(Press-News.org) (TORONTO, Canada – July 17, 2014) – The journal Cancer Cell today published research led by Dr. Tak Mak mapping the path of discovery to developing a potential anticancer agent.
"What began with the question 'what makes a particular aggressive form of breast cancer cells keep growing?' turned into 10 years of systematic research to identify the enzyme PLK4 as a promising therapeutic target and develop a small molecule inhibitor to block it," says Dr. Mak, Director of The Campbell Family Institute for Breast Cancer Research at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network. He is also Professor, University of Toronto, in the Departments of Medical Biophysics and Immunology. Dr. Mak talks about his research at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vl3J_TtWYZQ.
In the lab, the scientific team used an approach that combined functional RNAi analysis with gene expression analysis in breast cancer-derived cell lines and in human breast cancers replicated in mice. Using these multidimensional datasets for human breast cancer, PLK4 was identified as a candidate target among 10,000 other targets for the development of anticancer therapeutics.
"The research showed that the aggressive form of basal breast cancer cells may be dependent on PLK4 for survival and that depleting it induced cell death," says Dr. Mak. "This finding led to the identification of CFI-400945, a selective and orally active inhibitor of PLK4, which was shown to have significant antitumor activity as a single agent in a variety of preclinical tumor models."
Another key finding was observing the inhibitor effect on tumor models with a gene PTEN deficiency as a biomarker – of huge interest because PTEN, a tumor suppressor, is known to be defective in as many as half of all advanced solid tumor cancers.
"If clinical testing supports our hypothesis that PTEN is a predictive biomarker for CFI-40095, we will have another way to tailor personalized cancer medicine based on an individual's genetics," says Dr. Mak.
Although breast cancer was the initial focus and featured in the study published online today, the team has also conducted experiments with other types of solid tumors, with similar results. The next phase of research will involve testing in humans, which was approved last year by Health Canada and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
"It may take several more years to determine the benefit for patients," says Dr. Mak, "but we are happy to be able to provide this opportunity for our patients. We remain optimistic that we may have found a novel way to treat cancer." Dr. Mak is an internationally acclaimed immunologist renowned for his 1984 cloning of the genes encoding the human T-cell receptor.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by The Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and Genome Canada.
About Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network
The Princess Margaret Cancer Centre has achieved an international reputation as a global leader in the fight against cancer and delivering personalized cancer medicine. The Princess Margaret, one of the top five international cancer research centres, is a member of the University Health Network, which also includes Toronto General Hospital, Toronto Western Hospital and Toronto Rehabilitation Institute. All are research hospitals affiliated with the University of Toronto. For more information, go to http://www.theprincessmargaret.ca, http://www.campbellfamilyinstitute.ca or http://www.uhn.ca .
Media contact: Jane Finlayson
Public Affairs
(416) 946-2846
jane.finlayson@uhn.ca
Tak Mak study in Cancer Cell maps decade of discovery to potential anticancer agent
2014-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gender quotas work in 'tight' cultures, says new paper from the University of Toronto
2014-07-17
Toronto – Quotas probably won't get more women into the boardroom in places like the U.S. and Canada.
They have a better chance however in countries such as China or Germany where people place a higher value on obeying authority and conforming to cultural norms, say a pair of researchers at the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management. Their conclusions are published in the journal Organizational Dynamics and in a blog for the Harvard Business Review.
It all comes down to a culture's "tightness" or "looseness" -- the degree to which a culture maintains social ...
A new view of the world
2014-07-17
New research out of Queen's University has shed light on how exercise and relaxation activities like yoga can positively impact people with social anxiety disorders.
Adam Heenan, a Ph.D. candidate in the Clinical Psychology, has found that exercise and relaxation activities literally change the way people perceive the world, altering their perception so that they view the environment in a less threatening, less negative way. For people with mood and anxiety disorders, this is an important breakthrough.
For his research, Mr. Heenan used point-light displays, a depiction ...
Transplant patients who receive livers from living donors more likely to survive
2014-07-17
(PHILADELPHIA) – Research derived from early national experience of liver transplantation has shown that deceased donor liver transplants offered recipients better survival rates than living donor liver transplants, making them the preferred method of transplantation for most physicians. Now, the first data-driven study in over a decade disputes this notion. Penn Medicine researchers found that living donor transplant outcomes are superior to those found with deceased donors with appropriate donor selection and when surgeries are performed at an experienced center. The ...
GW researcher unlocks next step in creating HIV-1 immunotherapy using fossil virus
2014-07-17
WASHINGTON (July 17, 2014) — The road to finding a cure for HIV-1 is not without obstacles. However, thanks to cutting-edge research by Douglas Nixon, M.D., Ph.D., and colleagues, performed at the George Washington University (GW), Oregon Health & Science University, the University of Rochester, and UC San Francisco, the scientific community is one step closer to finding a viable immunotherapy option for HIV-1, using an immune attack against a fossil virus buried in the genome.
A major hurdle in eradicating HIV-1 has been outsmarting the frequent mutations, or changing ...
Oregon geologist says Curiosity's images show Earth-like soils on Mars
2014-07-17
EUGENE, Ore. -- Soil deep in a crater dating to some 3.7 billion years ago contains evidence that Mars was once much warmer and wetter, says University of Oregon geologist Gregory Retallack, based on images and data captured by the rover Curiosity.
NASA rovers have shown Martian landscapes littered with loose rocks from impacts or layered by catastrophic floods, rather than the smooth contours of soils that soften landscapes on Earth. However, recent images from Curiosity from the impact Gale Crater, Retallack said, reveal Earth-like soil profiles with cracked surfaces ...
Is the universe a bubble? Let's check
2014-07-17
Never mind the big bang; in the beginning was the vacuum. The vacuum simmered with energy (variously called dark energy, vacuum energy, the inflation field, or the Higgs field). Like water in a pot, this high energy began to evaporate – bubbles formed.
Each bubble contained another vacuum, whose energy was lower, but still not nothing. This energy drove the bubbles to expand. Inevitably, some bubbles bumped into each other. It's possible some produced secondary bubbles. Maybe the bubbles were rare and far apart; maybe they were packed close as foam.
But here's the thing: ...
Orthopedic surgery generally safe for patients age 80 and older
2014-07-17
ROSEMONT, Ill.─Over the past decade, a greater number of patients, age 80 and older, are having elective orthopaedic surgery. A new study appearing in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (JBJS) found that these surgeries are generally safe with mortality rates decreasing for total hip (THR) and total knee (TKR) replacement and spinal fusion surgeries, and complication rates decreasing for total knee replacement and spinal fusion in patients with few or no comorbidities (other conditions or diseases).
"Based on the results of this study, I think very elderly patients, ...
Study led by indigenous people uncovers grizzly bear 'highway'
2014-07-17
A novel, First Nations-led research collaboration has revealed a previously undocumented grizzly bear aggregation in coastal British Columbia, one of the most southerly aggregations of salmon-feeding grizzlies in North America. Using non-invasive DNA analysis, the authors describe a grizzly bear "highway," identifying nearly 60 individual bears, many who travelled hundreds of miles from surrounding areas to feed on autumn-spawning salmon in the Koeye River. The research was guided by the customary law and cultural practices of the Heiltsuk First Nation and recently published ...
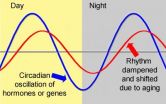
Lipoic acid helps restore, synchronize the 'biological clock'
2014-07-17
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers have discovered a possible explanation for the surprisingly large range of biological effects that are linked to a micronutrient called lipoic acid: It appears to reset and synchronize circadian rhythms, or the "biological clock" found in most life forms.
The ability of lipoic acid to help restore a more normal circadian rhythm to aging animals could explain its apparent value in so many important biological functions, ranging from stress resistance to cardiac function, hormonal balance, muscle performance, glucose metabolism and the aging ...
How the brain stabilizes its connections in order to learn better
2014-07-17
Throughout our lives, our brains adapt to what we learn and memorise. The brain is indeed made up of complex networks of neurons and synapses that are constantly re-configured. However, in order for learning to leave a trace, connections must be stabilized. A team at the University of Geneva (UNIGE) discovered a new cellular mechanism involved in the long-term stabilization of neuron connections, in which non-neuronal cells, called astrocytes, play a role unidentified until now. These results, published in Current Biology, will lead to a better understanding of neurodegenerative ...