(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, July 21, 2014—In Alzheimer's disease, accumulation of amyloid plaque in the brain is believed to play an important role in many characteristic disease symptoms, including memory loss and other mental state changes. But how these plaque deposits affect brain function is not well understood. Important new study results showing that plaque buildup in one area of the brain can negatively affect metabolism in a more distant brain region have been published in Brain Connectivity, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Brain Connectivity website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/brain.2013.0212 until August 21, 2014.
As part of a special issue focused on Alzheimer's disease, Elisabeth Klupp and coauthors, Technische Universtät München (Munich and Garching, Germany) and University Hospital of Cologne, Germany, present the results of an imaging-based study demonstrating that
amyloid buildup in one brain region can impair brain cell metabolism and activity another in remote brain region not affected by amyloid plaque accumulation. The regions studied were part of the same functional network but are located remotely from each other in the brain. The authors suggest this long-distance effect may be the result of diminished neuronal signals originating from the amyloid-affected brain region to the remote amyloid-unaffected brain region. The findings are discussed in the article "In Alzheimer's Disease, Hypometabolism in Low-Amyloid Brain Regions May Be a Functional Consequence of Pathologies in Connected Brain Regions."
"This research may be an important new discovery that links two important hypotheses in Alzheimer's disease research: the amyloid buildup hypothesis and the network degenerating hypothesis," says Christopher Pawela, PhD, Co-Editor-in-Chief and Assistant Professor, Medical College of Wisconsin.
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Brain Connectivity is the essential peer-reviewed journal covering groundbreaking findings in the rapidly advancing field of connectivity research at the systems and network levels. Published 10 times per year in print and online, the Journal is under the leadership of Founding and Co-Editors-in-Chief Christopher Pawela, PhD, Assistant Professor, Medical College of Wisconsin, and Bharat Biswal, PhD, Chair of Biomedical Engineering, New Jersey Institute of Technology. It includes original peer-reviewed papers, review articles, point-counterpoint discussions on controversies in the field, and a product/technology review section. To ensure that scientific findings are rapidly disseminated, articles are published Instant Online within 72 hours of acceptance, with fully typeset, fast-track publication within 4 weeks. Tables of content and a sample issue may be viewed on the Brain Connectivity website at http://www.liebertpub.com/brain.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative medical and biomedical peer-reviewed journals, including Journal of Neurotrauma and Therapeutic Hypothermia and Temperature Management. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 80 journals, newsmagazines, and books is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website at http://www.liebertpub.com.
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 140 Huguenot Street, New Rochelle, NY 10801-5215 http://www.liebertpub.com
Phone (914) 740-2100 (800) M-LIEBERT Fax (914) 740-2101
Contact: Kathryn Ruehle, Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., (914) 740-2100, kruehle@liebertpub.com
Can amyloid plaque in Alzheimer's disease affect remote regions of the brain?
2014-07-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Increased overall survival for advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer patients is associated with availability of less toxic chemotherapy
2014-07-21
DENVER – A 10-year population-based study shows that increased availability of better systemic chemo- and targeted-therapies for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) coincides with increased usage of these therapies. This in turn leads to a significant increase in overall survival.
Researchers from the British Columbia Cancer Agency, Vancouver, Canada, performed a retrospective chart review of all patients referred to the agency with advanced stage (IIIB or IV) lung cancer and grouped the patients into 4 one-year time frame cohorts; one termed "baseline" ...
ROS1 gene fusions are found in 2.4 percent of Asian patients with lung adenocarcinoma
2014-07-21
DENVER -- ROS1 fusion genes were successfully detected independent of gender or smoking history in young East Asian patients with lung adenocarcinoma, a histological subgroup in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), using multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) diagnostic tests.
In NSCLC treatment algorithms, a personalized therapy approach is now being taken based on the genetic characteristics of the cancer. Patients with specific oncogenic molecular aberrations, for example EGFR mutations and ALK gene fusions, ...
New accurate epigenetic test could eliminate unnecessary repeat biopsies for prostate cancer
2014-07-21
New York, NY -- More than one million prostate biopsies are performed each year in the U.S. alone, including many repeat biopsies for fear of cancer missed. Therefore there is a need to develop diagnostic tests that will help avoid unnecessary repeat biopsies. Two independent trials have now validated the performance of an epigenetic test that could provide physicians with a better tool to help eliminate unnecessary repeat prostate biopsies, report investigators in The Journal of Urology®.
In the previously reported independent MATLOC (Methylation Analysis To Locate Occult ...
Oregon chemists eye improved thin films with metal substitution
2014-07-21
EUGENE, Ore. – (July 21, 2014) – The yield so far is small, but chemists at the University of Oregon have developed a low-energy, solution-based mineral substitution process to make a precursor to transparent thin films that could find use in electronics and alternative energy devices.
A paper describing the approach is highlighted on the cover of the July 21 issue of the journal Inorganic Chemistry, which draws the most citations of research in the inorganic and nuclear chemistry fields. The paper was chosen by the American Chemical Society journal as an ACS Editor's ...
Overcoming barriers to physical activity for African-American women
2014-07-21
AURORA, Colo. (July 21, 2014) - According to the Centers for Disease Control, approximately four out of five black women are overweight or obese and 36 percent meet physical activity objectives as determined by the CDC. That's compared to 50 percent of white women meeting the same objectives.
A study conducted by the Center for African American Health and the University of Colorado School of Medicine's Center for Women's Health Research finds that African American women whose hairstyle is affected by perspiration may avoid physical activity altogether. Prior studies ...
Study offers new clues about the source of racial health disparities
2014-07-21
A first-of-its-kind study by researchers at USC and Loyola Marymount University (LMU) has found evidence that the persistent health disparities across race may, in part, be related to anxiety about being confronted by negative racial stereotypes while receiving healthcare.
Stereotype threat, which is the threat of being judged by or confirming a negative stereotype about a group you belong to, has already been shown to influence the outcome of standardized testing, such as performance on the SAT (the most widely used college admissions exam). For example, when confronted ...
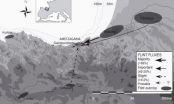
The economic territory of Upper Palaeolithic groups is specified by flint
2014-07-21
This news release is available in Spanish.
Never before had the mobility patterns and management of lithic resources in the Upper Palaeolithic been determined so precisely. The study of flint remains found in the open-air Ametzagaina site in Donostia-San Sebastian has determined the economic territory of the human groups that lived there for about 2,000 years. The paper, Where to and What for? Mobility Patterns and the Management of Lithic Resources by Gravettian Hunter-Gatherers in the Western Pyrenees, has been published in the Journal of Anthropological Research.
The ...
Cost of World Cup may be too high for Brazil
2014-07-21
Brazil's World Cup has been estimated to be the priciest of any yet, with a projected cost of $11.5 billion. Some predictions even claim that the Brazilian government will have spent up to $14 billion on building and renovating 12 stadiums; upgrading federal, state and city infrastructure; and ensuring security.
In a country with many economic and social issues that need to be addressed, such amounts of spending—more than three times the amount spent on the last World Cup—seem irresponsible to Brazilian citizens who are eager to understand the benefits of such spending, ...
Filter bed substrates, plant types recommended for rain gardens
2014-07-21
RALEIGH, NC – Urban stormwater runoff is causing problems for the world's water sources. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency found stormwater runoff to be one of the top 10 causes of compromised environments in rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, bays, and estuaries. The pollutants from urban stormwater runoff can harm fish and wildlife populations, foul drinking water, and make recreational areas unsafe.
Researchers from North Carolina State University are looking to rain gardens as one way to remediate the water quality concerns caused by ...
Organic apple orchards benefit from green compost applications
2014-07-21
FAYETTEVILLE, AR – In traditional apple orchards, effective management practices rely on two interrelated components: finding ways to manage competitive vegetation under the trees, and supplying important supplemental nutrition to trees. These factors are further complicated in organic management systems where limited tools are available, and producers need to meet the stringent soil fertility and crop nutrient management standards of the National Organic Program. University of Arkansas scientists published a study that includes recommendations for the use of various groundcover ...