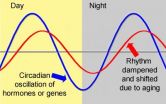
(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers have discovered a possible explanation for the surprisingly large range of biological effects that are linked to a micronutrient called lipoic acid: It appears to reset and synchronize circadian rhythms, or the "biological clock" found in most life forms.
The ability of lipoic acid to help restore a more normal circadian rhythm to aging animals could explain its apparent value in so many important biological functions, ranging from stress resistance to cardiac function, hormonal balance, muscle performance, glucose metabolism and the aging process.
The findings were made by biochemists from the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University, and published in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, a professional journal. The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, through the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
Lipoic acid has been the focus in recent years of increasing research by scientists around the world, who continue to find previously unknown effects of this micronutrient. As an antioxidant and compound essential for aerobic metabolism, it's found at higher levels in organ meats and leafy vegetables such as spinach and broccoli.
"This could be a breakthrough in our understanding of why lipoic acid is so important and how it functions," said Tory Hagen, the Helen P. Rumbel Professor for Healthy Aging Research in the Linus Pauling Institute, and a professor of biochemistry and biophysics in the OSU College of Science.
"Circadian rhythms are day-night cycles that affect the daily ebb and flow of critical biological processes," Hagen said. "The more we improve our understanding of them, the more we find them involved in so many aspects of life."
Almost one-third of all genes are influenced by circadian rhythms, and when out of balance they can play roles in cancer, heart disease, inflammation, hormonal imbalance and many other areas, the OSU researchers said.
Of particular importance is the dysfunction of circadian rhythms with age.
"In old animals, including elderly humans, it's well-known that circadian rhythms break down and certain enzymes don't function as efficiently, or as well as they should," said Dove Keith, a research associate in the Linus Pauling Institute and lead author on this study.
"This is very important, and probably deserves a great deal more study than it is getting," Keith said. "If lipoic acid offers a way to help synchronize and restore circadian rhythms, it could be quite significant."
In this case the scientists studied the "circadian clock" of the liver. Lipid metabolism by the liver is relevant to normal energy use, metabolism, and when dysfunctional can help contribute to the "metabolic syndrome" that puts millions of people at higher risk of heart disease, diabetes and cancer.
Researchers fed laboratory animals higher levels of lipoic acid than might be attained in a normal diet, while monitoring proteins known to be affected by disruption of the circadian clock in older animals.
They found that lipoic acid helped remediate some of the liver dysfunction that's often common in old age, and significantly improved the function of their circadian rhythms.
In previous research, scientists found that the amount of lipoic acid that could aid liver and normal lipid function was the equivalent of about 600 milligrams daily for a 150-pound human, more than could normally be obtained through the diet.
A primary goal of research in the Linus Pauling Institute and the OSU Center for Healthy Aging Research is to promote what scientists call "healthspan" – not just the ability to live a long life, but to have comparatively good health and normal activities during almost all of one's life. Research on lipoic acid, at OSU and elsewhere, suggests it has value toward that goal.
Continued research will explore this process and its role in circadian function, whether it can be sustained, and optimal intake levels that might be needed to improve health.
INFORMATION:
Editor's Notes: A digital graphic of changing circadian rhythms that occur with age is available online: http://bit.ly/1rhDRfY
The study this story is based on is available online: http://bit.ly/1ysKJrU
Lipoic acid helps restore, synchronize the 'biological clock'
2014-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How the brain stabilizes its connections in order to learn better
2014-07-17
Throughout our lives, our brains adapt to what we learn and memorise. The brain is indeed made up of complex networks of neurons and synapses that are constantly re-configured. However, in order for learning to leave a trace, connections must be stabilized. A team at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) discovered a new cellular mechanism involved in the long-term stabilization of neuron connections, in which non-neuronal cells, called astrocytes, play a role unidentified until now. These results, published in Current Biology, will lead to a better understanding of neurodegenerative ...
NASA's Aqua satellite sees birth of Tropical Depression 10W
2014-07-17
The tenth tropical depression of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean was born as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression 10W on July 17, as it came together northwest of the island of Yap. As Aqua passed overhead the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard captured infrared data that showed powerful thunderstorms developed around the storm's center. When AIRS gathered the data on the cloud tops, the temperatures were already as cold as -63F/-52C, indicating strong uplift has pushed them to the top of the troposphere.
At ...
NASA's TRMM satellite adds up Typhoon Rammasun's Philippines deluge
2014-07-17
Typhoon Rammasun dropped large amounts of rainfall over the Philippines, and the TRMM satellite was used to measure it from space. Rammasun is now making its way toward Hainan Island, China.
NASA and the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency partner on the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite. As TRMM orbits the Earth it has the ability to calculate rainfall occurring in storms and a rainfall analysis using TRMM and other data helps scientists calculate total rainfall.
A preliminary analysis of rainfall during the period when typhoon Rammasun was moving ...
Scientists track gene activity when honey bees do and don't eat honey
2014-07-17
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Many beekeepers feed their honey bees sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup when times are lean inside the hive. This practice has come under scrutiny, however, in response to colony collapse disorder, the massive -- and as yet not fully explained -- annual die-off of honey bees in the U.S. and Europe. Some suspect that inadequate nutrition plays a role in honey bee declines.
In a new study, described in Scientific Reports, researchers took a broad look at changes in gene activity in response to diet in the Western honey bee (Apis mellifera), and found ...
Measuring nurture: Study shows how 'good mothering' hardwires infant brain
2014-07-17
By carefully watching nearly a hundred hours of video showing mother rats protecting, warming, and feeding their young pups, and then matching up what they saw to real-time electrical readings from the pups' brains, researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center have found that the mother's presence and social interactions — her nurturing role — directly molds the early neural activity and growth of her offsprings' brain.
Reporting in the July 21 edition of the journal Current Biology, the NYU Langone team showed that the mother's presence in the nest regulated and controlled ...
Scripps Florida scientists identify gene that plays a surprising role in combating aging
2014-07-17
JUPITER, FL, July 17, 2014 – It is something of an eternal question: Can we slow or even reverse the aging process? Even though genetic manipulations can, in fact, alter some cellular dynamics, little is known about the mechanisms of the aging process in living organisms.
Now scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have found in animal models that a single gene plays a surprising role in aging that can be detected early on in development, a discovery that could point toward the possibility of one day using therapeutics, even some commonly ...
Crohn's disease research
2014-07-17
University of Delaware researchers have identified a protein, hiding in plain sight, that acts like a bodyguard to help protect and stabilize another key protein, that when unstable, is involved in Crohn's disease. The fundamental research points to a possible pathway for developing an effective therapy for the inflammatory bowel disease.
The research, by Catherine Leimkuhler Grimes, assistant professor of chemistry and biochemistry at UD, and Vishnu Mohanan, doctoral student in biological sciences, is published in the July 4 issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry. ...
Carnegie Mellon combines hundreds of videos to reconstruct 3D motion without markers
2014-07-17
PITTSBURGH—Carnegie Mellon University researchers have developed techniques for combining the views of 480 video cameras mounted in a two-story geodesic dome to perform large-scale 3D motion reconstruction, including volleyball games, the swirl of air currents and even a cascade of confetti.
Though the research was performed in a specialized, heavily instrumented video laboratory, Yaser Sheikh, an assistant research professor of robotics who led the research team, said the techniques might eventually be applied to large-scale reconstructions of sporting events or performances ...
Incidence of stroke in the elderly has dropped by 40 percent over the last 20 years
2014-07-17
Philadelphia, PA, July 17, 2014 – A new analysis of data from 1988-2008 has revealed a 40% decrease in the incidence of stroke in Medicare patients 65 years of age and older. This decline is greater than anticipated considering this population's risk factors for stroke, and applies to both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. Investigators also found death resulting from stroke declined during the same period. Their findings are published in the July issue of The American Journal of Medicine.
Preventable but deadly, stroke is the fourth leading cause of mortality in the ...
NYU Langone investigators to present new research at 2014 Alzheimer's Association International Conference
2014-07-17
(New York, NY, July 12, 2014) - Researchers from the Center for Cognitive Neurology (CCN) at NYU Langone Medical Center, NYU School of Medicine, and the Nathan S. Kline Research Institute will present new findings at the 2014 Alzheimer's Association International Conference in Copenhagen, Denmark, July 12 – 17, 2014.
The Center for Cognitive Neurology is a multidisciplinary, integrated center devoted to research, clinical care and clinical advances toward the treatment and cure of neurological diseases affecting cognition -- focused on memory, language, attention, auditory, ...