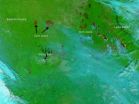
(Press-News.org) The burn scars on this false-color image from the Terra satellite show the different areas that have been affected by this year's rash of wildfires in Eastern Russia. The burn scars show up as reddish-brown splotches of color against the green background. The wildfires have broken across the remote parts of Eastern Russia in the Sakha Republic. Even in this false-color image from the MODIS instrument, it is still possible to see the smoke rising from the fires that continue. Two recent image features noted below show the devastating number of fires that have plagued this season in Russia.
Smoke Haze and Fires in Russia - July 2014 - July 24, 2014
Fires in Eastern Russia in July 2014 - July 21, 2014
INFORMATION:
This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra satellite on July 25, 2014. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team. Caption: NASA/Goddard, Lynn Jenner
Burn scars in Eastern Russia
2014-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Anti-inflammatory drug can prevent neuron loss in Parkinson's model
2014-07-25
An experimental anti-inflammatory drug can protect vulnerable neurons and reduce motor deficits in a rat model of Parkinson's disease, researchers at Emory University School of Medicine have shown.
The results were published in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease.
The findings demonstrate that the drug, called XPro1595, can reach the brain at sufficient levels and have beneficial effects when administered by subcutaneous injection, like an insulin shot. Previous studies of XPro1595 in animals tested more invasive modes of delivery, such as direct injection into the brain.
"This ...
New EMS system in Arizona dramatically improves survival from cardiac arrest
2014-07-25
WASHINGTON -- A new system that sent patients to designated cardiac receiving centers dramatically increased the survival rate of victims of sudden cardiac arrest in Arizona, according to a study published online yesterday in Annals of Emergency Medicine.
"We knew lives would be saved if the hospitals implemented the latest cutting edge guidelines for post-cardiac arrest care and we were able to get cardiac arrest patients to those hospitals, similar to what is done for Level 1 trauma patients," said lead study author Daniel Spaite, MD, Director of EMS Research at the ...
Tropical Storm Genevieve forms in Eastern Pacific
2014-07-25
The seventh tropical depression of the Eastern Pacific Ocean formed and quickly ramped up to a tropical storm named "Genevieve." NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of the newborn storm being trailed by two other areas of developing low pressure to its east.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) noted that Tropical Storm Genevieve was born on July 25 at 5 a.m. EDT. At that time, Genevieve had maximum sustained winds near 40 mph (65 kph). It was located near 12.2 north latitude and 134.4 west longitude, about 1,490 miles (2,400 km) east-southeast of South ...
Climate change increases risk of crop slowdown in next 20 years
2014-07-25
BOULDER -- The world faces a small but substantially increased risk over the next two decades of a major slowdown in the growth of global crop yields because of climate change, new research finds.
The authors, from Stanford University and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), say the odds of a major production slowdown of wheat and corn even with a warming climate are not very high. But the risk is about 20 times more significant than it would be without global warming, and it may require planning by organizations that are affected by international food ...
Whitehead Institute researchers create 'naïve' pluripotent human embryonic stem cells
2014-07-25
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (July 24, 2014) – For years, researchers and patients have hoped that embryonic stem cells (ESCs)—capable of forming nearly any cell type in the body—could provide insight into numerous diseases perhaps even be used to treat them. Yet progress has been hampered by the inability to transfer research and tools from mouse ESC studies to their human counterparts, in part because human ESCs are "primed" and slightly less plastic than the mouse cells.
Now Thorold Theunissen, Benjamin Powell, and Haoyi Wang, who are scientists in the lab of Whitehead Institute ...
Scientists test nanoparticle 'alarm clock' to awaken immune systems put to sleep by cancer
2014-07-25
(Lebanon, NH, 7/25/14) — Researchers at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Norris Cotton Cancer Center are exploring ways to wake up the immune system so it recognizes and attacks invading cancer cells. Tumors protect themselves by tricking the immune system into accepting everything as normal, even while cancer cells are dividing and spreading.
One pioneering approach, discussed in a review article published this week in WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, uses nanoparticles to jumpstart the body's ability to fight tumors. Nanoparticles are too small to imagine. One billion ...
Clearing cells to prevent cervical cancer
2014-07-25
Boston, MA – A study published online in the International Journal of Cancer earlier this month describes a novel approach to preventing cervical cancer based on findings showing successful reduction in the risk of cervical cancer after removal of a discrete population of cells in the cervix.
The findings come from a study that looked at squamocolumnar junction cells, or SCJ cells. These cells reside in the cervical canal and have been implicated as the origins of cervical cancer. A research team co-led by Christopher Crum, MD, director, Brigham and Women's Hospital ...
Manipulating key protein in the brain holds potential against obesity and diabetes
2014-07-25
DALLAS -- A protein that controls when genes are switched on or off plays a key role in specific areas of the brain to regulate metabolism, UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have found.
The research potentially could lead to new therapies to treat obesity and diabetes, since the transcription factor involved – spliced X-box binding protein 1 (Xbp1s) – appears to influence the body's sensitivity to insulin and leptin signaling. Insulin and leptin are hormones central to the body's regulation of food intake and sugar disposal, and obesity and diabetes are conditions ...
Why do men prefer nice women?: Responsiveness and desire
2014-07-25
People's emotional reactions and desires in initial romantic encounters determine the fate of a potential relationship. Responsiveness may be one of those initial "sparks" necessary to fuel sexual desire and land a second date. However, it may not be a desirable trait for both men and women on a first date. Does responsiveness increase sexual desire in the other person? Do men perceive responsive women as more attractive, and does the same hold true for women's perceptions of men? A study published in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin seeks to answer those questions. ...
ACR statement on cancer study regarding patient anxiety from CT lung cancer screening
2014-07-25
Anxiety regarding inconclusive cancer screening test results among some patients is real and is only natural. However, as evidenced by Gareen et al, published July 25 in Cancer, the incidence and effects of anxiety associated with false positive or other results of computed tomography (CT) lung cancer screening exams are far less than claimed by some in the medical community.
"Unsubstantiated claims of systemic and harmful patient anxiety should now be put to rest and not continue to delay implementation of CT lung cancer screening programs or Medicare coverage for these ...