setting insurance premiums that reflect risk and dealing with equity/affordability issues. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) in the United States recently moved toward elimination of certain premium discounts, but this raised issues with respect to the affordability of coverage for homeowners in flood-prone areas. Ultimately, Congress reversed course and reinstated discounted rates for certain classes of policyholders.
Carolyn Kousky (Resources for the Future, USA) and Howard Kunreuther's (The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania, USA) paper in the inaugural issue of the Journal of Extreme Events, "Addressing Affordability in the National Flood Insurance Program", examines the tension between risk-based rates and affordability through a case study of Ocean County, New Jersey, an area heavily damaged by Hurricane Sandy. Kousky and Kunreuther argue that the NFIP must address affordability, but that this should not be done through discounted premiums. Instead, the authors propose a means-tested voucher program coupled with a loan program for investments in hazard mitigation. As a condition for a voucher, homeowners would be required to take steps to invest in flood loss reduction measures such as elevating their property. They show that that the cost of a program to homeowners and the federal government would be considerably less than if a voucher were just provided to cover the cost of insurance.
Kousky and Kunreuther conclude that a more detailed, nationwide (United States) analysis is needed to estimate the costs to the federal government of a coupled voucher and mitigation loan program, as well as the expected benefits of reduced flooding losses in the future. This could include an assessment of the amount households could reasonably be expected to pay toward insurance and investing in flood loss reduction measures. Surveys of residents, both in and out of floodplains, regarding their perception of the equity of risk based pricing and insurance vouchers could help inform the public dialogue on the subject.
Financial support for this project was provided by the Center for Risk and Economic Analysis of Terrorism Events (CREATE) at USC, the Center for Research on Environmental Decisions (CRED; NSF Cooperative Agreement SES-0345840 to Columbia University), the Travelers Foundation, National Science Foundation Grant No. SES-1062039/1061882, and the Wharton Risk Management and Decision Processes Center of the University of Pennsylvania.
INFORMATION:
To read more about the research, the paper can be found in the inaugural issue of the Journal of Extreme Events at the following URL, http://www.worldscientific.com/doi/pdf/10.1142/S2345737614500018.
Is the US National Flood Insurance Program affordable?
2014-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Plasmon-enhanced Polarization-selective filter
2014-07-17
As we all know, some optical devices can only work with a certain incident polarization direction. In this case, a polarizer is necessary to shift the polarization direction of linearly polarized light. A common polarizer is also called half-wave plate, which constructed out of a birefringent material (such as quartz or mica). The behaviour of a half-wave plate depends on the thickness of the crystal, the wavelength of light. Considering the fabrication of crystal, a half-wave plate is difficulty to integrate on circuits. Then what kind of polarizer can be integrated on ...
Do urban casinos increase local crime? Not in this case study
2014-07-17
Philadelphia's SugarHouse Casino opened its doors in September 2010 after years of protests from community members who feared that the casino would lead to an increase in neighborhood crime. However, a new study by researchers at Drexel University and Temple University reveals that these concerns were unfounded.
The study, which used geolocated crime data to examine changes in crime volume in the immediate neighborhood of the casino since its opening, found that crime rates in the Fishtown neighborhood of Philadelphia were largely unaffected by the introduction of the ...
University of Houston researchers create new method to draw molecules from live cells
2014-07-17
University of Houston researchers have devised a new method for extracting molecules from live cells without disrupting cell development, work that could provide new avenues for the diagnosis of cancer and other diseases.
The researchers used magnetized carbon nanotubes to extract biomolecules from live cells, allowing them to retrieve molecular information without killing the individual cells. A description of the work appears this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Most current methods of identifying intracellular information result ...
Study: Hour-long home coaching decreases re-admission, costs for Medicare patients
2014-07-17
CLEVELAND -- A new study in Journal of General Internal Medicine reports that an hour-long educational coaching session and two or three follow-up phone calls after a hospital stay reduced re-admission odds by 39 percent among Medicare patients. The study also found that the average cost of care was reduced by $3,700 per patient for those patients who received the education session versus those who did not.
This study is the first to report on a more comprehensive picture of healthcare use in the six months following the patient-centered coaching, called Care Transitions ...
Splice-switching oligonucleotide therapeutics is new method for editing gene transcript
2014-07-17
Splice-Switching Oligonucleotide Therapeutics Is Promising New Method for Editing Gene Transcripts
New Rochelle, NY, July 17, 2014—In splice-switching, an innovative therapeutic approach, targeted oligonucleotide drugs alter the editing of a gene transcript to produce the desired form of a protein. Developments in this rapidly advancing field have already led to promising treatments for such diseases as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy, as described in an article in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. ...
Preventing foodborne illness, naturally -- with cinnamon
2014-07-17
PULLMAN, Wash. – Seeking ways to prevent some of the most serious foodborne illnesses caused by pathogenic bacteria, two Washington State University scientists have found promise in an ancient but common cooking spice: cinnamon.
Recent findings published in Food Control journal online suggest Cinnamomum cassia oil can work effectively as a natural antibacterial agent in the food industry. The study results add to a body of knowledge that will help improve food safety and reduce or eliminate cases of food poisoning and related deaths.
In the study, the essential oil ...
Anti-tank missile detector joins the fight against malaria
2014-07-17
State-of-the-art military hardware could soon fight malaria, one of the most deadly diseases on the planet.
Researchers at Monash University and the University of Melbourne have used an anti-tank Javelin missile detector, more commonly used in warfare to detect the enemy, in a new test to rapidly identify malaria parasites in blood.
Scientists say the novel idea, published in the journal Analysis, could set a new gold standard for malaria testing.
The technique is based on Fourier Transform Infrared (FITR) spectroscopy, which provides information on how molecules ...
Acupuncture and moxibustion reduces neuronal edema in Alzheimer's disease rats
2014-07-17
Aberrant Wnt signaling is possibly related to the pathological changes in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Axin and β-catenin protein is closely related to Wnt signaling. Zhou Hua and his team, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, China confirmed that moxibustion or electroacupuncture, or both, at Baihui (GV20) and Shenshu (BL23) acupoints decreased axin protein expression, increased β-catenin protein expression, and alleviated neuronal cytoplasmic edema. These findings suggest that the mechanism underlying the neuroprotective effect of acupuncture in AD is associated ...
Who are responsible for protecting against neuron and synapse injury in immature rats?
2014-07-17
Fructose-1,6-diphosphate is a metabolic intermediate that promotes cell metabolism. Whether it can alleviate hippocampal neuronal injury caused by febrile convulsion remains unclear. Dr. Jianping Zhou, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Medical College of Xi'an Jiaotong University, China and his team established a repetitive febrile convulsion model in rats aged 21 days, equivalent to 3 years in humans, intraperitoneally administered fructose-1,6-diphosphate at 1,000 mg/kg into the rat model. Results showed that high-dose fructose-1,6-diphosphate reduced mitochondrial ...
Chemokine receptor 4 gene silencing blocks neuroblastoma metastasis in vitro
2014-07-17
Chemokine receptor 4 is a chemokine receptor that participates in tumor occurrence, growth and metastasis in vitro and its expression is upregulated during neuroblastoma metastasis. Dr. Xin Chen, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, China successfully constructed chemokine receptor 4 sequence-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) plasmids, transfected into SH-SY5Y cells and found that down-regulation of chemokine receptor 4 can inhibit in vitro invasion of neuroblastoma. This paper was published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 10, 2014).
Article: ...