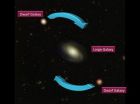
(Press-News.org) The discovery that many small galaxies throughout the universe do not 'swarm' around larger ones like bees do but 'dance' in orderly disc-shaped orbits is a challenge to our understanding of how the universe formed and evolved.
The finding, by an international team of astronomers, including Professor Geraint Lewis from the University of Sydney's School of Physics, has just been announced in Nature.
"Early in 2013 we announced our startling discovery that half of the dwarf galaxies surrounding the Andromeda Galaxy are orbiting it in an immense plane" said Professor Lewis. "This plane is more than a million light years in diameter, but is very thin, with a width of only 300 000 light years."
The universe contains billions of galaxies. Some, such as the Milky Way, are immense, containing hundreds of billions of stars. Most galaxies, however, are dwarfs, much smaller and with only a few billion stars.
For decades astronomers have used computer models to predict how these dwarf galaxies should orbit large galaxies. They had always found that they should be scattered randomly.
"Our Andromeda discovery did not agree with expectations, and we felt compelled to explore if it was true of other galaxies throughout the universe," said Professor Lewis.
Using the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, a remarkable resource of colour images and 3-D maps covering more than a third of the sky, the researchers dissected the properties of thousands of nearby galaxies.
"We were surprised to find that a large proportion of pairs of satellite galaxies have oppositely directed velocities if they are situated on opposite sides of their giant galaxy hosts", said lead author Neil Ibata of the Lycée International in Strasbourg, France.
"Everywhere we looked we saw this strangely coherent coordinated motion of dwarf galaxies. From this we can extrapolate that these circular planes of dancing dwarfs are universal, seen in about 50 percent of galaxies," said Professor Geraint Lewis.
"This is a big problem that contradicts our standard cosmological models. It challenges our understanding of how the universe works including the nature of dark matter."
The researchers believe the answer may be hidden in some currently unknown physical process that governs how gas flows in the universe, although, as yet, there is no obvious mechanism that can guide dwarf galaxies into narrow planes.
Some experts, however, have made more radical suggestions, including bending and twisting the laws of gravity and motion. "Throwing out seemingly established laws of physics is unpalatable," said Professor Lewis, "but if our observations of nature are pointing us in this direction, we have to keep an open mind. That's what science is all about."
INFORMATION:
Mysterious dance of dwarfs may force a cosmic rethink
2014-07-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study links enzyme to Alzheimer's disease
2014-07-21
Unclogging the body's protein disposal system may improve memory in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), according to a study from scientists at Kyungpook National University in Korea published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
In AD, various biochemical functions of brain cells go awry, leading to progressive neuronal damage and eventual memory loss. One example is the cellular disposal system, called autophagy, which is disrupted in patients with AD, causing the accumulation of toxic protein plaques characteristic of the disease. Jae-sung Bae and colleagues ...
Healing the heart with fat
2014-07-21
Too much dietary fat is bad for the heart, but the right kind of fat keeps the heart healthy, according to a paper published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Unsaturated dietary fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are known to protect against cardiovascular diseases. However, the mechanism and the specific fat metabolites responsible for this protection were unknown.
A group of Japanese scientists now show that mice engineered to produce their own EPA are protected against heart disease and have improved cardiac function. One particular EPA metabolite, ...
When temperatures get cold, newly-discovered process helps fruit flies cope
2014-07-21
Cold-blooded animals cannot regulate their body temperature, so their cells are stressed when facing temperature extremes. Worse still, even at slightly colder temperatures, some biological processes in the cell are slowed down more than others, which should throw the cells' delicate chemical balance out of whack. Yet, those cells manage to keep their biological processes coordinated. Now researchers from the University of Rochester and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory have found out how they do that.
"The production of proteins is a key process in all cells, ...
Scientists successfully generate human platelets using next-generation bioreactor
2014-07-21
Boston, MA – Scientists at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) have developed a scalable, next-generation platelet bioreactor to generate fully functional human platelets in vitro. The work is a major biomedical advancement that will help address blood transfusion needs worldwide.
The study is published July 21, 2014 in Blood.
"The ability to generate an alternative source of functional human platelets with virtually no disease transmission represents a paradigm shift in how we collect platelets that may allow us meet the growing need for blood transfusions," said Jonathan ...
Refined biological evolution model
2014-07-21
Models for the evolution of life are now being developed to try and clarify the long term dynamics of an evolving system of species. Specifically, a recent model proposed by Petri Kärenlampi from the University of Eastern Finland in Joensuu accounts for species interactions with various degrees of symmetry, connectivity, and species abundance. This is an improvement on previous, simpler models, which apply random fitness levels to species. The findings published in EPJ E demonstrate that the resulting replicator ecosystems do not appear to be a self-organised critical model, ...
Iodine may alleviate swelling in retinitis pigmentosa patients' retinas
2014-07-21
Boston – Cystoid macular edema (CME) is a common complication of retinitis pigmentosa (RP), a family of retinal diseases in which patients typically lose night and side vision first and then develop impaired central vision. CME can also decrease central vision. Current treatments for CME in RP are not always effective and can lead to adverse results.
Researchers from the Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Harvard Medical School, and Boston University School of Medicine tested whether the extent of retinal swelling due to CME was inversely related to dietary iodine intake in patients ...
Missing sleep may hurt your memory
2014-07-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Lack of sleep, already considered a public health epidemic, can also lead to errors in memory, finds a new study by researchers at Michigan State University and the University of California, Irvine.
The study, published in the journal Psychological Science, found participants deprived of a night's sleep were more likely to flub the details of a simulated burglary they were shown in a series of images.
Distorted memory can have serious consequences in areas such as criminal justice, where eyewitness misidentifications are thought to be the leading ...
Diagnostic criteria for Christianson Syndrome
2014-07-21
Because the severe autism-like condition Christianson Syndrome was only first reported in 1999 and some symptoms take more than a decade to appear, families and doctors urgently need fundamental information about it. A new study that doubles the number of cases now documented in the scientific literature provides the most definitive characterization of CS to date. The authors therefore propose the first diagnostic criteria for the condition.
"We're hoping that clinicians will use these criteria and that there will be more awareness among clinicians and the community about ...
Nearsightedness increases with level of education and longer schooling
2014-07-21
Education and behavior have a greater impact on the development of nearsightedness than do genetic factors: With each school year completed, a person becomes more nearsighted. The higher the level of education completed, the more severe is the impairment of vision. These are the conclusions drawn by researchers at the Department of Ophthalmology at the Mainz University Medical Center from the results of the first population-based cohort study of this condition. A nearsighted eye is one in which the eyeball is too long in relation to the refractive power of the cornea and ...
Heart disease: First Canadian survey shows women unaware of symptoms and risk factors
2014-07-21
OTTAWA, July 21, 2014 – A new survey, ordered by the University of Ottawa Heart Institute, shows that a majority of Canadian women lack knowledge of heart disease symptoms and risk factors, and that a significant proportion is even unaware of their own risk status. The findings underscore the opportunity for patient education and intervention regarding risk and prevention of heart disease.
Heart disease is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in men and women. Our understanding of heart disease stems chiefly from clinical trials on men, but key features of the disease ...