(Press-News.org) Nerve growth factor can be delivered to the brain by intranasal administration without risk for treatment of brain diseases. Dr. Luigi Aloe, Cellular Biology and Neurobiology Institute, National Research Council, Italy and his team performed a study to investigate whether, by intranasal administration, the nerve growth factor bypasses the blood-brain barrier and turns over the spinal cord neurons. Results showed that at 3 weeks after intranasal administration of nerve growth factor, the contents of nerve growth factor and its receptor in the spinal cord were increased, and the deficits in locomotor behaviors were improved. These findings indicate that intranasal nerve growth factor can bypass blood-brain barrier and affect spinal cord neurons in spinal cord injury. These results provide experimental evidence for intranasal nerve growth factor for repair of spinal cord injury. Related results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 10, 2014).
INFORMATION:
Article: "Intranasal nerve growth factor bypasses the blood-brain barrier and affects spinal cord neurons in spinal cord injury" by Luigi Aloe1, Patrizia Bianchi1, Alberto De Bellis2, Marzia Soligo3, Maria Luisa Rocco1 (1 Cellular Biology and Neurobiology Institute, National Research Council (CNR), Rome, Italy; 2 Maria Rosaria Maglione Foundation Onlus, Napoli, Italy; 3 Intitute of Translational Pharmacology, National Research Council (CNR), Rome, Italy)
Aloe L, Bianchi P, De Bellis A, Soligo M, Rocco ML. Intranasal nerve growth factor bypasses the blood-brain barrier and affects spinal cord neurons in spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(10):1025-1030.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Intranasal nerve growth factor repairs injured spinal cord neurons
2014-07-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How does L-carnitine maintain the normal structure of sciatic nerve in crush injury?
2014-07-18
Several studies have demonstrated that L-carnitine exhibits neuroprotective effects on injured sciatic nerve of rats with diabetes mellitus. Dr. Ümmü Zeynep Avsar, Faculty of Medicine, Ataturk University, Turkey and his team proposed a hypothesis that L-carnitine exhibits neuroprotective effects on injured sciatic nerve of rats. Rat sciatic nerve was crush injured by a forceps and exhibited degenerative changes. After intragastric administration of 50 and 100 mg/kg L-carnitine for 30 days, axon area, myelin sheath area, axon diameter, myelin sheath diameter, and numerical ...
Novel mechanism for invasion of EV71 virus demonstrated
2014-07-18
A new study determines glycosylation and pH-dependent conformational changes of virus receptor SCARB2 as crucial for EV71 attachment, entry and uncoating
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is the major causative agent of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in the Asia-Pacific region, having caused 8.8 million infections and 3,000 deaths in China in the past five years. Unlike other enteroviruses (e.g. Coxsackievirus), EV71 can cause severe aseptic meningitis, encephalitis, myocarditis and acute flaccid paralysis, thus leading to significant fatality rates. Unfortunately, the molecular ...
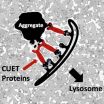
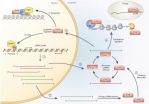
A new cellular garbage control pathway with relevance for human neurodegenerative diseases
2014-07-18
This news release is available in German.
Proteins, the components of our body that execute, control and organize basically all functions in our cells, are made out of strings of amino acids, which – like an origami - are folded into specific and complex three-dimensional structures according to their desired functions. However, since folding and maintaining of such structures is highly sensitive to cellular or environmental stress, proteins can potentially misfold or form clumps (aggregates). Such undesired protein waste can be toxic for cells and may even lead ...
New inexpensive and easy computer software provides real-time and highly accurate data on traffic
2014-07-18
Researchers at the University of Granada have designed new software that provides real time data on traffic. It is a device that provides information on traffic flow between cities. Drivers can use this information to choose the fastest route as they plan to drive to their destinations.
It is a highly reliable, low-cost method, easy and quick to install, which uses bluetooth devices. These devices collect real-time data on road traffic which it then sends to a central server. This information is then processed using complex data mining algorithms, evolutionary computing ...
Consuming probiotics for a month helps diminish fat accumulation in the liver, new study says
2014-07-18
Spanish scientists have demonstrated through an experiment on obese rats that the consumption of probiotics during thirty days helps diminish the accumulation of fat in the liver. This new finding, published today by the journal PLOS ONE, is a great step forward on the fight agains the Non-Alcolohic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), which is closely related to obesity and diabetes.
Researchers from the 'Nutrition Biochemistry: Theurapetic Applications' group (CTS-461) and the José Mataix Institute for Nutrition and Food Technology at the University of Granada have demonstrated ...
No evidence that California cellphone ban decreased accidents, says Colorado University Boulder researcher
2014-07-18
In a recent study, a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder found no evidence that a California ban on using hand-held cellphones while driving decreased the number of traffic accidents in the state in the first six months following the ban.
The findings, published in the journal Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, are surprising given prior research that suggests driving while using a cellphone is risky. For example, past laboratory studies have shown that people who talk on a cellphone while using driving simulators are as impaired as people ...
The differentially expressed genes in DRG that influence neural regeneration after SNI
2014-07-18
Slit-Robo GTPase-activating protein 3 contains a Rho GAP domain that regulates the activities of Rho family GTPases and affects actin polymerization, which influences dendrite elaboration, neurite outgrowth and axon guidance, contributing to neural regeneration. Anjie Lu, the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, China and his team performed a microRNA microarray analysis and identified 23 microRNAs whose expression were significantly changed in rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) after sciatic nerve injury (SNI). Bioinformatic analysis was used to determine microRNA-214 ...
The human δ2 glutamate receptor gene is not mutated in spinocerebellar ataxia patients
2014-07-18
Recent studies have demonstrated that glutamate receptor δ2 gene (GRID2) is closely related to cerebellar functions in mice. This gene is predominantly located in postsynaptic dendrites of parallel fiber–Purkinje cell synapses in the cerebellum and contains potential fragile sites within large introns. These fragile sites easily develop spontaneous mutation, which leads to Purkinje cell death, contributing to the manifestation of spinocerebellar ataxia in mice. The human GRID2 shares 90% homology with the orthologous mouse gene, and therefore it has become an important ...
PIWI proteins and piRNAs regulate genes in the germline and beyond
2014-07-18
Non-coding RNAs represent one of the most exciting aspects of current biomedical research. Non-coding RNAs include long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) which are generally longer than 200 nucleotides (nt) and small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) that are mostly 20-35 nt. Among sncRNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are commonly 21 nt in length, and both specifically bind to the AGO subfamily of the ARGONAUTE (AGO)/PIWI family proteins. PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), which are defined by their specific binding to the PIWI subfamily of AGO/PIWI family proteins, ...
'Support' cells in brain play important role in Down syndrome
2014-07-18
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) – Researchers from UC Davis School of Medicine and Shriners Hospitals for Children – Northern California have identified a group of cells in the brain that they say plays an important role in the abnormal neuron development in Down syndrome. After developing a new model for studying the syndrome using patient-derived stem cells, the scientists also found that applying an inexpensive antibiotic to the cells appears to correct many abnormalities in the interaction between the cells and developing neurons.
The findings, which focused on support cells ...