(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH—Using new statistical tools, Carnegie Mellon University's Kathryn Roeder has led an international team of researchers to discover that most of the genetic risk for autism comes from versions of genes that are common in the population rather than from rare variants or spontaneous glitches.
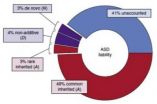
Published in the July 20 issue of the journal "Nature Genetics," the study found that about 52 percent of autism was traced to common genes and rarely inherited variations, with spontaneous mutations contributing a modest 2.6 percent of the total risk. The research team — from the Population-Based-Autism Genetics and Environment Study (PAGES) Consortium — used data from Sweden's universal health registry to compare roughly 3,000 subjects, including autistic individuals and a control group. The largest study of its kind to date, the team also showed that inheritability outweighs environmental risk.
"From this study, we can see that genetics plays a major role in the development of autism compared to environmental risk factors, making autism more like height than we thought — many small risk factors add up, each pushing a person further out on the spectrum," said Roeder, professor of statistics and computational biology at Carnegie Mellon and a leading expert on statistical genomics and the genetic basis of complex disease. "These findings could not have happened without statistics, and now we must build off of what we learned and use statistical approaches to determine where to put future resources, and decide what is the most beneficial direction to pursue to further pinpoint what causes autism."
Although autism is thought to be caused by an interplay of genetic and other factors, including environmental forces, consensus on their relative contributions and the outlines of its genetic architecture has remained elusive, until now. With this new study, the researchers believe that autism genetics is beginning to catch up.
Led by Roeder, the researchers used new statistical methods — such as machine learning techniques and dimension reduction tools — that allowed them to more reliably sort out the inheritability of the disorder. In addition, they were able to compare their results with a parallel family-based study in the Swedish population, which took into account data from twins, cousins, and factors like age of the father at birth and parents' psychiatric history. A best-fit statistical model took form, based mostly on additive genetic and non-shared environmental effects.
"Thanks to the boost in statistical power that comes with ample sample size, autism geneticists can now see the forest for the trees," said Thomas R. Insel, director of the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). "Knowing the nature of the genetic risk will help focus the search for clues to the molecular roots of the disorder."
Thomas Lehner, chief of the NIMH's Genomics Research Branch, agreed and added, "This is a different kind of analysis than employed in previous studies. Data from genome-wide association studies was used to identify a genetic model instead of focusing just on pinpointing genetic risk factors. The researchers were able to pick from all of the cases of illness within a population-based registry."
Now that the genetic architecture is better understood, the researchers are identifying specific genetic risk factors detected in the sample, such as deletions and duplications of genetic material and spontaneous mutations. The researchers said even though such rare spontaneous mutations accounted for only a small fraction of autism risk, the potentially large effects of these glitches make them important clues to understanding the molecular underpinnings of the disorder.
"Within a given family, the mutations could be a critical determinant that leads to the manifestation of ASD in a particular family member," said Joseph Buxbaum, the study's first author and professor of psychiatry, neuroscience, genetics and genomic sciences at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (ISMMS). "The family may have common variation that puts it at risk, but if there is also a 'de novo' mutation on top of that, it could push an individual over the edge. So for many families, the interplay between common and spontaneous genetic factors could be the underlying genetic architecture of the disorder."
Current studies have not been large enough to reveal the many common genetic variants that increase the risk of autism. On their own, none of these common variants will have sufficient impact to cause autism.
"Our group in Pittsburgh is working to develop a model that predicts the genetic risk for a family based on a myriad of small effects. Such a score could provide clinical benefit to families," Roeder said.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Roeder and Buxbaum, other lead investigators on the study included Christina Hultman of the Karolinska Institute; Bernie Devlin of the University of Pittsburgh; and Avraham Reichenberg of the ISMMS.
This study was supported by NIMH Grants MH057881 and MH097849, and also in part through the computational resources and staff expertise provided by the Scientific Computing Facility at the ISMMS.
For more information, visit http://www.stat.cmu.edu/people/faculty/roeder.
Genetic risk for autism stems mostly from common genes
Using new statistical tools, Carnegie Mellon's Kathryn Roeder also finds inheritability trumps spontaneous glitches and environmental risks
2014-07-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A noble gas cage
2014-07-20
Richland, Wash. -- When nuclear fuel gets recycled, the process releases radioactive krypton and xenon gases. Naturally occurring uranium in rock contaminates basements with the related gas radon. A new porous material called CC3 effectively traps these gases, and research appearing July 20 in Nature Materials shows how: by breathing enough to let the gases in but not out.
The CC3 material could be helpful in removing unwanted or hazardous radioactive elements from nuclear fuel or air in buildings and also in recycling useful elements from the nuclear fuel cycle. CC3 ...
New method for extracting radioactive elements from air and water
2014-07-20
LIVERPOOL, UK – 20 July 2014: Scientists at the University of Liverpool have successfully tested a material that can extract atoms of rare or dangerous elements such as radon from the air.
Gases such as radon, xenon and krypton all occur naturally in the air but in minute quantities – typically less than one part per million. As a result they are expensive to extract for use in industries such as lighting or medicine and, in the case of radon, the gas can accumulate in buildings. In the US alone, radon accounts for around 21,000 lung cancer deaths a year.
Previous ...
Singapore scientists discover genetic cause of common breast tumours in women
2014-07-20
Singapore, 21 July 2014 – A multi-disciplinary team of scientists from the National Cancer Centre Singapore, Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School Singapore, and Singapore General Hospital have made a seminal breakthrough in understanding the molecular basis of fibroadenoma, one of the most common breast tumours diagnosed in women. The team, led by Professors Teh Bin Tean, Patrick Tan, Tan Puay Hoon and Steve Rozen, used advanced DNA sequencing technologies to identify a critical gene called MED12 that was repeatedly disrupted in nearly 60% of fibroadenoma cases. Their findings ...
New technique maps life's effects on our DNA
2014-07-20
Researchers at the BBSRC-funded Babraham Institute, in collaboration with the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Single Cell Genomics Centre, have developed a powerful new single-cell technique to help investigate how the environment affects our development and the traits we inherit from our parents. The technique can be used to map all of the 'epigenetic marks' on the DNA within a single cell. This single-cell approach will boost understanding of embryonic development, could enhance clinical applications like cancer therapy and fertility treatments, and has the potential ...
CU, Old Dominion team finds sea level rise in western tropical Pacific anthropogenic
2014-07-20
A new study led by Old Dominion University and the University of Colorado Boulder indicates sea levels likely will continue to rise in the tropical Pacific Ocean off the coasts of the Philippines and northeastern Australia as humans continue to alter the climate.
The study authors combined past sea level data gathered from both satellite altimeters and traditional tide gauges as part of the study. The goal was to find out how much a naturally occurring climate phenomenon called the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, or PDO, influences sea rise patterns in the Pacific, said ...
Common gene variants account for most of the genetic risk for autism
2014-07-20
Nearly 60 percent of the risk of developing autism is genetic and most of that risk is caused by inherited variant genes that are common in the population and present in individuals without the disorder, according to a study led by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and published in the July 20 edition of Nature Genetics.
"We show very clearly that inherited common variants comprise the bulk of the risk that sets up susceptibility to autism," says Joseph D. Buxbaum, PhD, the study's lead investigator and Director of the Seaver Autism Center for ...
Tiny laser sensor heightens bomb detection sensitivity
2014-07-20
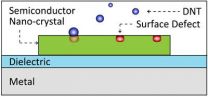
Berkeley — New technology under development at the University of California, Berkeley, could soon give bomb-sniffing dogs some serious competition.
A team of researchers led by Xiang Zhang, UC Berkeley professor of mechanical engineering, has found a way to dramatically increase the sensitivity of a light-based plasmon sensor to detect incredibly minute concentrations of explosives. They noted that it could potentially be used to sniff out a hard-to-detect explosive popular among terrorists.
Their findings are to be published Sunday, July 20, in the advanced online ...
Size and age of plants impact their productivity more than climate, study shows
2014-07-20
The size and age of plants has more of an impact on their productivity than temperature and precipitation, according to a landmark study by University of Arizona researchers.
UA professor Brian Enquist and postdoctoral researcher Sean Michaletz, along with collaborators Dongliang Cheng from Fujian Normal University in China and Drew Kerkhoff from Kenyon College in Gambier, Ohio, have combined a new mathematical theory with data from more than 1,000 forests across the world to show that climate has a relatively minor direct effect on net primary productivity, or the amount ...
Mixing it up: Study provides new insight into Southern Ocean behaviour
2014-07-20
A new study has found that turbulent mixing in the deep waters of the Southern Ocean, which has a profound effect on global ocean circulation and climate, varies with the strength of surface eddies – the ocean equivalent of storms in the atmosphere – and possibly also wind speeds.
It is the first study to link eddies at the surface to deep mixing on timescales of months to decades.
This new insight into how the Southern Ocean behaves will allow scientists to build computer models that can better predict how our climate is going to change in the future.
The findings ...
New HIV prevention recommendations combine biomedical and behavioral approaches
2014-07-19
In an innovative approach to HIV prevention, an interdisciplinary group of experts has come together for the first time to lay out a framework of best practices to optimize the role of the clinician in achieving an AIDS-free generation. The guidelines, which will be published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), integrate both cutting-edge biomedical advances and evidence-based behavioral interventions for the care of people living with HIV or at high risk for HIV infection.
The recommendations, developed by an expert volunteer panel assembled ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
[Press-News.org] Genetic risk for autism stems mostly from common genesUsing new statistical tools, Carnegie Mellon's Kathryn Roeder also finds inheritability trumps spontaneous glitches and environmental risks