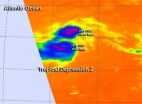
(Press-News.org) Two instruments aboard NASA's Aqua satellite provided different views of Typhoon Matmo on its approach to Taiwan today, July 22.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument snapped a visible picture of Typhoon Matmo's clouds on July 22 at 1:10 a.m. EDT. The MODIS image showed a center obscured by clouds. Bands of thunderstorms wrapped tightly into the center of circulation, creating the signature comma shape of a mature tropical cyclone. At the time of the image, the center was southeast of the southeastern tip of Taiwan. The image also showed that the southernmost band of thunderstorms were affecting Luzon, in the northern Philippines.
The second instrument aboard Aqua captured infrared data that showed temperatures of clouds. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument gathered infrared data that was false-colored at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California and made into an image. The AIRS image also did not show an open eye in Matmo, but did show powerful thunderstorms with very cold cloud top temperatures wrapped tightly around the center. Matmo's northwestern side was already over eastern Taiwan, while the southwestern quadrant blanketed the northern Philippines.
By 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that radar data from Taiwan showed the eye had become more visible as the storm was making landfall on the country's east coast. Maximum sustained winds were near 85 knots (97.8 mph/157.4 kph). Matmo was centered near 23.0 north latitude and 121.6 east longitude, about 158 nautical miles (181.8 miles/292.6 km) south of Taipei, Taiwan. Matmo was moving to the northwest at 9 knots (10.3 mph).
Matmo is generating 30-foot (9.1 meter) high seas which means rough seas and dangerous swells for the east coast of Taiwan in addition to typhoon-force winds, heavy rainfall and flash flooding potential. The Taiwan Central Weather Bureau has issued warnings for the entire country. Those warnings can be seen on their website: http://www.cwb.gov.tw/.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) expects the system to dissipate in two days but only after moving across Taiwan, moving into the Taiwan Strait and landfalling again in eastern China. Once Matmo exits Taiwan, the JTWC doesn't expect Matmo to strengthen before its second landfall.
INFORMATION:
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA provides double vision on Typhoon Matmo
2014-07-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Carlton Fire Complex, Washington -- July 22, 2014
2014-07-22
The Carlton Complex fires started on July 14, 2014, by lightning from a weather system that moved through the Methow Valley. The Carlton Complex consists of four fires: Stokes Fire, Gold Hikes Fire, French Creek Fire and the Cougar Flat. The Stokes and Gold Hikes fires are now one larger fire. The fires are burning in timber and grass and the area burning is currently over 243,000 acres in size. The present fire situation continues to rapidly change due to the high fire danger. Public and firefighter safety is the priority on the Carlton Complex fires. Thirty-five primary ...
African elephant genome suggests they are superior smellers
2014-07-22
July 22, 2014 – Sense of smell is critical for survival in many mammals. The ability to distinguish different odors, which is important for sniffing out food, avoiding predators, and finding mates, depends on the number and type olfactory receptors found in an organism's genome. In a study published today in Genome Research, researchers examined the olfactory receptor (OR) repertoire encoded in 13 mammalian species and found that African elephants have the largest number of OR genes ever characterized; more than twice that found in dogs, and five times more than in humans.
To ...
High-salt diet doubles threat of cardiovascular disease in people with diabetes
2014-07-22
Washington, DC -- People with Type 2 diabetes who eat a diet high in salt face twice the risk of developing cardiovascular disease as those who consume less sodium, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Diabetes occurs when there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. People develop Type 2 diabetes when their bodies become resistant to the hormone insulin, which carries sugar from the blood to cells.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 29.1 million Americans ...
Vitamin D deficiency raises risk of schizophrenia diagnosis
2014-07-22
Washington, DC -- Vitamin D-deficient individuals are twice as likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia as people who have sufficient levels of the vitamin, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and is needed for bone and muscle health. The skin naturally produces this vitamin after exposure to sunlight. People also obtain smaller amounts of the vitamin through foods, such as milk fortified with vitamin D. More than 1 billion people worldwide are estimated ...
New study reveals vulnerability of sharks as collateral damage in commercial fishing
2014-07-22
MIAMI –A new study that examined the survival rates of 12 different shark species when captured as
unintentional bycatch in commercial longline fishing operations found large differences in survival
rates across the 12 species, with bigeye thresher, dusky, and scalloped hammerhead being the most
vulnerable. The study, led by researchers at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of
Marine and Atmospheric Science and UM Abess Center for Ecosystem Science and Policy, provides
new information to consider for future conservation measures for sharks in the Northwest ...
Are state Medicaid policies sentencing people with mental illnesses to prison?
2014-07-22
Researchers from the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy and Economics have linked tighter Medicaid policies governing antipsychotic drugs with increased incarceration rates for schizophrenic individuals.
The study comes amid media scrutiny over whether cutbacks in mental health actually save money, when other costs are taken into account.
Some health plans require an extra approval step before tests or treatments can be ordered for patients. This step – called prior authorization – is intended to encourage physicians to select cost-effective options by requiring ...
Should men at risk for cardiovascular disease receive earlier cholesterol treatment?
2014-07-22
New Rochelle, NY -- New guidelines on cholesterol treatment and cardiovascular risk assessment state that men have at least double the risk of dying from atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or of having a heart attack or stroke as do women with a similar risk profile (based on age, smoking history, and cholesterol and blood pressure levels). The implications of this finding for when and how aggressively to treat high cholesterol are examined in an Editorial in Journal of Men's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is ...
Communication between nostril/skin microbiome bacteria can influence pathogen behavior
2014-07-22
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., July 22, 2014--A team of scientists has made an important discovery about the molecular interactions that occur between generally benign species of Propionibacterium bacteria and the pathogenic bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, the cause of most "staph" infections. These bacterial species are commonly found in the human nostrils and, also, on human skin. S. aureus is a potential pathogen that inhibits the nostrils of about a quarter of all adults. It is also a common cause of skin and more invasive infections. The team, led by Forsyth scientists, discovered ...
Research brings us nearer to understanding how neuro cells turn cancerous
2014-07-22
Scientists from the Sloan-Kettering Institute for Cancer Research in New York with the help of Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry have completed research which for the first time brings us nearer to understanding how some cells in the brain and nervous system become cancerous.
The results of their study are published in the prestigious journal Cancer Cell.
The research team led by Sloan-Kettering researchers studied a tumour suppressor called Merlin.
The results of the study have identified a new mechanism whereby Merlin suppresses ...
Retail pricing strategies: Do consumers prefer deep discounts or everyday low prices?
2014-07-22
Sometimes finding the best bang for your buck feels like a wild goose chase. It's hard to know which stores offer the best prices at any given time. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, when trying to maximize savings, consumers will choose retailers they believe offer the lowest prices the majority of the time.
"We looked at the impact different pricing strategies have on the stores people shop at when they do not know the product prices unless they visit the store," write authors Shai Danziger (Tel Aviv University), Liat Hadar (IDC Herzliya), ...