(Press-News.org) RENO – Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen became the first man to reach the South Pole in December of 1911. More than 100 years later, an international team of scientists led by Joe McConnell of Nevada's Desert Research Institute (DRI) have proven that air pollution from industrial activities arrived long before.
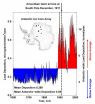
Using data from 16 ice cores collected from widely spaced locations around the Antarctic continent, including the South Pole, McConnell's team created the most accurate and precise reconstruction to date of lead pollution over the Earth's southernmost continent. The new record, described in an article published today in the online edition of the Nature journal Scientific Reports, spans a 410-year period from 1600 to 2010 A.D.
"Our new record shows the dramatic impact of industrial activities such as smelting, mining, and fossil fuel burning on even the most remote parts of the world," said McConnell, the study's lead author, research professor and director of DRI's ultra-trace ice core analytical laboratory, located on the institute's campus in Reno, Nev.
"It is very clear that industrial lead contamination was pervasive throughout Antarctica by the late 19th century, more than two decades before the first explorers made it to the South Pole," he added. "The idea that Amundsen and Scott were traveling over snow that clearly was contaminated by lead from smelting and mining in Australia, and that lead pollution at that time was nearly as high as any time ever since, is surprising to say the least."
All measurements of lead and other chemicals used in this study were made using DRI's unique continuous ice core analytical system. Low background atmospheric concentrations, together with well-known and often distinct isotopic characteristics of industrial sources make lead an ideal tracer of industrial pollution.
"Lead is a toxic heavy metal with strong potential to harm ecosystems," said co-author Paul Vallelonga of the University of Copenhagen. "While concentrations measured in Antarctic ice cores are very low, the records show that atmospheric concentrations and deposition rates increased approximately six-fold in the late 1880's, coincident with the start of mining at Broken Hill in southern Australia and smelting at nearby Port Pirie."
The similar timing and magnitude of changes in lead deposition across Antarctica, as well as the characteristic isotopic signature of Broken Hill lead found throughout the continent, suggest that this single emission source in southern Australia was responsible for the introduction of lead pollution into Antarctica at the end of the 19th century and remains a significant source today, the authors report.
This study included ice cores collected as part of projects funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation. Additional ice cores were contributed to the study by international collaborators including the British Antarctic Survey, the Australian Antarctic Division, and the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany.
"The ice cores obtained through international collaborations were critical to the success of this study in that they allowed us to develop records from parts of Antarctica not often visited by U.S.-based scientists," said co-author Tom Neumann of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. "This included the Law Dome region of East Antarctica and a big section of East Antarctica visited by the Norwegian-United States Scientific Traverse of East Antarctica."
McConnell explained the hazards of working in such extreme environments. "I remember the day in 1999 we drilled the shallow core about 15 km from South Pole. The temperature was negative 100 degrees Fahrenheit with the wind chill so it was hard to motivate the field team to leave the galley at the South Pole station that day, he said."
Data from the new ice core array illustrates that Antarctic lead concentrations reached a peak in 1900 and remained high until the late 1920's, with brief declines during the Great Depression and the end of World War II. Concentrations then increased rapidly until 1975 and remained elevated until the 1990's.
Concentrations across the Antarctic continent have since declined, but still are about four-fold higher than before industrialization, despite the phase out of leaded gasoline and other mitigation efforts in many countries in the Southern Hemisphere, the report states.
"Our measurements indicate that approximately 660 tonnes (1.5 million pounds) of industrial lead have been deposited on the snow-covered surface of Antarctic during the past 130 years," McConnell said. "While recent contamination levels are lower, clearly detectable industrial contamination of the Antarctic continent persists today… so we still have a ways to go."
INFORMATION:
About the Desert Research Institute: DRI, the nonprofit research campus of the Nevada System of Higher Education, strives to be the world leader in environmental sciences through the application of knowledge and technologies to improve people's lives throughout Nevada and the world. All DRI news releases are available at http://news.dri.edu/.
Industrial lead pollution beat explorers to the South Pole by 22 years and persists today
Dramatic impact of late 19th century industrial activities revealed in Antarctic ice cores
2014-07-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Building 'invisible' materials with light
2014-07-28
A new method of building materials using light, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, could one day enable technologies that are often considered the realm of science fiction, such as invisibility cloaks and cloaking devices.
Although cloaked starships won't be a reality for quite some time, the technique which researchers have developed for constructing materials with building blocks a few billionths of a metre across can be used to control the way that light flies through them, and works on large chunks all at once. Details are published today (28 ...
Superconductivity could form at high temperatures in layered 2D crystals
2014-07-28
An elusive state of matter called superconductivity could be realized in stacks of sheetlike crystals just a few atoms thick, a trio of physicists has determined.
Superconductivity, the flow of electrical current without resistance, is usually found in materials chilled to the most frigid temperatures, which is impractical for most applications. It's been observed at higher temperatures–higher being about 100 kelvin or minus 280 degrees below zero Fahrenheit–in copper oxide materials called cuprate superconductors. But those materials are brittle and unsuitable for fabricating ...
Lifestyle choices may affect the long-term heart health of childhood cancer survivors
2014-07-28
A new study has found that following a healthy lifestyle may lower childhood cancer survivors' risk of developing the metabolic syndrome. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings indicate that children with cancer and adults who had cancer when they were children should receive information about how their lifestyle may influence their long-term health.
Adults who had cancer as children are known to be at increased risk for the metabolic syndrome, a group of risk factors that increases the likelihood of developing ...
Nicotine found to inhibit DNA-strand break caused by a certain carcinogen in smoke
2014-07-28
A new in vitro study has revealed that nicotine and cotinine, a metabolite of nicotine, can potentially inhibit DNA damage caused by a certain carcinogen in smoke.
The carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone or NNK is produced during the curing of tobacco leaves and ultimately ends up in the tobacco smoke. Once inhaled, it is metabolised in the lung and liver, where it is activated by a variety of enzymes called Cytochrome P450 (CYP). Previous research in mice has revealed that nicotine can partially interfere with the activation of NNK, and this has ...
Dinosaurs fell victim to perfect storm of events, study shows
2014-07-28
Dinosaurs might have survived the asteroid strike that wiped them out if it had taken place slightly earlier or later in history, scientists say.
A fresh study using up-to-date fossil records and improved analytical tools has helped palaeontologists to build a new narrative of the prehistoric creatures' demise, some 66 million years ago.
They found that in the few million years before a 10km-wide asteroid struck what is now Mexico, Earth was experiencing environmental upheaval. This included extensive volcanic activity, changing sea levels and varying temperatures. ...
Hepatitis C virus genotype 1 is most prevalent worldwide
2014-07-28
In one of the largest prevalence studies to date, researchers from the U.K. provide national, regional, and global genotype prevalence estimates for the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Findings published in Hepatology, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, indicate that genotype 1 is the most prevalent worldwide, with over 83 million patients infected of which one-third reside in East Asia. Genotype 3, at just over 54 million cases, is the next most prevalent, followed by genotypes 2, 4, 6, and 5.
Despite efforts to control HCV, it remains one ...
New species of mayfly discovered in India
2014-07-28
Scientists have discovered a new species of mayfly in the southern Western Ghats, a mountain range along the west coast of India. In fact, this is the first time that any mayfly belonging to the genus Labiobaetis has been collected in peninsular India.
The new species, called Labiobaetis soldani, "is named in honor of Dr. T. Soldan for his substantial contribution to the understanding of the Ephemeroptera of Palaearctic and Oriental realms," according to the authors of a study that describes the new mayfly in the Journal of Insect Science.
The larvae have light-brown ...
Scientists discover new, noncommittal mechanism of drug resistance
2014-07-27
DURHAM, N.C. -- Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi can evade treatment by acquiring mutations in the genes targeted by antibiotics or antifungal drugs. These permanent mutations were once thought to be the only way for drug-resistant strains to evolve. Now a new study has shown that microorganisms can use a temporary silencing of drug targets -- known as epimutations -- to gain the benefits of drug resistance without the commitment.
Though the new mechanism was discovered in a fungus called Mucor circinelloides, it is likely to be employed by other fungi as well as ...
Study: Climate change and air pollution will combine to curb food supplies
2014-07-27
Many studies have shown the potential for global climate change to cut food supplies. But these studies have, for the most part, ignored the interactions between increasing temperature and air pollution — specifically ozone pollution, which is known to damage crops.
A new study involving researchers at MIT shows that these interactions can be quite significant, suggesting that policymakers need to take both warming and air pollution into account in addressing food security.
The study looked in detail at global production of four leading food crops — rice, wheat, corn, ...
Drugs used to treat lung disease work with the body clock
2014-07-27
Scientists from The University of Manchester have discovered why medication to treat asthma and pneumonia can become ineffective.
The findings, published in Nature Medicine, show that drugs widely used to treat lung diseases work with the body clock.
In the UK pneumonia, which is caused by an infection, affects around 1 in 1000 adults each year and is more serious for babies, young children, the elderly, smokers and those with an underlying health condition.
More than 5 million people in the UK are affected by asthma and the NHS spends around £1 billion a year ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
[Press-News.org] Industrial lead pollution beat explorers to the South Pole by 22 years and persists todayDramatic impact of late 19th century industrial activities revealed in Antarctic ice cores