(Press-News.org) Recent studies have demonstrated that glutamate receptor δ2 gene (GRID2) is closely related to cerebellar functions in mice. This gene is predominantly located in postsynaptic dendrites of parallel fiber–Purkinje cell synapses in the cerebellum and contains potential fragile sites within large introns. These fragile sites easily develop spontaneous mutation, which leads to Purkinje cell death, contributing to the manifestation of spinocerebellar ataxia in mice. The human GRID2 shares 90% homology with the orthologous mouse gene, and therefore it has become an important candidate gene for screening the virulence gene of spinocerebellar ataxia. Dr. Chaodong Wang, Affiliated Sanming First Hospital of Fujian Medical University, China and his team screened for mutations in the coding sequence of GRID2 in 24 patients with familial or sporadic spinocerebellar ataxia and in 52 normal controls. They detected no point mutations or insertion/deletion mutations in the 16 exons of GRID2. However, a polymorphic 4 nucleotide deletion (IVS5-121_-118 GAGT) and two single nucleotide polymorphisms (c.1251G>T and IVS14-63C>G) were identified. The frequency of these polymorphisms was similar between spinocerebellar ataxia patients and normal controls. These data indicate that spontaneous mutations do not occur in GRID2 and that the incidence of spinocerebellar ataxia in humans is not associated with GRID2 mutation or polymorphisms. Related results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 10, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: " The human δ2 glutamate receptor gene is not mutated in patients with spinocerebellar ataxia," by Jinxiang Huang1, Aiyu Lin2, Haiyan Dong3, Chaodong Wang3 (1 Department of Neurosurgery, Changzheng Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China; 2 Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian Province, China; 3 Department of Neurology, The Affiliated Sanming First Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Sanming, Fujian Province, China)
Huang JX, Lin AY, Dong HY, Wang CD. The human δ2 glutamate receptor gene is not mutated in patients with spinocerebellar ataxia. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(10):1068-1074.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
The human δ2 glutamate receptor gene is not mutated in spinocerebellar ataxia patients
2014-07-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
PIWI proteins and piRNAs regulate genes in the germline and beyond
2014-07-18
Non-coding RNAs represent one of the most exciting aspects of current biomedical research. Non-coding RNAs include long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) which are generally longer than 200 nucleotides (nt) and small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) that are mostly 20-35 nt. Among sncRNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are commonly 21 nt in length, and both specifically bind to the AGO subfamily of the ARGONAUTE (AGO)/PIWI family proteins. PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), which are defined by their specific binding to the PIWI subfamily of AGO/PIWI family proteins, ...
'Support' cells in brain play important role in Down syndrome
2014-07-18
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) – Researchers from UC Davis School of Medicine and Shriners Hospitals for Children – Northern California have identified a group of cells in the brain that they say plays an important role in the abnormal neuron development in Down syndrome. After developing a new model for studying the syndrome using patient-derived stem cells, the scientists also found that applying an inexpensive antibiotic to the cells appears to correct many abnormalities in the interaction between the cells and developing neurons.
The findings, which focused on support cells ...
Four new species of tuco-tucos identified from Bolivia
2014-07-18
Lincoln, Neb., July 18, 2014 -- A research team led by Scott Gardner of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln has identified four new species of Ctenomys, a genus of gopher-like mammal found throughout much of South America.
Commonly called tuco-tucos, the burrowing rodents range from 7 to 12 inches long and weigh less than a pound. They demonstrate the broad range of biological diversity in the lowlands and central valleys of Bolivia, where all four new species were found, Gardner said.
It is very rare to identify a new species of mammal, said Gardner, director of the H.W. ...
New material puts a twist in light
2014-07-18
Scientists at The Australian National University (ANU) have uncovered the secret to twisting light at will. It is the latest step in the development of photonics, the faster, more compact and less carbon-hungry successor to electronics.
A random find in the washing basket led the team to create the latest in a new breed of materials known as metamaterials. These artificial materials show extraordinary properties quite unlike natural materials.
"Our material can put a twist into light – that is, rotate its polarisation – orders of magnitude more strongly than natural materials," ...
In alcohol abusers, fish oil may reduce risk of neurodegeneration and ensuing dementia
2014-07-18
MAYWOOD, Ill-- Omega-3 fish oil might help protect against alcohol-related neurodamage and the risk of eventual dementia, according to a study published in the journal PLOS ONE.
Many human studies have shown that long-term alcohol abuse causes brain damage and increases the risk of dementia. The new study found that in brain cells exposed to high levels of alcohol, a fish oil compound protected against inflammation and neuronal cell death.
The study was conducted by Michael A. Collins, PhD, Edward J. Neafsey, PhD, and colleagues at Loyola University Chicago Stritch ...
Weight management program also reduces depression among black women
2014-07-18
DURHAM, N.C. -- An intervention program aimed at helping obese women maintain their weight without adding pounds also significantly reduced depression in nearly half the participants, according to a new study from Duke University.
The study was conducted with 185 low-income black women ages 25-44, each with a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to 35, who were receiving primary care at five community health centers in central North Carolina.
The program used software built by Duke researchers that personalized a weight-gain prevention intervention called the Shape Program for ...
Catastrophic debris avalanches -- a second volcanic hazard
2014-07-18
Boulder, Colo., USA – Volcanic hazards aren't limited to eruptions. Debris avalanche landslides can also cause a great deal of damage and loss of life. Stratovolcanoes, with their steep, conical shapes made up of lava and unconsolidated mixed materials, can reach a critical point of instability when they overgrow their flanks. This leads to partial collapse, and the product of this slope failure is a large-scale, rapid mass movement known as a catastrophic landslide or debris avalanche.
In a matter of minutes, a debris avalanche can drastically modify the shape and nature ...
Bowel cancer breakthrough may benefit thousands of patients
2014-07-18
Researchers at Queen's University have made a significant breakthrough that may benefit patients with bowel cancer.
Dr Sandra van Schaeybroeck and her team have discovered how two genes cause bowel cancer cells to become resistant to treatments used against the disease. The research, which was funded by Cancer Research UK, was published this month in the prestigious international journal Cell Reports.
The activity of the two genes, called MEK and MET, was uncovered when the researchers looked at all the different pathways and interactions taking place in bowel cancer ...
Scientists enlist big data to guide conservation efforts
2014-07-18
Despite a deluge of new information about the diversity and distribution of plants and animals around the globe, "big data" has yet to make a mark on conservation efforts to preserve the planet's biodiversity. But that may soon change.
A new model developed by University of California, Berkeley, biologist Brent Mishler and his colleagues in Australia leverages this growing mass of data – much of it from newly digitized museum collections – to help pinpoint the best areas to set aside as preserves and to help biologists understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. ...
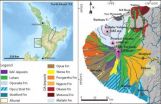
A new measure of biodiversity
2014-07-18
A new approach to measuring biodiversity has uncovered some biologically important but currently unprotected areas in Western Australia, while confirming the significance of the world heritage listed Wet Tropics rainforests in the country's north-east.
In a paper published yesterday (Friday 18 July) in Nature Communications, scientists from CSIRO, University of California, University of Canberra, the Australian Tropical Herbarium at James Cook University and University of New South Wales applied the new method to Australia's iconic Acacia.
The genus Acacia includes ...